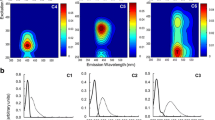
Abstract
Gaining rapid knowledge of dissolved organic matter (DOM) proves to be decisive for wastewater treatment plant operators in efforts to achieve good treatment efficiency in light of current legislation. DOM can be monitored by application of fluorescence spectroscopy both online and in real time in order to derive an assessment of DOM oxidation potential. This work presents an eco-friendly alternative method for measuring the soluble chemical oxygen demand (COD) in raw sewage by means of three-dimensional fluorescence spectroscopy. A peak-picking approach has been developed based on a previous parallel factor analysis (PARAFAC) model dedicated to Paris raw sewage. Fluorescence spectroscopy parameters were used to obtain a good prediction model of soluble COD (r2 = 0.799; p < 0.0001; n = 80) for raw sewage. The approach employed in this study serves as a guideline for purposes of implementing online wastewater monitoring and conducting environmentally friendly soluble COD measurements in the laboratory.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad, S.R., & Reynolds, D.M. (1995). Synchronous fluorescence spectroscopy of wastewater and some potential constituents. https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1354(94)00266-A.
Carstea, E.M., Bridgeman, J., Baker, A., & Reynolds, D.M. (2016). Fluorescence spectroscopy for wastewater monitoring: a review. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2016.03.021.
Coble, P.G. (1996) Characterization of marine and terrestrial DOM in seawater using excitation-emission matrix spectroscopy. https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-4203(95)00062-3.
Cohen, E., Levy, G.J., & Borisover, M. (2014) Fluorescent components of organic matter in wastewater: efficacy and selectivity of the water treatment. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2014.02.040.
Goffin, A., Guérin, S., Rocher, V., & Varrault, G. (2018). Towards a better control of the wastewater treatment process: excitation-emission matrix fluorescence spectroscopy of dissolved organic matter as a predictive tool of soluble BOD 5 in influents of six Parisian wastewater treatment plants. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-1205-1.
Li, J., Luo, G., He, L., Xu, J. & Lyu J. (2017) Analytical approaches for determining chemical oxygen demand in water bodies: a review. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408347.2017.1370670.
Moens, P.D.J., Helms, M.K., & Jameson, D.M. (2004) Detection of tryptophan to tryptophan energy transfer in proteins. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:JOPC.0000016261.97474.2e.
Murphy, K.R, Butler, K.D., Spencer, R.G.M., Stedmon, C.A, Boehme, J.R, & Aiken, G.R. (2010). Measurement of dissolved organic matter fluorescence in aquatic environments: an interlaboratory comparison. https://doi.org/10.1021/es102362t.
Murphy, K.R., Hambly, A., Singh, S., Henderson, R.K., Baker A., Stuetz, R., & Khan, S.J. (2011). Organic matter fluorescence in municipal water recycling schemes: toward a unified PARAFAC model. https://doi.org/10.1021/es103015e.
Murphy, K.R., Stedmon, C.A., Graeber, D., Bro, R. (2013). Fluorescence spectroscopy and multi-way techniques. PARAFAC. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3ay41160e.
Parlanti, E., Wörz, K., Geoffroy, L., & Lamotte, M. (2000). Dissolved organic matter fluorescence spectroscopy as a tool to estimate biological activity in a coastal zone submitted to anthropogenic inputs. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0146-6380(00)00124-8.
Wang, J.Q., Wu, C., Wu, K.B., Cheng, Q., & Zhou, Y.K. (2012). Electrochemical sensing oxygen demand based on the catalytic activity of cobalt oxide film. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2012.05.046.
Yang, L., Shin, H.S., & Hur, J. (2014). Estimating the concentration and biodegradability of organic matter in 22 wastewater treatment plants using fluorescence excitation emission matrices and parallel factor analysis. https://doi.org/10.3390/s140101771.
Yang, L., Hur, J., & Zhuang, W. (2015). Occurrence and behaviors of fluorescence EEM-PARAFAC components in drinking water and wastewater treatment systems and their applications: a review. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4214-3.
Yu, X.D., Yang, H.Z., & Sun , L. (2016). Determination of chemical oxygen demand using UV/O3. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-016-3154-y.
Zhang, S., Li, L., & Zhao, H. (2009). A portable photoelectrochemical probe for rapid determination of chemical oxygen demand in wastewater. https://doi.org/10.1021/es901320a.
Zhang, A.R., Zhou, M.H., & Zhou, Q.X.A. (2011). A combined photocatalytic determination system for chemical oxygen demand with a highly oxidative reagent. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2010.11.049.
Zhao, H., Jiang, D., Zhang, S., Catterall, K., & John, R. (2003). Development of a direct photoelectrochemical method for determination of chemical oxygen demand, https://doi.org/10.1021/ac0302298.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the French Ministry of Research and the MOCOPEE Research Program for their support. Thanks are also addressed to the SIAAP Laboratory for having conducted the global parameter analyses.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Supporting Table 1
(DOCX 27 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Goffin, A., Guérin-Rechdaoui, S., Rocher, V. et al. An environmentally friendly surrogate method for measuring the soluble chemical oxygen demand in wastewater: use of three-dimensional excitation and emission matrix fluorescence spectroscopy in wastewater treatment monitoring. Environ Monit Assess 191, 421 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-7570-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-7570-5