Abstract
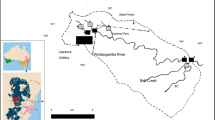
To investigate the influence of mangrove forest on heavy metal accumulation and storage in intertidal sediments, core sediments from natural mangrove, restored mangrove, and adjacent mud flat spanning the intertidal zone along the south coastline of the most heavily urbanized Deep bay, Guangdong province, China were analyzed. The average concentrations of mercury (Hg) in surface sediments of natural mangrove and restored mangrove were 172 and 151 ng g−1, whereas those of copper (Cu) were 75 and 50 μg g−1, respectively. Compared to those from other typical mangrove wetlands of the world, the metal levels in Shenzhen were at median to high levels, which is consistent with the fact that Shenzhen is in high exploitation and its mangrove suffer intensive impact from human activities. Hg and Cu concentration profiles indicated a higher metal accumulation in surface layers of sediments, in agreement with enrichment of organic matter contents. Maximum concentration, enrichment factors, and excess (background-deducted) concentration inventories of metals (Hg and Cu) were substantially different between environments, decreasing from natural mangrove sediments to restored mangrove sediments to mud flat. Furthermore, metal inputs to Futian mangrove decreased in the order natural mangrove > restored mangrove > mud flat, indicating that mangrove facilitated the accumulation and storage of Hg and Cu in sediment layers.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Birch, G., Nath, B., & Chaudhuri, P. (2015). Effectiveness of remediation of metal-contaminated mangrove sediments (Sydney estuary, Australia). Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 22, 6185–6197.
Bodin, N., N′Gom-Kâ, R., Kâ, S., Thiaw, O. T., de Morais, T., Le Loc′h, F., et al. (2013). Assessment of trace metal contamination in mangrove ecosystems from Senegal West Africa. Chemosphere, 90, 150–157.
Bouillon, S., Borges, A.V., Castañeda-Moya, E., Diele, K., Dittmar, T., Duck, N.C., et al. (2008). Mangrove production and carbon sinks: A revision of global budget estimates. Global Biogeochemical Cycles 22, GB 2013
Carney, J., Gillespie, T. W., & Rosomoff, R. (2014). Assessing forest change in a priority West African mangrove ecosystem: 1986–2010. Gemforum, 53, 126–135.
Chai, M. W., Shi, F. C., Li, R. L., Qiu, G. Y., Liu, F. C., & Liu, L. M. (2014). Growth and physiological responses to copper stress in a halophyte Spartina alterniflora (Poaceae). Acta Physiologiae Plantarum, 36, 745–754.
Chowdhury, A., & Maiti, S. K. (2014). Mangrove reforestation through participation of vulnerable population: Engineering a sustainable management solution for resource conservation. International Journal of Environmental Research and Development, 4, 1–8.
Cui, W.Z. (2007). Temporal and spatial variation of water environment and its impact on the ecosystem of the Pearl River estuary. Hehai University Doctor thesis
Cuong, D. T., Bayen, S., Wurl, O., Subramanian, K., Wong, K. K. S., Sivasothi, N., et al. (2005). Heavy metal contamination in mangrove habitats of Singapore. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 50, 1713–1744.
Defew, L. H., Mair, J. M., & Guzman, H. M. (2005). An assessment of metal contamination in mangrove sediments and leaves from Punta Mala Bay, Pacific Panama. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 50, 547–552.
Fung, Y. S. (1993). Analysis and assessment of heavy metal pollution in Hong Kong’s marine environment. In In The Marine Biology of the South China Sea. Proceedings of the First International Conference on the Marine Biology of Hong Kong and the South China Sea, Hong Kong, 28 October-3 November 1990. (B. Morton, ed.) (pp. 261–272).
Guedron, S., Devin, S., & Vignati, D.A.L. (2015). Total and methylmercury partitioning between colloids and true solution: From case studies in sediment overlying and pore waters to a generalized model. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, doi: 10.1002/etc.3190
Harbison, P. (1986). Mangrove muds: A sink and a source for trace metals. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 17, 246–250.
Kehrig, H. A., Pinto, F. N., Moreira, I., & Malm, O. (2003). Heavy metals and methylmercury in a tropical coastal estuary and a mangrove in Brazil. Organic Geochemistry, 34, 661–669.
Kopittke, P. M., Asher, C. J., Blamey, F. P. C., & Menzies, N. W. (2009). Toxic effects of Cu2+ on growth, nutrition, root morphology, and distribution of Cu in roots of Sabi grass. Science of Total Environment, 407, 4616–4621.
Kopittke, P. M., & Menzies, N. W. (2006). Effect of Cu toxicity on growth of cowpea (Vigna unguiculata). Plant and Soil, 279, 287–296.
Krauss, K. W., Lovelock, C. E., & McKee, K. L. (2008). Environmental drivers in mangrove establishment and early development: A review. Aquatic Botany, 89, 105–127.
Kristensen, E., Bouillon, S., Dittmar, T., & Marchand, C. (2008). Organic carbon dynamics in mangrove ecosystem. Aquatic Botany, 89, 210–219.
Lacerda, L.D. (1998). Biogechemistry of trace metals and diffuse pollution in mangrove ecosystems. International Society for Mangrove Ecosystems, Okinawa, 63
Leivouri, M. (1998). Heavy metal contamination in surface sediment in the Gulf of Finland and comparison with the Gulf of Bothnia. Chemosphere, 36, 43–59.
Lewis, M. A., & Russell, M. J. (2015). Contaminant profiles for surface water, sediment, flora and fauna associated with the mangrove fringe along middle and lower eastern Tampa Bay. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 95, 273–282.
Liao, J. F. (1990). The chemical properties of the mangrove solonchak in the northeast part of Hainan Island. Supplement of Acta Scientiarum, Naturalium Universitatis Sunyatseni, 9, 67–72.
Long, E. R., MacDonald, D. D., Smith, S. L., & Calder, F. D. (1995). Incidence of adverse biological effects within ranges of chemical concentrations in marine estuarine sediments. Environmental Management, 19, 81–97.
MacDonald, D. D., Ingersol, C. G., & Berger, T. A. (2000). Development and evaluation of consensus-based sediment quality guidelines for freshwater ecosystems. Archives in Environmental Contaminant Toxicology, 39, 20–31.
MacFarlane, G. R., Pulkownik, A., & Burchett, M. D. (2003). Accumulation and distribution of heavy metals in the grey mangrove, Avicennia marina (Forsk.) Vierh: Biological indication potential. Environmental Pollution, 123, 139–151.
Machado, W., Moscatelli, M., Rezende, L. G., & Lacerda, L. D. (2002). Mercury, zinc, and copper accumulation in mangrove sediments surrounding a large landfill in southeast Brazil. Environmental Pollution, 120, 455–461.
Marchand, C., Allenbach, M., & Lallier-Vergès, E. (2011). Relationships between heavy metals distribution and organic matter cycling in mangrove sediments (Conception Bay, New Caledonia). Geoderma, 160, 444–456.
Marchand, C., Disnar, J. R., Lallier-Vergès, E., & Lottier, N. (2005). Early diagenesis of carbohydrates and lignin in mangrove sediments subject to variable redox conditions (French Guiana). Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 69, 131–142.
Marchand, C., Lallier-Verges, E., Baltzer, F., Alberic, P., Cossa, D., & Baillif, P. (2006). Heavy metals distribution in mangrove sediments along the mobile coastline of French Guiana. Marine Chemistry, 98, 1–17.
Mayer, L. M., & Xing, B. S. (2001). Organic matter-surface area relationships in acid soils. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 65, 250–258.
Mei, X. Q., Yang, Y., Tam, N. F. Y., Wang, Y. W., & Li, L. (2014). Roles of root porosity, radial oxygen loss, Fe plaque formation on nutrient removal and tolerance of wetland plants to domestic wastewater. Water Research, 50, 147–159.
Morgan, B., Rate, A. W., & Burton, E. D. (2012). Trace element reactivity in FeS-rich estuarine sediments: Influence of formation environment and acid sulfate soil drainage. Science of the Total Environment, 438, 463–476.
Pacyna, E. G., Pacyna, J. M., Steenhuisen, F., & Wilson, S. (2006). Global anthropogenic mercury emission inventory for 2000. Atmospheric Environment, 40, 4048–4063.
Perdomo, L., Ensminger, I., Espinos, L. F., Elster, C., Wallner-kersanach, M., & Schnetter, M. (1999). The mangrove ecosystem of the Ciénaga Grande de Santa Marta (Colombia): Observations on regeneration and trace metals in sediment. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 37, 393–403.
Perry, C. T., & Berkeley, A. (2009). Intertidal substrate modification as a result of mangrove planting: Impacts of introduced mangrove species on sediment microfacies characteristics. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 81, 225–237.
Preda, M., & Cox, M. E. (2002). Trace metal occurrence and distribution in sediments and mangroves, Pumicestone region, southeast Queensland, Australia. Environment International, 28, 433–449.
Qiu, Y. W., & Yu, K. F. (2011). Accumulation of heavy metals in sediment of mangrove wetland from Hainan Island. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 30, 102–108 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Rajmohan, N., Prathapar, S. A., Jayaprakash, M., & Nagarajan, R. (2014). Vertical distribution of heavy metals in soil profile in a seasonally waterlogging agriculture field in Eastern Ganges Basin. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 186, 5411–5427.
Ren, H., Shen, W. J., Lu, H. F., Wen, X. Y., & Jian, S. G. (2007). Degraded ecosystems in China: Status, causes, and restoration efforts. Landscape and Ecological Engineering, 3, 1–13.
Ren, H., Wu, X. M., Ning, T. Z., Huang, G., Wang, J., Jian, S. G., et al. (2011). Wetland changes and mangrove restoration planning in Shenzhen Bay, Southern China. Landscape and Ecological Engineering, 7, 241–250.
Sanders, C. J., Santos, I. R., Silva-Filho, E. V., & Patchineelam, S. R. (2006). Mercury flux to estuarine sediments, derived from Pb-210 and Cs-137 geochronologies (Guaratuba Bay, Brazil). Marine Pollution Bulletin, 52, 1085–1089.
Sandilyan, S., & Kathiresan, K. (2012). Mangrove conservation: A global perspective. Biodiversity and Conservation, 21, 3523–3542.
Sandilyan, S., & Kathiresan, K. (2014). Decline of mangroves—a threat of heavy metal poisoning in Asia. Ocean &Coastal Management, 102, 161–168.
Silva, L. F. F., Machado, W., Lisboa Filho, S. D., & Lacerda, L. D. (2003). Mercury accumulation in sediments of a mangrove ecosystem in SE Brazil. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 145, 67–77.
Tam, N. F. Y., & Wang, Y. S. (1995). Spatial and temporal variations of heavy metal contamination in sediments of a mangrove swamp in Hongkong. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 31, 254–261.
Tam, N. F. Y., & Wong, W. S. (2000). Spatial variation of heavy metals in surface sediments of Hong Kong mangrove swamps. Environmental Pollution, 110, 195–205.
Tam, N. F. Y., & Wong, Y. S. (1996). Retention of wastewater-borne nitrogen and phosphorus in mangrove soils. Environmental Technology, 17, 851–859.
Tam, N. F. Y., & Yao, M. W. Y. (2002). Concentrations of PCBs in coastal mangrove sediments of Hong Kong. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 44, 642–651.
Ullrich, S. M., Tanton, T. W., & Abdrashitova, S. A. (2001). Mercury in the aquatic environment: A review of factors affecting methylation. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 31, 241–293.
Usman, A. R. A., Alkredaa, R. S., & Al-Wabel, M. I. (2013). Heavy metal contamination in sediments and mangroves from the coast of Red Sea: Avicennia marina as potential metal bioaccumulator. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 97, 263–270.
Vane, C. H., Harrison, I., Kim, A. W., Moss-Hayes, V., Vickers, B. P., & Hong, K. (2009). Organic and metal contamination in surface mangrove sediments of South China. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 58, 134–144.
Wang, B. S., Liao, B. W., Wang, Y. J., & Zan, Q. J. (2002). Mangrove ecosystem and sustainable development in Shenzhen Bay. Beijing: Science Press (in Chinese).
Wu, Q. H., Tam, N. F. Y., Leung, J. Y. S., Zhou, X. Z., Fu, J., Yao, B., et al. (2014). Ecological risk and pollution history of heavy metals in Nansha mangrove, South China. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 104, 143–151.
Xie, C. X., Ding, Z. H., Gao, W. Q., Xie, Z., & Wu, Y. M. (2006). Distribution and speciation of Cu, Zn, and Cr in mangrove sediments from Zhangjiang Estuary. Journal of Xiamen University (Natural Science), 45, 100–104.
Yan, Z. Z., Li, X. Z., Chen, J., & Tam, N. F. Y. (2015). Combined toxicity of cadmium and copper in Avicennia marina seedlings and the regulation of exogenous jasmonic acid. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 113, 124–132.
Yang, Q., Tam, N. F. Y., Wong, Y. S., Luan, T. G., Su, W. S., Lan, C. Y., et al. (2008). Potential use of mangroves as constructed wetland for municipal sewage treatment in Futian, Shenzhen, China. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 57, 735–743.
Zhang, H., Feng, X. B., Larssen, T., Shang, L., & Li, P. (2010). Bioaccumulation of methylmercury versus inorganic mercury in rice (Oryza sativa L.) grain. Environmental Science and Technology, 44, 4499–4504.
Zheng, D. Z., Li, M., Zheng, S. F., Liao, B. W., & Chen, Y. J. (2003). Headway of study on mangrove recovery and development in China. Guangdong Forestry Science and Technology, 19, 10–14.
Zheng, W. J., Lian, Y. W., Zheng, F. Z., & Lin, P. (1996a). Accumulation and dynamic of heavy metal elements in Rhizophora stylosa community at Yingluo Bay in Guangxi. Acta Phytoecologica Sinica, 20, 20–27.
Zheng, W. J., Wang, W. Q., & Lin, P. (1996b). Absorption and accumulation of heavy metals in Aegiceras corniculatum mangrove forest in the estuary of the Jiulong River in Fujian. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology, 2, 207–213.
Zhou, Y. W., Zhao, B., Peng, Y. S., & Chen, G. Z. (2010). Influence of mangrove reforestation on heavy metal accumulation and speciation in intertidal sediments. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 60, 1319–1324.
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the Program of Science and Technology of Shenzhen (JCYJ20130402164725017, JCYJ20140903101847739, JCYJ20150331100946599), the Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China (31400446), and the Program of Assessment and Restoration of Mangrove Geiwei of Shenzhen Bay.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, R., Xu, H., Chai, M. et al. Distribution and accumulation of mercury and copper in mangrove sediments in Shenzhen, the world’s most rapid urbanized city. Environ Monit Assess 188, 87 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5103-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5103-z