Abstract
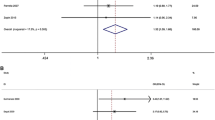
Genetic variants in the immunomodulatory gene mannose-binding lectin 2 (MBL2), were associated with risk, severity, and frequency of viral infections. In a case-control setting, we investigated the association of MBL2 functional polymorphisms with Human Papillomas Virus (HPV) infection. No differences between cases (HPV+) and controls (HPV−) were found in the distribution of each single genotypes or allele. Haplotype analysis did not show any difference between HPV+ and HPV− groups.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- MBL2:
-
Mannose-Binding Lectin 2
- MBP:
-
Mannose-Binding Protein
- HPV:
-
Human Papillomas Virus
- CIN:
-
Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia
- RFLP:
-
Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphisms
- SNP:
-
Single Nucleotide Polymorphism
- GLM:
-
General Regression Model
- HW:
-
Hardy-Weinberg
- HIV:
-
Human Immunodeficiency Virus
- HBV:
-
human Hepatitis B Virus
- HCV:
-
Human Hepatitis C Virus
References
Woodman CB, Collins S, Winter H, et␣al (2001) Natural history of cervical human papillomavirus infection in young women: a longitudinal cohort study. Lancet 357:1831–836
Stentella P, Frega A, Ciccarone M, et␣al (1998) HPV and intraepithelial neoplasia recurrent lesions of the lower genital tract: assessment of the immune system. Eur J Gynaecol Oncol 19:466–69
Turner MW, Hamvas RM (2000) Mannose-binding lectin: structure, function, genetics and disease associations. Rev Immunogenet 2:305–22
Garred P, Madsen HO, Balslev U, et␣al (1997) Susceptibility to HIV infection and progression of AIDS in relation to variant alleles of mannose-binding lectin. Lancet 349:236–40
Garred P, JS J, Quist L, Taaning E, Madsen HO (2003) Association of mannose-binding lectin polymorphisms with sepsis and fatal outcome, in patients with systemic inflammatory response syndrome. J Infect Dis 188:1394–403
Roy S, Knox K, Segal S, et␣al (2002) MBL genotype and risk of invasive pneumococcal disease: a case-control study. Lancet 359:1569–573
Thio CL, Mosbruger T, Astemborski J, et␣al (2005) Mannose binding lectin genotypes influence recovery from hepatitis B virus infection. J Virol 79:9192–196
Tang YW, Cleavinger PJ, Li H, Mitchell PS, Smith TF, Persing DH. (2000) Analysis of candidate-host immunogenetic determinants in herpes simplex virus-associated Mollaret’s meningitis. Clin Infect Dis 30:176–78
Hartshorn KL, Sastry K, White MR, et␣al (1993) Human mannose-binding protein functions as an opsonin for influenza A viruses. J Clin Invest 91:1414–420
Sasaki K, Tsutsumi A, Wakamiya N, et␣al (2000) Mannose-binding lectin polymorphisms in patients with hepatitis C virus infection. Scand J Gastroenterol 35:960–65
Devlin B, Risch N. (1995) A comparison of linkage disequilibrium measures for fine-scale mapping. Genomics 29:311–22
Acknowledgements
This study was partly supported by grants from “Ministero della Salute” IRCCS Research Program, Ricerca Corrente 2006–2008, Linea n. 4 “Tumori” and Linea n. 2 “Malattie di Rilevanza Sociale”
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Paola Parrella and Davide Seripa contribute equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Parrella, P., Seripa, D., Matera, M.G. et al. Lack of association between genetic variants in the mannose-binding lectin 2 (MBL2) gene and HPV infection. Eur J Epidemiol 22, 159–162 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10654-007-9111-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10654-007-9111-8