Abstract
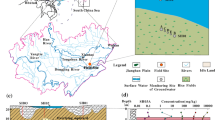
The Xiong’an New Area (XA) was established as a development hub in China. Excessive exploitation of groundwater has caused a series of environmental and geological problems, restricting further development of XA. The widely distributed ponds in this area have been targeted as convenient and efficient sites of artificial groundwater recharge. However, nitrogen accumulation in the shallow vadose zone associated with agricultural activities may pose environmental risks to groundwater during the recharge and infiltration process. Therefore, this study investigated the effects, transfer, and transformation of nitrogen during artificial groundwater recharge. The aeration zone is thick and the medium comprises fine particles, with total nitrogen and nitrate accumulation mainly in the shallow aeration zone. In indoor experiments, the nitrate removal rate reached 83.5% when organic carbon in the source water was increased by 10 mg/L. For Baigou diversion river water(BW) with slightly higher (14.46 mg/L) and lower (5.04 mg/L) nitrate contents, the nitrate content decreased by 26.0% (10.70 mg/L) and 26.8% (3.69 mg/L), respectively, after 150 days. When the water head was increased by 20 cm to increase the recharge rate, the time required for nitrate and ammonium to reach the maximum and equilibrium concentration was reduced by 50%. These findings indicate that nitrogen concentration in the source water, aeration zone media, and groundwater should be considered in pond replenishment. It is also necessary to control the concentration of organic carbon and the rate of recharge, which would provide guidance for other similar projects.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beganskas, S., Gorski, G., Weathers, T., Fisher, A. T., Schmidt, C., Saltikov, C., et al. (2018). A horizontal permeable reactive barrier stimulates nitrate removal and shifts microbial ecology during rapid infiltration for managed recharge. Water Research, 144, 274–284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2018.07.039
Bekele, E., Toze, S., Patterson, B., & Higginson, S. (2011). Managed aquifer recharge of treated wastewater: Water quality changes resulting from infiltration through the vadose zone. Water Research, 45(17), 5764–5772. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2011.08.058
Bouwer, H. (2002). Artificial recharge of groundwater: Hydrogeology and engineering. Hydrogeology Journal, 10(1), 121–142. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-001-0182-4
Burri, N. M., Weatherl, R., Moeck, C., & Schirmer, M. (2019). A review of threats to groundwater quality in the anthropocene. Science of the Total Environment, 684, 136–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.05.236
Cai, Z. (2017). The strategic intention, historical significance and the key to success or failure of Xiongan New Area. China Development Observation, 08, 9–13.
Christianson, L. E., Lepine, C., Sibrell, P. L., Penn, C., & Summerfelt, S. T. (2017). Denitrifying woodchip bioreactor and phosphorus filter pairing to minimize pollution swapping. Water Research, 121, 129–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2017.05.026
Connor, J. A., Paquette, S., McHugh, T., Gie, E., Hemingway, M., & Bianchi, G. (2017). Application of natural resource valuation concepts for development of sustainable remediation plans for groundwater. Journal of Environmental Management, 204, 721–729. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2017.03.053
Ganot, Y., Holtzman, R., Weisbrod, N., Russak, A., Katz, Y., & Kurtzman, D. (2018). Geochemical processes during managed aquifer recharge with desalinated seawater. Water Resources Research, 54(2), 978–994. https://doi.org/10.1002/2017WR021798
Gorski, G., Dailey, H., Fisher, A. T., Schrad, N., & Saltikov, C. (2020). Denitrification during infiltration for managed aquifer recharge: Infiltration rate controls and microbial response. Science of the Total Environment, 668, 1030–1037. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138642
Grau-Martínez, A., Folch, A., Torrentó, C., Valhondo, C., Barba, C., Domènech, C., et al. (2018). Monitoring induced denitrification during managed aquifer recharge in an infiltration pond. Journal of Hydrology, 561, 123–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2018.03.044
Hampton, T. B., Zarnetske, J. P., Briggs, M. A., Singha, K., Harvey, J. W., Day-Lewis, F. D., et al. (2019). Residence time controls on the fate of nitrogen in flow-through lakebed sediments. Journal of Geophysical Research: Biogeosciences, 124(3), 689–707. https://doi.org/10.1029/2018JG004741
Han, P. P., Huang, J. L., Li, R. D., Wang, L., Hu, Y., & Huang, W. (2015). Remote sensing monitoring and dynamic analysis of ponds based on object-oriented rules. Transactions of the CSAM, 46(1), 272–277.
Hartog, N., Griffioen, J., & Van der Weijden, C. H. (2002). Distribution and reactivity of O2-reducing components in sediments from a layered aquifer. Environmental Science & Technology, 36(11), 2338–2344. https://doi.org/10.1021/es015681s
Hellegers, P., Immerzeel, W., & Droogers, P. (2013). Economic concepts to address future water supply-demand imbalances in Iran, Morocco and Saudi Arabia. Journal of Hydrology, 502, 62–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2013.08.024
Hu, H., Mao, X., & Yang, Q. (2018). Impacts of Yongding River ecological restoration on the groundwater environment: Scenario prediction. Vadose Zone Journal, 17(1), 180121. https://doi.org/10.2136/vzj2018.06.0121
Hua, G., Salo, M. W., Schmit, C. G., & Hay, C. H. (2016). Nitrate and phosphate removal from agricultural subsurface drainage using laboratory woodchip bioreactors and recycled steel byproduct filters. Water Research, 102, 180–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2016.06.022
Izbicki, J. A., Flint, A. L., O’Leary, D. R., Nishikawa, T., Martin, P., Johnson, R. D., et al. (2015). Storage and mobilization of natural and septic nitrate in thick unsaturated zones, California. Journal of Hydrology, 524, 147–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2015.02.005
Karges, U., Ott, D., De Boer, S., & Puettmann, W. (2020). 1,4-Dioxane contamination of German drinking water obtained by managed aquifer recharge systems: Distribution and main influencing factors. Science of the Total Environment, 711, 134783. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134783
Liu, Y., Wang, M., Webber, M., Zhou, C., & Zhang, W. (2020). Alternative water supply solutions: China’s South-to-North-water-diversion in Jinan. Journal of Environmental Management, 276, 111337. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.111337
Lü, M., Wang, S., Qi, Y., Kong, X., & Sun, H. (2018). Study on the relationship between precipitation and pond water storage in lowland area of North China Plain—A case study in Nanpi County, Hebei Province. Journal of Natural Resources, 33, 1796–1805.
Ma, Y., Li, M., Wu, M., Li, Z., & Liu, X. (2015). Occurrences and regional distributions of 20 antibiotics in water bodies during groundwater recharge. Science of the Total Environment, 518, 498–506. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.02.100
McBurnett, L. R., Holt, N. T., Alum, A., & Abbaszadegan, M. (2018). Legionella - A threat to groundwater: Pathogen transport in recharge basin. Science of the Total Environment, 621, 1485–1490. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.10.080
Nolan, B. T., Hitt, K. J., & Ruddy, B. C. (2002). Probability of nitrate contamination of recently recharged groundwaters in the conterminous United States. Environmental Science & Technology, 36(10), 2138–2145. https://doi.org/10.1021/es0113854
Nordström, A., Herbert, R. B., & Herbert, R. B. (2017). Denitrification in a low-temperature bioreactor system at two different hydraulic residence times: Laboratory column studies. Environmental Technology, 38(11), 1362–1375. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2016.1228699
Page, D. W., Peeters, L., Vanderzalm, J., Barry, K., & Gonzalez, D. (2017). Effect of aquifer storage and recovery (ASR) on recovered stormwater quality variability. Water Research, 117, 1–8.
Palmer, S. C., Kutser, T., & Hunter, P. D. (2015). Remote sensing of inland waters: Challenges, progress and future directions. Remote Sensing of Environment, 157, 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2014.09.021
Patterson, B. M., Shackleton, M., Furness, A. J., Pearce, J., Descourvieres, C., Linge, K. L., et al. (2010). Fate of nine recycled water trace organic contaminants and metal(loid)s during managed aquifer recharge into a anaerobic aquifer: Column studies. Water Research, 44, 1471–1481. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2009.10.044
Peterson, M. E., Curtin, D., Thomas, S., Clough, T. J., & Meenken, E. D. (2013). Denitrification in vadose zone materia lamended with dissolved organic matter from topsoil and subsoil. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 61, 96–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2013.02.010
Prommer, H., & Stuyfzand, P. J. (2005). Identification of temperature-dependent water quality changes during a deep well injection experiment in a pyritic aquifer. Environmental Science & Technology, 39(7), 2200–2209. https://doi.org/10.1021/es0486768
Sallwey, J., Valverde, J. P. B., Vásquez López, F., Junghanns, R., & Stefan, C. (2019). Suitability maps for managed aquifer recharge: A review of multi-criteria decision analysis studies. Environmental Reviews, 27(2), 138–150. https://doi.org/10.1139/er-2018-0069
Schmidt, F., Koch, B. P., Elvert, M., Schmidt, G., Witt, M., & Hinrichs, K. U. (2011). Diagenetic transformation of dissolved organic nitrogen compounds under contrasting sedimentary redox conditions in the Black Sea. Environmental Science & Technology. https://doi.org/10.1021/es2003414
Seitzinger, S., Harrison, J. A., Böhlke, J. K., Bouwman, A. F., Lowrance, R., Peterson, B., et al. (2006). Denitrification across landscapes and waterscapes: A synthesis. Ecological Applications, 16(6), 2064–2090. https://doi.org/10.1890/1051-0761(2006)016[2064:DALAWA]2.0.CO;2
Tafteh, A., & Sepaskhah, A. R. (2012). Application of HYDRUS-1D model for simulating water and nitrate leaching from continuous and alternate furrow irrigated rapeseed and maize fields. Agricultural Water Management, 113, 19–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2012.06.011
Tao, Y., Li, N., Wang, S., Chen, H., Guan, X., & Jia, M. (2021). Simulation study on performance of nitrogen loss of an improved subsurface drainage system for one-time drainage using HYDRUS-2D. Agricultural Water Management, 246, 106698. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2020.106698
Tzoraki, O., Dokou, Z., Christodoulou, G., Gaganis, P., & Karatzas, G. P. (2018). Assessing the efficiency of a coastal managed aquifer recharge (MAR) system in Cyprus. Science of the Total Environment, 626, 875–886. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.01.160
Valhondo, C., Martinez-Landa, L., Carrera, J., Ayora, C., Nödler, K., & Licha, T. (2018). Evaluation of EOC removal processes during artificial recharge through a reactive barrier. Science of the Total Environment, 612, 985–994. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.08.054
Van Drecht, G., Bouwman, A. F., Knoop, J. M., Beusen, A. H. W., & Meinardi, C. R. (2003). Global modeling of the fate of nitrogen from point and nonpoint sources in soils, groundwater, and surface water. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 17(4), 1115. https://doi.org/10.1029/2003gb002060
Williamson, C. E., Saros, J. E., Vincent, W. F., & Smol, J. P. (2009). Lakes and reservoirs as sentinels, integrators, and regulators of climate change. Limnology and Oceanography, 54, 2273–2282. https://doi.org/10.4319/lo.2009.54.6_part_2.2273
Xu, G., Su, X., Zhang, Y., & You, B. (2021) Identifying Potential sites for artificial recharge in the plain area of the Daqing River catchment using GIS-based multi-criteria analysis. Sustainability, 13(7), 3978. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13073978.
Zammouri, M., & Brini, N. (2020). Efficiency of artificial groundwater recharge, quantification through conceptual modelling. Water Resources Management, 34(10), 3345–3361. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-020-02617-1
Zhang, Y., Lee, D., Ding, J., & Lu, J. (2020). Environmental impact of high concentration nitrate migration in soil system using HYDRUS simulation. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(9), 3147. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17093147
Zheng, L., Zhao, X., Zhu, G., Yang, W., Xia, C. & Xu, T. (2017). Occurrence and abundance of ammonia-oxidizing archaea and bacteria from the surface to below the water table in deep soil and their contributions to nitrification. MicrobiologyOpen, 6(4), e00488. https://doi.org/10.1002/mbo3.488.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the National Key R&D Program of China for financially supporting this research under the project entitled “Artificial Replenishment and Regulation of Groundwater in Xiong’an New Area” (Grant Number: 2018YFC0406503).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, G., Su, X., Yuan, Z. et al. Nitrogen behavior during artificial groundwater recharge through ponds: A case study in Xiong’an New Area. Environ Geochem Health 44, 2545–2561 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-021-01041-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-021-01041-7