Abstract
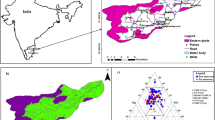
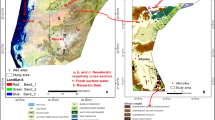
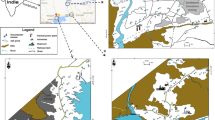
The objectives of this study were to measure some trace element concentrations in the groundwater of the Khoy area in northwestern Iran, understand their potential origins using multivariate statistical approaches (correlation analysis, cluster analysis and factor analysis), and evaluate their non-carcinogenic human health risks to local residents through drinking water intake. The trace element status of the groundwater and the associated health risks in the study area have not previously been reported. Groundwater water samples were collected from 54 water sources in July 2017 in the study area. Samples were measured for EC, pH, major and minor elements and some trace elements (Fe, Mn, Al, Zn, Cr, Pb, Cd, Co, Ni and As). The levels of EC, F, Cd, Pb, Zn, As and all the major ions except K exceeded permissible levels for drinking water. Multivariate analysis showed that the quality of groundwater was mainly controlled by geogenic factors followed by anthropogenic impacts. Health risk assessment results indicated that Cr and As in the groundwater, with hazard quotient values of 0.0001 and 11.55, respectively, had the lowest and highest impacts of non-carcinogenic risk to adults and children in the area. The high-risk samples were mainly situated in the northeast and southwest of the Khoy plain where the groundwater was saline. The health risk associated with water consumption from the unconfined aquifer was higher than that from the confined aquifer in the study area. Special attention should be paid to groundwater management in the high-risk areas to control factors (e.g., EC, pH and redox) that stimulate the release of trace elements into groundwater.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adriano, D. C. (2001). Trace elements in terrestrial environments: Biogeochemistry, bioavailability, and risks of metals (2nd ed.). New York: Springer.
Anawar, H. M., Akai, J., & Sakugaqa, H. (2003). Mobilization of arsenic from subsurface sediments by the effect of bicarbonate ions in groundwater. Chemosphere, 54, 753–762.
Anawar, H. M., Akai, J., Mihaljevič, M., Sikder, A. M., Ahmed, G., Tareq, S. M., et al. (2011). Arsenic contamination in groundwater of Bangladesh: Perspectives on geochemical, microbial and anthropogenic issues. Water, 3, 1050–1076. https://doi.org/10.3390/w3041050.
Arslan, H. (2013). Application of multivariate statistical techniques in the assessment of groundwater quality in seawater intrusion area in Bafra Plain, Turkey. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 185, 2439–2452.
Balkhair, K. S., & Ashraf, M. A. (2016). Field accumulation risks of heavy metals in soil and vegetable crop irrigated with sewage water in western region of Saudi Arabia. Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences, 23(1), 32–44.
Barzegar, R., Asghari Moghaddam, A., & Kazemian, N. (2015). Assessment of heavy metals concentrations with emphasis on arsenic in the Tabriz plain aquifers, Iran. Environmental Earth Sciences, 74(1), 297–313.
Barzegar, R., Asghari Moghaddam, A., Soltani, S., Fijani, E., Tziritis, E., & Kazemian, N. (2018). Heavy metal(loid)s in the groundwater of Shabestar area (NW Iran): Source identification and health risk assessment. Exposure and Health. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-017-0267-5.
Barzegar, R., Asghari Moghaddam, A., & Tziritis, E. (2016). Assessing the hydrogeochemistry and water quality of the Aji-Chay River, northwest of Iran. Environmental Earth Sciences, 75(23), 1486.
Barzegar, R., Asghari Moghaddam, A., Tziritis, E., Fakhri, M. S., & Soltani, S. (2017). Identification of hydrogeochemical processes and pollution sources of groundwater resources in the Marand plain, northwest of Iran. Environmental Earth Sciences, 76(7), 297.
Belzile, N., Chen, Y. W., Gunn, J. M., & Dixit, S. S. (2004). Sediment trace metal profiles in lakes of Killarney Park, Canada: From regional to continental influence. Environmental Pollution, 130(2), 239–248.
Bhuiyan, M., Rakib, M. A., Dampare, S. B., Ganyaglo, S., & Suzuki, S. (2011). Surface water quality assessment in the central part of Bangladesh using multivariate analysis. KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering, 15(6), 995–1003.
Bingöl, D., Ay, Ü., Bozbaş, S. K., & Uzgören, N. (2013). Chemometric evaluation of the heavy metals distribution in waters from the Dilovası region in Kocaeli, Turkey. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 68(1–2), 134–139.
Bortey-Sam, N., Nakayama, S. M., Ikenaka, Y., Akoto, O., Baidoo, E., Mizukawa, H., et al. (2015). Health risk assessment of heavy metals and metalloid in drinking water from communities near gold mines in Tarkwa, Ghana. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 187(7), 397.
Celebi, A., Sengour, B., & Klove, B. (2014). Human health risk assessment of dissolved metals in groundwater and surface waters in the Melen watershed, Turkey. Journal of Environmental Science and Health, Part A: Toxic/Hazardous Substances & Environmental Engineering, 49, 153–161.
Domenico, P. A., & Schwartz, F. W. (1998). Physical and chemical hydrogeology (2nd ed., p. 506). New York: John Wiley.
Duggal, V., Rani, A., Mehra, R., & Balaram, V. (2017). Risk assessment of metals from groundwater in northeast Rajasthan. Journal of Geological Society of India, 90(1), 77–84.
El Alfy, M., Lashin, A., Abdalla, F., & Al-Bassam, A. (2017). Assessing the hydrogeochemical processes affecting groundwater pollution in arid areas using an integration of geochemical equilibrium and multivariate statistical techniques. Environmental Pollution, 229, 760–770. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.05.052.
Esmaeili, S., Asghari Moghaddam, A., Barzegar, R., & Tziritis, E. (2018). Multivariate statistics and hydrogeochemical modeling for source identification of major elements and heavy metals in the groundwater of Qareh-Ziaeddin plain, NW Iran. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 11, 5.
Giri, S., & Singh, A. K. (2015). Human health risk assessment via drinking water pathway due to metal contamination in the groundwater of Subarnarekha River Basin, India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 187, 63–76.
Guo, H., Zhang, B., Li, Y., Berner, Z., Tang, X., Norra, S., et al. (2011). Hydrogeological and biogeochemical constrains of arsenic mobilization in shallow aquifers from the Hetao basin, Inner Mongolia. Environmental Pollution, 159(4), 876–883.
Hardle, W., & Simar, L. (2007). Applied multivariate statistical analysis (2nd ed.). Berlin: Springer.
Hylander, L. D., Meili, M., Oliveira, L. J., Silva, E. D. E., Guimaraes, J. R. D., Araujo, D. M., et al. (2000). Relationship of mercury with aluminum, iron and manganese oxy-hydroxides in sediments from the Alto Pantanal, Brazil. The Science of the Total Environment, 260, 97–107.
IBM Corp. (2012). IBM SPSS statistics for windows, version 21.0. Armonk, NY: IBM Corp.
Järup, L. (2003). Hazards of heavy metal contamination. British Medical Bulletin, 68, 167–182.
Kaiser, H. F. (1960). The application of electronic computers to factor analysis. Educational and Psychological Measurement, 20, 141–151.
Kumaresan, P. R. M. (2008). Factor analysis and linear regression model (LRM) of metal speciation and physico-chemical characters of groundwater samples. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 138, 65–79.
Levins, I., & Gosk, G. (2008). Trace elements in groundwater as indicators of anthropogenic impact. Environmental Geology, 55, 285–290.
Li, P., Li, X., Meng, X., Li, M., & Zhang, Y. (2016). Appraising groundwater quality and health risks from contamination in a semiarid region of northwest China. Exposure and Health, 8(3), 361–379. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-016-0205-y.
Li, P., & Qian, H. (2011). Human health risk assessment for chemical pollutants in drinking water source in Shizuishan City, Northwest China. Iranian Journal of Environmental Health Science and Engineering, 8(1), 41–48.
Li, P., Qian, H., Howard, K. W. F., & Wu, J. (2015). Heavy metal contamination of Yellow River alluvial sediments, northwest China. Environmental Earth Sciences, 73(7), 3403–3415. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3628-4.
Li, P., Tian, R., Xue, C., & Wu, J. (2017). Progress, opportunities and key fields for groundwater quality research under the impacts of human activities in China with a special focus on western China. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 24(15), 13224–13234. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-8753-7.
Li, P., Wu, J., Qian, H., Lyu, X., & Liu, H. (2014). Origin and assessment of groundwater pollution and associated health risk: A case study in an industrial park, northwest China. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 36(4), 693–712. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-013-9590-3.
Liang, C. P., Wang, S. W., Kao, Y. H., & Chen, J. S. (2016). Health risk assessment of groundwater arsenic pollution in southern Taiwan. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 38, 1271–1281.
Ma, H. W., Hung, M. L., & Chen, P. C. (2007). A systemic health risk assessment for the chromium cycle in Taiwan. Environment International, 33(2), 206–218.
Nabavi, M. H. (1976). An introduction to the geology of Iran (p. 109). Tehran: Geological Survey of Iran. (in Persian).
Nguyen, V. A., Bang, S., Viet, P. H., & Kim, K. W. (2009). Contamination of groundwater and risk assessment for arsenic exposure in Ha Nam Province, Vietnam. Environment International, 35(3), 466–472.
Otto, M. (1998). Multivariate methods. In R. Kellner, J. M. Mermet, M. Otto, & H. M. Widmer (Eds.), Analytical chemistry (p. 916). Weinheim: WileyVCH.
Piper, A. M. (1944). A graphic procedure in the geochemical interpretation of water analyses. Transactions American Geophysical Union, 25, 914–928.
Prüss-Ustün, A., Vickers, C., Haefliger, P., & Bertollini, R. (2011). Knowns and unknowns on burden of disease due to chemicals: A systematic review. Environmental Health, 10, 9.
Purushothaman, P., Rao, M. S., Rawat, Y. S., Kumar, C. P., Krishan, G., & Parveen, T. (2014). Evaluation of hydrogeochemistry and water quality in Bist-doab region, Punjab, India. Environmental Earth Sciences, 72(3), 693–706.
Radfar, H., Amini, B., Khalaatbari, M., Emami, M. H., & Bahremand, M. (2005). Geological map of Khoy sheet (1:100,000). Tehran: Geological Survey of Iran.
Rahman, M. M., Ng, J. C., & Naidu, R. (2009). Chronic exposure of arsenic via drinking water and its adverse health impacts on humans. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 31, 189–200.
Rowland, H. A. L., Polya, D. A., Lloyd, J. R., & Pancost, R. D. (2006). Characterisation of organic matter in a shallow, reducing, arsenicrich aquifer, West Bengal. Organic Geochemistry, 37, 1101–1114.
Sakizadeh, M., & Mirzaei, R. (2016). Health risk assessment of Fe, Mn, Cu, Cr in drinking water in some wells and springs of Shush and Andimeshk, Khuzestan Province, Southern Iran. Iranian Journal of Toxicology, 10(2), 29–35.
Salminen, R., Batista, M. J., Bidovec, M., Demetriades, A., De Vivo, B., De Vos, W., Duris, M., Gilucis, A., Gregorauskiene, V., Halamic, J., Heitzmann, P., Lima, A., Jordan, G., Klaver, G., Klein, P., Lis, J., Locutura, J., Marsina, K., Mazreku, A., O’Connor, P. J., Olsson, S., Ottesen, R. T., Petersell, V., Plant, J. A., Reeder, S., Salpeteur, I., Sandström, H., Siewers, U., Steenfeldt, A., & Tarvainen, T. (2005). FOREGS geochemical atlas of Europe, part 1: Background information, methodology and maps. Geological Survey of Finland, Espoo, p 525, 36 figures, 362 maps.
Singh, H., Singh, D., Singh, S. K., & Shukla, D. N. (2017). Assessment of river water quality and ecological diversity through multivariate statistical techniques, and earth observation dataset of rivers Ghaghara and Gandak, India. International Journal of River Basin Management, 15(3), 347–360.
Soltani, S., Asghari Moghaddam, A., Barzegar, R., Kazemian, N., & Tziritis, E. (2017). Hydrogeochemistry and water quality of the Kordkandi-Duzduzan plain, NW Iran: Application of multivariate statistical analysis and PoS index. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 189(9), 455.
Srivastava, S. K., & Ramanathan, A. L. (2008). Geochemical assessment of groundwater quality in vicinity of Bhalswa landfill, Delhi, India, using graphical and multivariate statistical methods. Environmental Geology, 53(7), 1509–1528.
Su, H., Kang, W., Xu, Y., & Wang, J. (2017). Assessing groundwater quality and health risks of nitrogen pollution in the Shenfu mining area of Shaanxi Province, Northwest China. Exposure and Health. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-017-0247-9.
Sun, L., Peng, W., & Cheng, C. (2016). Source estimating of heavy metals in shallow groundwater based on UNMIX. Model: A case study. Indian Journal of Geo-Marine Sciences, 45(6), 756–762.
Tziritis, E., Datta, P. S., & Barzegar, R. (2017). Characterization and assessment of groundwater resources in a complex hydrological basin of central Greece (Kopaida basin) with the joint use of hydrogeochemical analysis, multivariate statistics and stable isotopes. Aquatic Geochemistry, 23(4), 271–298.
Tziritis, E., Skordas, K., & Kelepertsis, A. (2016). The use of hydrogeochemical analyses and multivariate statistics for the characterization of groundwater resources in a complex aquifer system. A case study in Amyros River basin, Thessaly, central Greece. Environmental Earth Sciences, 75(4), 1–11.
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. (1999). A risk assessment multi-way exposure spreadsheet calculation tool. Washington, DC: United States Environmental Protection Agency.
Usman, U. N., Toriman, M. E., Juahir, H., Abdullahi, M. G., Rabiu, A. A., & Isiyaka, H. (2014). Assessment of groundwater quality using multivariate statistical techniques in Terengganu. Science and Technology, 4(3), 42–49. https://doi.org/10.5923/j.scit.20140403.02.
Ward, J. H. (1963). Hierarchical grouping to optimize an objective function. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 301, 236–244.
Wedephol, K. H. (1978). Manganese. In K. H. Wedepohl (Ed.), Handbook of geochemistry (Vol. 11/3, pp. 25-K-1/25-K-17). Berlin: Springer.
Wongsasuluk, P., Chotpantarat, S., Siriwong, W., & Robson, M. G. (2014). Heavy metal contamination and human health risk assessment in drinking water from shallow groundwater wells in an agricultural area in Ubon Ratchathani Province, Thailand. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 36, 169–182.
World Health Organization. (2011). Guidance for immunotoxicity risk assessment for chemicals. IPCS harmonization project document; no. 10, Geneva.
Wu, J., Li, P., Qian, H., Duan, Z., & Zhang, X. (2014). Using correlation and multivariate statistical analysis to identify hydrogeochemical processes affecting the major ion chemistry of waters: Case study in Laoheba phosphorite mine in Sichuan, China. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 7(10), 3973–3982. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-013-1057-4.
Wu, J., & Sun, Z. (2016). Evaluation of shallow groundwater contamination and associated human health risk in an alluvial plain impacted by agricultural and industrial activities, mid-west China. Expo Health, 8(3), 311–329. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-015-0170-x.
Wu, M. L., Wang, Y. S., Su, C. C., Wang, H., Dong, J. D., Yin, J. P., et al. (2010). Identification of coastal water quality by statistical analysis methods in Daya Bay, South China Sea. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 60(6), 852–860.
Yang, M., & Sanudo-Wilhelmy, S. (1998). Cadmium and manganese distribution in the Hudson River estuary: Interannual and seasonal variability. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 19, 982–992.
Yeganeh, J., Nazemi, S., & Yousefzadeh, A. (2015). Assessment of the effect of human and industrial activities on groundwater within the city of Khoy. International Journal of Health Studies, 1(2), 26–33. https://doi.org/10.22100/ijhs.v1i2.59.
Yidana, S. M., Yakubo, B. B., & Akabzaa, T. M. (2010). Analysis of groundwater quality using multivariate and spatial analyses in the Keta basin, Ghana. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 58, 220–234.
Zhang, Y., Wu, J., & Xu, B. (2018). Human health risk assessment of groundwater nitrogen pollution in Jinghui canal irrigation area of the loess region, northwest China. Environmental Earth Sciences, 77(7), 273. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-018-7456-9.
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the Iran Ministry of Science, Research and Technology for providing a scholarship to Rahim Barzegar to conduct this research at McGill University under the supervision of Professor J. Adamowski. We would like to thank Mrs. N. Kazemian for analyzing the trace elements at the Water Quality Control Lab of East Azerbaijan Province. Anonymous reviewers are sincerely acknowledged for their useful comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barzegar, R., Asghari Moghaddam, A., Adamowski, J. et al. Assessing the potential origins and human health risks of trace elements in groundwater: A case study in the Khoy plain, Iran. Environ Geochem Health 41, 981–1002 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-018-0194-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-018-0194-9