Abstract
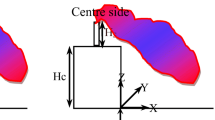
In this study, motion and deposition of various sizes of aerosols in turbulent flow of air inside and outside of two-dimensional buildings with closed and open windows have been investigated, numerically. This simulation was based on FVM solving of RANS equations with k–ε model. Eulerian–Lagrangian method was used to simulate fluid and particles motions, respectively, and one-way coupling between them was considered. Effect of particles size on deposition efficiency has been calculated. The results shown that, the particles deposition outside and inside of the building with domical roof is less than triangular and flat roof buildings.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Soltani Goharrizi A, Taheri M, Fathikalajahi J (1998) Prediction of particle deposition from a turbulent stream around a surface-mounted Ribbon. Aerosol Sci Technol 15:129–141
Jahanara M, Yaghoubi MA (1996) Two-demensional numerical Simulation of wind flow and ventilation in a single building using turbulence model. Iran J Sci Technol 20(1):45–67
Yaghoubi MA, Sabzevari A, Golneshan AA (1991) Wind towers measurement and performance. Sol Energy 47:97–106
Grimsrud DT (1992) Natural ventilation and indoor air quality. In: International symposium on room air convection and ventilation effectiveness. University of Tokyo, Japan
Abdellatif E, Abdel Gawad F (2004) Experimental and numerical investigation of internal and external experimental flow fields for buildings with porous canopy roofs. Al-Azhar engineering, 8th international conference, Cairo, Egypt
Ahmadi G, Li A (2000) Computer simulation of particle transport and deposition near a small isolated building. J Wind Eng Ind Aerodyn 84:23–46
Liu CH, Ahmadi G (2006) Transport and deposition of particles near a building model. Build Environ 41:828–836
Mirzai MH, Harvey JK, Jones CD (1994) Wind tunnel investigation of dispersion of pollutants due to wind flow around a small building. Atmos Environ 28(18):19–26
Chang TJ, Hu TS (2008) Transport mechanisms of airborne particulate matters in partitioned indoor environment. Build Environ 43:886–895
Chatoutsidou SE, Maskova L, Ondrackova L, Ondracek J, Lazaridis M, Smolik J (2015) Modeling of the aerosol infiltration characteristics in a cultural heritage building: the Baroque Library Hall in Prague. Build Environ 89:253–263
Chen C, Lin CH, Wei D, Chen Q (2016) Modeling particle deposition on the surface around a multi-slot diffuser. Build Environ 107:79–81
Limam K, El Hamdani S, Abadie M, Linder G, Bendou A (2017) Numerical study of transport and particle deposition inside buildings. Energy Proc 139:430–436
Young DF, Munson BR, Okiishi TH, Huebsch WW (2011) A brief introduction to fluid mechanics. Wiley, Hoboken
Abdolzadeh M (2010) Study of particles deposition and investigation of effective factors on the particles transfer over an flat inclined surface on turbulent flow, PhD dissertation, Shahid Bahonar University of Kerman, Kerman, Iran
Harris CK, Rowkawrts D, Rosendal FJ, Buitendijk FG, Deskopoulos P, Vreenegoor AJ, Wang H (1996) Computational fluid dynamics for chemical engineering. J Chem Eng Sci 51(10):1565–1594
Hosseini SMJ, Soltani Goharrizi A, Abolpour B (2014) Numerical study of aerosol particle deposition in simple and converging-diverging micro-channels with a slip boundary condition at the wall. Particuology 13:100–105
May KR, Clifford R (1967) The impaction of aerosol particles on cylinder, sphere, ribbons and discs. Ann Occup Hyg 10:83
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Momeni, M., Soltani Goharrizi, A. & Abolpour, B. Numerical study of aerosols motion and deposition outside and inside buildings with different geometries. Environ Fluid Mech 18, 759–767 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10652-018-9583-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10652-018-9583-y