Abstract
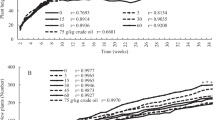
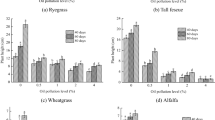
The oil industry has inherent risks of spills or leaks due to natural or anthropogenic causes, which cause alterations in the soil and damage to the plant. An experiment was carried to investigate the effect of oil on the growth, biomass production, biosynthesis of crude protein of Leersia hexandra grass and the remove of oil from the soil. The results showed different responses by L. hexandra depending on the age, low concentrations of oil induced a significant increase in stolon length, in relative growth rate, in dry matter production and in the biosynthesis of crude protein. The same parameters decreased at high concentrations of oil. However, at the end of the evaluation period of 180 days, high concentrations of oil induced a significant increase in the number of young plants and secondary roots, the terminal third of the main root and root dry matter. The dose response curves had the shape of an inverted U, showing that at days 15, 45, 90 and 180, in stolon length, aerial dry matter production, crude protein (day 90) and young plants (days 45 and 90) exhibited a typical biphasic response. The increase in oil concentration correlated with increases in young plants, number of secondary roots, number of roots at the middle, terminal third and root dry matter. After 180 days exposure the rhizosphere of L. hexandra a total oil removal of oil of 76.7 ± 4 was achieved; 61.7, 51, 44.6, 38 and 52% in soils that initially contained 7.9, 54, 102, 126, 145 and 238 g oil.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agrawal M, Singh B, Agrawal SB, Bell JNB, Marshall F (2006) The effect of air pollution on yield and quality of mung bean grown in peri-urban areas of Varanasi. Water Air Soil Pollut 169(1):239–254. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-006-2237-6
AOAC (Association of Official Analytical Chemists) (1980) Official Methods of Analysis, 13th edn. Association of Official Analytical Chemists, Washington DC
Aparicio R, González-Ronquillo M, Torres R, Astudillo L, Córdova L, Carrasquel J (2007) Degradabilidad de los pastos lambedora (Leersia hexandra) y paja de agua (Hymenachne amplesicaulis) en cuatro épocas del año de una sábana inundable del estado Apure, Venezuela. Zootec Trop 25(3):225–228
Arias TA (2012) La ecotoxicidad y el pasto japonesa (Leersia sp) en la fitorremediación de un Gleysol contaminado con petróleos fresco, intemperizado y sulfato. Tesis de Maestría en Ciencias en Producción Agroalimentaria en el Trópico. Colegio de Postgraduados Campus Tabasco. H. Cárdenas, Tabasco, México
Arias-Trinidad A, Rivera-Cruz MC, Roldán-Garrigós A, Aceves-Navarro LA, Quintero-Lizaola R, Hernández-Guzmán J (2017) Uso de Leersia hexandra (Poaceae) en la fitorremediación de suelos contaminados con petróleo fresco e intemperizado. Int J Trop Biol Conserv 65(1):21–30. https://doi.org/10.15517/RBT.V65I1.22967
Azcón-Bieto J, Talón M (2008) Fundamentos de Fisiología Vegetal. McGraw-Hill. Interamericana, Madrid, España
Baldan E, Basaglia M, Fontana F, Shapleigh PJ, Casella S (2015) Development, assessment and evaluation of a biopile for hydrocarbons soil remediation. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 98:66–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2014.12.002
Bouyoucos G (1962) Hydrometer method for particle-size analysis of soils. Agron J. 54(5):464–465. https://doi.org/10.2134/agronj1962.00021962005400050028x
Brady CN, Weil RR (2008) The nature and properties of soils. Pearson Prentice Hall, New Jersey, Columbus Ohio, USA
CABI (Centre for Agricultural Bioscience International) (2018) Invasive species compendium. CAB International, Wallingford, Reino Unido. https//www.cabi.org/isc/datasheet/30391
Calabrese EJ (2012) Hormesis: improving predictions in the low-dose zone. In: Luch A (ed) Molecular, clinical and environmental toxicology, vol 101. Experientia, Amherst, MA, USA. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-7643-8340-4_19
Calabrese EJ, Blain RB (2009) Hormesis and plant biology. Environ Pollut 157(1):42–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2008.07.028
Chaudhry Q, Blom-Zandstra M, Gupta S, Joner EJ (2005) Utilizing the synergy between plants and rhizosphere microorganisms to enhance breakdown of organic pollutants in the environment. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 12(1):34–48. https://doi.org/10.1065/espr2004.08.213
DOF (2006) Norma Mexicana NMX-AA-134-SCFI (2006) Suelos. Hidrocarburos Fracción Pesada por Extracción y Gravimetría. Método de Prueba. Diario Oficial de la Federación. D.F., México, http://legismex.mty.itesm.mx/normas/aa/nmx-aa-06/proy-nmx-aa-134-scfi-2006.pdf
Eichert T, Fernández V (2012) Uptake and release of elements by leaves and other aerial plant parts. In: Marschner P (ed.) Marschner's mineral nutrition of higher plants, 3rd edn. Academic Press Elsevier, San Diego CA, USA, p 71–83
Elgersma A, Soegaard K (2016) Effects of species diversity on seasonal variation in herbage yield and nutritive value of seven binary grass-legume mixtures and pure grass under cutting. Eur J Agron 78:73–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eja.2016.04.011
EPA (1986) Method 418.1 modif. Petroleum hydrocarbons total recoverable spectrophotometric infrared. Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, DC, USA
Escaso SF, Martínez GJL, Planelló CMR (2010) Fundamentos Básicos de Fisiología Vegetal y Animal. Pearson Educación, S.A, Madrid, España
Etchevers BJD (1992) Manual de métodos para análisis de suelos, plantas agua y fertilizantes. Análisis rutinarios en estudios y programas de fertilidad. Laboratorio de Fertilidad, Centro de Edafología. Colegio de Postgraduados en Ciencias Agrícolas. Montecillos. edo, México
González-Moscoso M, Rivera-Cruz MC, Delgadillo-Martínez J, Lagunes-Espinoza LC (2017) Growth analysis and plant production of Leersia hexandra Swartz in tropic wet mexican in fuction on petroleum and surfactant. Polibotánica 43:177–196. https://doi.org/10.18387/polibotanica.43.8
Greenberg BM (2007) Field and laboratory test of multi-process phytoremediation system for decontamination of petroleum and salt impacted soils. Simposium Batelle Press. In: Proceeding of the 9th International in situ and on site Remediation. Ontario, Canada. http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.503.6423&rep=rep1&type=pdf
Hunt R, Causton DR, Shipley B, Askew AP (2002) A modern tool for classical plant growth analysis. Ann Bot 90(4):485–488. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mcf214
Hussain I, Puschenreiter M, Gerhard S, Schöftner P, Yousaf S, Wang A, Hussain SJ, Reichenauer TG (2018) Rhizoremediation of petroleum hydrocarbon-contaminated soils: improvement opportunities and field applications. Environ Exp Bot 147:202–219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2017.12.016
Janzen SJ, Teresinha ML (2018) Rhizospheric microorganisms as a solution for the recovery of soils contaminated by petroleum: a review. J Environ Manag 210:104–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.01.015
Jia L, He X, Chen W, Liu Z, Huang Y, Yu S (2013) Hormesis phenomena under Cd stress in a hyperaccumulator - Lonicera japonica Thunb. Ecotoxicology 22(3):476–485. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-013-1041-5
Jones JB, Wolf B, Mills HA (1992) Plant analysis handbook. A practical sampling, preparation, analysis, and interpretation guide. Micro-Macro Publishing, Inc., USA
Juárez-Hernández J, Bolaños ED, Reinoso M (2004) Contenido de proteína por unidad de materia seca acumulada en pastos tropicales. Época nortes. Rev Cubana Cienc Agrícola 38(4):423–430
Juárez-Hernández J, Bolaños-Aguilar ED (2007) Las curvas de dilución de la proteína como alternativa para la evaluación de pastos tropicales. Univ Cienc 23(1):81–90
Lee SH, Lee WS, Lee CH, Kim JG (2007) Degradation of phenanthrene and pyrene in rhizosphere of grasses and legumes. J Hazard Mater 153(1–2):892–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.09.041
Liao C, Liang X, Lu G, Thai T, Xu W, Dang Z (2015) Effect of surfactant amendment to PAHs-contaminated soil for phytoremediation by maize (Zea mays L.). Ecotoxicol Environ Safe 112:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2014.10.025
Lichtenthaler HK (1996) Vegetation stress: an introduction to the stress concept in plants. J Plant Physiol 148(1–2):4–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0176-1617(96)80287-2
López-Martínez S, Gallegos-Martínez ME, Pérez-Flores LJ, Gutiérrez-Rojas M (2008) Contaminated soil phytoremediation by Cyperus laxus Lam. cytochrome p 450 erod-activity induced by hydrocarbons in roots. Int J Phytoremed 10(4):289–301. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226510802096069
Lynch J, Marschner P, Rengel Z (2012) Effect of internal and external factors on root growth and development. In: Marschner P (ed.) Marschner's mineral nutrition of higher plants, 3rd edn. Academic Press, San Diego, CA, p 331–346
Ma B, He Y, Chen HH, Xu JM, Rangel Z (2010) Dissipation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in the rhizosphere: synthesis through meta-analysis. Environ Pollut 158(3):855–861. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2009.09.024
Madigan TM, Martinko MJ, Bender SK, Buckley HD, Stahl AD (2015) Brock. Biología de los Microorganismos, 14a. edn. Pearson Educación S.A, Madrid, España
Maldonado-Chávez E, Rivera-Cruz MC, Izquierdo-Reyes F, Palma-López DJ (2010) Efectos de rizosfera, microorganismos y fertilización en la biorremediación y fitorremediación de suelos con petróleos crudo nuevo e intemperizado. Univ Cienc 26(2):121–136
Maliszewska-Kordybach B, Smreczak B (2000) Ecotoxicological activity of soils polluted with polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHS)–effect on plants. Environ Technol 21(10):1099–1110. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2000.9618996
Marschner H (1995) Mineral nutrition of higher plants, 3th edn. Academic. Press, San Diego, CA, USA
Muratova YA, Golubev NS, Dubrovskaya VE, Pozdnyakova NN, Panchenko VL, Pleshakova VE, Chernyshova PM, Turkovskaya VO (2012) Remediating abilities of different plant species grown in diesel-fuel-contaminated leached chernozem. Appl Soil Ecol 56:51–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2012.01.002
Nkojo KL, Akinola MO, Oboh BO (2008) Growth and performance of Glycine max L. (Merrill) grown in crude oil contaminated soil augmented with cow dung. Life Sci J 5(3):89–93
Novelo RA (2006) Plantas Acuáticas de la Reserva de la Biosfera Pantanos de Centla, 1a. edn. Editorial Espacios Naturales y Desarrollo Sustentable AC, México D.F
Obayori OS, Llori MO, Abebusoye SA, Amund OO, Oyetibo GO (2008) Microbial population changes in tropical agricultural soil experimentally contaminated with crude petroleum. Afr J Biotechnol 7(24):4512–4520
Okolo JC, Amadi EN, Odu CTI (2005) Effects of soil treatments containing poultry manure on crude oil degradation in sandy loam soil. Appl Ecol Env Res 3(1):47–53
Osuji LC, Onojake CM (2004) The Ebocha-8 oil spillage II. Fate of associated heavy metals six months after. AJEAM-RAGEE 9:78–87
Paria S (2008) Surfactant-enhanced remediation of organic contaminated soil and water. Adv Coll Inter Sci 138(1):24–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cis.2007.11.001
Pérez-Hernández I, Ochoa-Gaona S, Adams RH, Rivera-Cruz MC, Pérez-Hernández V, Jarquín-Sánchez A, Geissen V, Martínez-Zurimendi P (2017) Growth of four tropical tree species in petroleum-contaminated soil and effects of crude oil contamination. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24(24):1769–1783. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7877-5
Reyes-Purata A, Bolaños-Aguilar ED, Hernández-Sánchez D, Aranda-Ibáñez EM, Izquierdo-Reyes F (2009) Producción de materia seca y concentración de proteína en 21 genotipos del pasto humidícola Brachiaria humidicola (Rendle) Schweick. Univ Cienc 25(3):213–224
Rhoades J (1982) Cation exchange capacity. In: Page AL (ed.) Methods of soil analysis. Part 2. Chemical and microbiological properties, 2nd edn. American Society of Agronomy/Soil Science Society of America, Madison, WI, USA, p 178–190
Rincon CA, Ligarreto MA, Garay E (2008) Forage production in the grasses Brachiaria decumbens cv. Amargo and Brachiaria brizantha cv. Toledo subjected to three frequencies and two of defoliation intensities under conditions of Colombian plain piedmont. Rev Facultad Nacional Agrícola Medellín 61(1):4336–4346
Rivera-Cruz MC, Trujillo-Narcía A, Trujillo-Rivera EA, Arias-Trinidad A, Mendoza- López MR (2016) Natural attenuation of weathered oil using aquatic plants in a farm in southeast Mexico. Int J Phytoremediat 18(9):877–884. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226514.2016.1156632
Salisbury FB, Ross CW (2000) Fisiología de las Plantas: Desarrollo de las Plantas y Fisiología Ambiental. Thomson Editores, Madrid, España
SAS (Statiscal Analysis Systems) (2005) “User's guide”, versión 9.1.3. SAS Institute, Inc, Cary, NC, p 664
Swart R, Schultz DW, Ozretich R, Lamberson JO, Cole FA, DeWitt TH, Redmond MS, Ferraro SP (1995) ΣPAH: a model to predict the toxicity of polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbon mixtures in field-collected sediments. Environ Toxicol Chem 14(11):1977–1987. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.5620141120
Tadeo RF (2000) Fisiología de las Plantas y el Estrés. In: Azcon-Bieto J, Talon M (eds) Fundamentos de Fisiología Vegetal. McGraw-Hill Interamericana (Ed.), Madrid, España, p 577–598
Trujillo-Narcía A, Rivera-Cruz MC, Lagunes-Espinosa LC, Palma-López DJ, Soto-Sánchez S, Ramírez-Valverde G (2012) Efecto de la restauración de un Fluvisol contaminado con petróleo crudo. Rev Int Contam Ambient 28(4):361–374
Trujillo-Narcía A, Rivera-Cruz MC, Trujillo-Rivera EA, Roldán-Garrigos A (2018) Reintroducing plant coverage in a tropical wetland contaminated with oil and sulfate: rhizosphere effects on Desulfovibrio populations. Int J Trop Biol 66(2):908–917. https://doi.org/10.15517/RBT.V66I2.33422
Walkley A, Black IA (1934) An examination of Degtjareff method for determining soil organic matter and aprosed modification of the chromic acid titration method. Soil Sci 37(1):29–38. https://doi.org/10.1097/00010694-193401000-00003
Zhuang X, Chen J, Shim H, Bai Z (2007) New advances in plant growth promoting rhizobacteria for bioremediation. Environ Intern 33(3):406–413. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2006.12.005
Acknowledgements
This study was financially supported by funds from the Colegio de Postgraduados en Ciencias Agrícolas. The first author thanks the Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnología of Mexico for the scholarship 619174.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alberto Orocio-Carrillo, J., del Carmen Rivera-Cruz, M., Manuel Aranda-Ibañez, E. et al. Hormesis under oil-induced stress in Leersia hexandra Sw. used as phytoremediator in clay soils of the Mexican humid tropic. Ecotoxicology 28, 1063–1074 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-019-02106-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-019-02106-1