Abstract
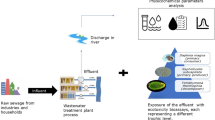
On July 7, 2008, a leak of effluent from an Installation of Cleansing and Uranium Recovery (Tricastin, France) led to the spillage of uranium in a stream. The acute toxicity of the effluent was evaluated, and compared to the toxicity of uranium nitrate in bioassays using several organisms: Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, Daphnia magna, Chironomus riparius and Danio rerio. A sediment bioassay was also performed on C. riparius using water and sediment sampled along the river. Results showed that effluent EC50 72 h was 0.65 mg U/l for algae and LC50 48 h was 1.67 mg U/l for daphnia, while values obtained for uranium nitrate were higher. The LC50 96 h of effluent to C. riparius was 22.7 mg U/l, similar to value for uranium nitrate; the sediment collected was not toxic to C. riparius larvae. The LOEC of effluent and uranium nitrate on HT50 of D. rerio were similar (0.03 mg U/l), but larvae were more sensitive to uranium nitrate than to effluent. Our results suggest that other substances contained in the effluent could potentially be toxic to wildlife in association with uranium. In parallel, the modelling of the transfers based on uranium measurements in the surface water was used to fill data gaps and assess the impact along the river. These results provided an estimate of exposure conditions that occurred along the river. This approach allowed us to see that the risk to ecosystem during this incident was certainly low and concerned a short period of time, but it could have existed at least for some species.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
AFNOR (1985) Nf T 90–303 essai des eaux : Détermination de la toxicité aiguë d’une substance vis-à-vis de Brachydanio rerio. Afnor, Paris
AFNOR (2004) Nf XP T 90–339-1 qualité de l’eau: Détermination de la toxicité des sédiments d’eau douce vis-à-vis de Chironomus riparius. Partie 1 : Sédiments naturels. Afnor, Paris
Antunes SC, de Figueiredo DR, Marques SM, Castro BB, Pereira R, Goncalves F (2007) Evaluation of water column and sediment toxicity from an abandoned uranium mine using a battery of bioassays. Sci Total Environ 74(2–3):252–259
AREVA (2008) Point sur l’incident à l’usine Socatri : Suivi des mesures environnementales. http://www.Areva-nc.Fr/scripts/areva-nc/publigen/content/templates/show.Asp?P=7818&l=fr
Banerjee BD, Seth V, Ahmed RS (2001) Pesticide-induced oxidative stress: perspectives and trends. Rev Environ Health 16(1):1–40
Barata C, Baird DJ, Markich SJ (1998) Influence of genetic and environmental factors on the tolerance of Daphnia magna Straus to essential and non-essential metals. Aquat Toxicol 42(2):115–137
Barillet S, Buet A, Adam C, Devaux A (2005) Does uranium exposure induce genotoxicity in the teleostean Danio rerio? Radioprotection 40(Suppl 1):175–181
Barillet S, Adam C, Palluel O, Devaux A (2007) Bioaccumulation, oxidative stress, and neurotoxicity in Danio rerio exposed to different isotopic compositions of uranium. Environ Toxicol Chem 26(3):497–505
Bourrachot S, Simon O, Gilbin R (2008) The effects of waterborne uranium on the hatching success, development, and survival of early life stages of zebrafish (Danio rerio). Aquat Toxicol 90(1):29–36
Boyer P, Beaugelin-Seiller K, Ternat F, Anselmet F, Amielh M (2005) A dynamic box model to predict the radionuclide behaviour in rivers for medium and long-term periods. Radioprotection 40(Suppl 1):S307–S313
Dave G, Xiu R (1991) Toxicity of mercury, copper, nickel, lead, and cobalt to embryos and larvae of zebrafish, brachydanio rerio. Arch Environ Cont Tox 21(1):126–134
Denison FH, Garnier-Laplace J (2005) The effects of database parameter uncertainty on uranium(VI) equilibrium calculations. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 69(9):2183–2191
Dias V, Vasseur C, Bonzom JM (2008) Exposure of Chironomus riparius larvae to uranium: effects on survival, development time, growth, and mouthpart deformities. Chemosphere 71(3):574–581
Duchesne S, Boyer P, Beaugelin-Seiller K (2003) Sensitivity and uncertainty analysis of a model computing radionuclides transfers in fluvial ecosystems (Casteaur): application to 137cs accumulation in chubs. Ecol Model 166(3):257–276
Elendt BP (1990) Selenium deficiency in crustacea—an ultrastructural approach to antennal damage in Daphnia magna Straus. Protoplasma 154(1):25–33
Environnement Canada (1997) Méthode d’essai biologique: Essai de survie et de croissance des larves dulcicoles de chironomes (Chironomus tentans ou Chironomus riparius) dans les sédiments. Ottawa, Ontario
European Commission (2003) Technical guidance document in support of commission directive 93/67/EEC on risk assessment for new notified substances and commission regulation (EC) no 1488/94 on risk assessment for existing substances. Directive 98/8/EC of the European parliament and of the council concerning the placing of biocidal products on the market; part ii. Luxembourg
Fisher HB, List EJ, Koh RCY, Imberger J, Brooks NH (1979) Mixing in inland and coastal waters. Academic Press, London
Fortin C, Dutel L, Garnier-Laplace J (2004) Uranium complexation and uptake by a green alga in relation to chemical speciation: the importance of the free uranyl ion. Environ Toxicol Chem 23(4):974–981
Fraysse B, Mons R, Garric J (2006) Development of a zebrafish 4-day embryo-larval bioassay to assess toxicity of chemicals. Ecotox Environ Safe 63(2):253–267
Holdway DA (1992) Uranium toxicity to two species of Australian tropical fish. Sci Total Environ 125:137–158
INERIS (2005) Chrome et ses dérivés Fiche de données toxicologiques et environnementales des substances chimiques. INERIS, Paris
IRSN (2008) Rejet accidentel d’uranium de l’usine Socatri : L’IRSN rend publics ses résultats d’analyse sur la composition isotopique de l’uranium contenu dans les effluents. In: http://www.Irsn.Fr/fr/actualites_presse/communiques_et_dossiers_de_presse/pages/socatri_tricastin_composition_isotopique_uranium_effluents.Aspx
Kaniewska-Prus M (1982) The effect of ammonia, chlorine, and chloramine toxicity on the mortality of Daphnia magna Straus. Pol Arch Hydrobiol 29(3–4):607–624
Kurnaz A, Kucukomeroglu B, Keser R, Okumusoglu NT, Korkmaz F, Karahan G, Cevik U (2007) Determination of radioactivity levels and hazards of soil and sediment samples in Firtina valley (Rize, Turkey). Appl Radiat Isotopes 65(11):1281–1289
Labrot F, Ribera D, Saint Denis M, Narbonne JF (1996) In vitro and in vivo studies of potential biomarkers of lead and uranium contamination: lipid peroxidation, acetylcholinesterase, catalase and glutathione peroxidase activities in three non-mammalian species. Biomarkers 1(1):21–28
Liden LH, Burton DT (1977) Survival of juvenile atlantic menhaden (brevoortia tyrannus) and spot (leiostomus xanthurus) exposed to bromine chloride and chlorine treated estuarine waters. J Environ Sci Health A A12(8):375–388
Martins J, Oliva Teles L, Vasconcelos V (2007) Assays with Daphnia magna and Danio rerio as alert systems in aquatic toxicology. Environ Int 33(3):414–425
McKim JM (1985) Early life stage toxicity tests. In: Rand GM, Petrocellli SR (eds) Fundamentals of aquatic toxicology. Hemisphere, New York, pp 58–95
Metcalfe-Smith JL, Holtze KE, Sirota GR, Reid JJ, de Solla SR (2003) Toxicity of aqueous and sediment-associated fluoride to freshwater organisms. Environ Toxicol Chem 22(1):161–166
Oberdorff T, Pont D, Hugueny B, Belliard J, Berrebi Dit Thomas R, Porcher JP (2002) Adaptation et validation d’un indice poisson (FBI) pour l’évaluation de la qualité biologique des cours d’eau français. Bulletin Français de la Pêche et de la Pisciculture (365–366):405–433
OECD (1984) OECD guidelines for testing of chemicals. Test 201: Algal growth inhibition test
OECD (1995) Guidance document for aquatic effects assessment. Environment monograph
OECD (2000a) OECD guidelines for testing of chemicals, revised proposal. Test 202: Daphnia sp, acute immobilization test
OECD (2000b) OECD guidelines for testing of chemicals. Test 219: Sediment-water chironomid toxicity test using spiked water
OECD (2004) OECD guidelines for testing of chemicals, advance copy. Test 210 : Fish, early-life stage toxicity test
Pawlisz AV, Kent RA, Schneider UA, Jefferson C (1997) Canadian water quality guidelines for chromium. Environ Toxicol Water Qual 12(2):123–183
R Development Core Team (2004) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. Vienna, Austria
Ribera D, Labrot F, Tisnerat G, Narbonne JF (1996) Uranium in the environment: occurrence, transfer, and biological effects. Rev Environ Contam T 146:53–89
Ritz C, Streibig JC (2005) Bioassay analysis using R. J Stat Softw 12:1–22
Ruoppa M, Nakari T (1988) The effects of pulp and paper industry (Tervakoski Oy) waste waters on the fertilized eggs and alevins of zebrafish and on the physiology of rainbow trout. Water Sci Technol 20(2):201
Sheppard SC, Sheppard MI, Gallerand MO, Sanipelli B (2005) Derivation of ecotoxicity thresholds for uranium. J Environ Radioactiv 79(1):55–83
Sueoka N, Chiang KS, Kates JR (1967) Deoxyribonucleic acid replication in meiosis of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. I Isotopic transfer experiments with a strain producing eight zoospores. J Mol Biol 25(1):47–66
USEPA (1998) Guidelines for ecological risk assessment. Risk Assessment Forum EPA/630/R-95/002F
Videau C, Khalanski M, Penot M (1979) Preliminary results concerning effects of chlorine on monospecific marine phytoplankton. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 36(2):111–123
Yosha SF, Cohen GM (1979) Effect of intermittent chlorination of developing zebrafish embryos (Brachydanio rerio). B Environ Contam Tox 21(4–5):703–710
Zeman FA, Gilbin R, Alonzo F, Lecomte-Pradines C, Garnier-Laplace J, Aliaume C (2008) Effects of waterborne uranium on survival, growth, reproduction and physiological processes of the freshwater cladoceran Daphnia magna. Aquat Toxicol 86(3):370–378
Zurita JL, Jos A, Camean AM, Salguero M, Lopez-Artiguez M, Repetto G (2007) Ecotoxicological evaluation of sodium fluoroacetate on aquatic organisms and investigation of the effects on two fish cell lines. Chemosphere 67(1):1–12
Acknowledgments
N. Dal-Pos and P. Signoret are acknowledged for their technical assistance in midge bioassays. SOCATRI industry is acknowledged for providing the effluent sample. This study was supported by the ENVIRHOM project of IRSN.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gagnaire, B., Boyer, P., Bonzom, JM. et al. Transfer modelling and toxicity evaluation of the effluent from an installation of cleansing and uranium recovery using a battery of bioassays. Ecotoxicology 20, 187–201 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-010-0570-4
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-010-0570-4