Abstract
Background/Aims
Rodent obesity models have been shown to display impaired bile secretory functions. We have shown that glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) attenuates hepatic lipogenesis, and in the present study we investigated whether GLP-1 also improves high fat diet-associated cholestatic injury.
Methods
Wild type (WT) and dipeptidyl peptidase 4-deficient rats (DPP4-) with chronic elevated serum levels of active GLP-1 were fed regular chow and a Western diet for 2 months. Primary hepatocytes were used to assess GLP-1 effects on mRNA expression and transcription of genes encoding bile acid synthesis enzymes and transporters.
Results
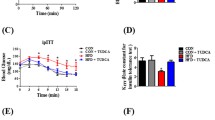
DPP4- exhibited attenuated liver injury as expressed by lower serum AST and ALT after 2 months of a Western diet. In addition, DPP4- had better insulin sensitivity, lower serum triglycerides, cholesterol and bile acids. Hepatic expression of cyp7A1, the rate limiting enzyme in conversion of cholesterol into bile acids, was strongly attenuated in DPP4- fed with a Western diet. Moreover, hepatic expression of bile transporter, ABCB11, was increased, facilitating a higher rate of bile secretion. Mechanistically, we showed that GLP-1 directly reduced basal and LXR-induced cyp7A1 mRNA expression and suppressed cyp7A1 transcription in transient transfection assays in primary hepatocytes. However, GLP-1 and its analog exendin 4 also induced mRNA expression of bile acid transporter ABCC3 in primary rat hepatocyte cultures.
Conclusions
Our data suggest that GLP-1 analogs may serve as a novel therapeutic drug to alleviate obesity-induced liver injury by reducing bile acid synthesis and improving liver bile secretory function.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baggio LL, Drucker DJ. Biology of incretins: GLP-1 and GIP. Gastroenterology. 2007;132:2131–2157.
Holst JJ. The physiology of glucagon-like peptide 1. Physiol Rev. 2007;87:1409–1439.
Ben-Shlomo S, Zvibel I, Shnell M, et al. Glucagon-like peptide-1 reduces hepatic lipogenesis via activation of AMP-activated protein kinase. J Hepatol. 2011;54:1214–1223.
Ding X, Saxena NK, Lin S, et al. Exendin-4, a glucagon-like protein-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist, reverses hepatic steatosis in ob/ob mice. Hepatology. 2006;43:173–181.
Li T, Kong X, Owsley E, et al. Insulin regulation of cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase expression in human hepatocytes: roles of forkhead box O1 and sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1c. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:28745–28754.
Pizarro M, Balasubramaniyan N, Solís N, et al. Bile secretory function in the obese Zucker rat: evidence of cholestasis and altered canalicular transport function. Gut. 2004;53:1837–1843.
Trauner M, Boyer JL. Bile salt transporters: molecular characterization, function, and regulation. Physiol Rev. 2003;83:633–671.
Trauner M, Arrese M, Soroka CJ, et al. The rat canalicular conjugate export pump (Mrp2) is down-regulated in intrahepatic and obstructive cholestasis. Gastroenterology. 1997;113:255–264.
Trauner M, Arrese M, Lee H, et al. Endotoxin downregulates rat hepatic ntcp gene expression via decreased activity of critical transcription factors. J Clin Invest. 1998;101:2092–2100.
Thomas C, Gioiello A, Noriega L, et al. TGR5-mediated bile acid sensing controls glucose homeostasis. Cell Metab. 2009;10:167–177.
Berry MN, Friend DS. High-yield preparation of isolated rat liver parenchymal cells: a biochemical and fine structure study. J Cell Biol. 1969;43:506–520.
Block GD, Locker J, Bowen WC, et al. Population expansion, clonal growth and specific differentiation patterns in primary cultures of hepatocytes induced by HGF/SF, EGF and TGF α in a chemically defined (HGM) medium. J Cell Biol. 1996;132:1133–1149.
Song KH, Chiang JY. Glucagon and cAMP inhibit cholesterol 7alpha-hydroxylase (CYP7A1) gene expression in human hepatocytes: discordant regulation of bile acid synthesis and gluconeogenesis. Hepatology. 2006;43:117–125.
Lefebvre P, Cariou B, Lien F, et al. Role of bile acids and bile acid receptors in metabolic regulation. Physiol Rev. 2009;89:147–191.
van Waarde WM, Verkade HJ, Wolters H, et al. Differential effects of streptozotocin-induced diabetes on expression of hepatic ABC-transporters in rats. Gastroenterology. 2002;122:1842–1852.
Li T, Chanda D, Zhang Y, et al. Glucose stimulates cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase gene transcription in human hepatocytes. J Lipid Res. 2010;51:832–842.
Goodwin B, Jones SA, Price RR, et al. A regulatory cascade of the nuclear receptors FXR, SHP-1, and LRH-1 represses bile acid biosynthesis. Mol Cell. 2000;6:517–526.
Donner MG, Keppler D. Up-regulation of basolateral multidrug resistance protein 3 (Mrp3) in cholestatic rat liver. Hepatology. 2001;34:351–359.
Belinsky MG, Dawson PA, Shchaveleva I, et al. Analysis of the in vivo functions of Mrp3. Mol Pharmacol. 2005;68:160–168.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shlomo, S.B., Zvibel, I., Rabinowich, L. et al. Dipeptidyl Peptidase 4-Deficient Rats Have Improved Bile Secretory Function in High Fat Diet-Induced Steatosis. Dig Dis Sci 58, 172–178 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-012-2353-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-012-2353-7