Abstract
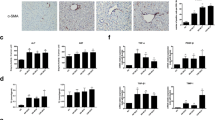
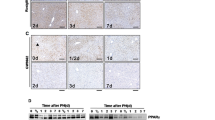
Peroxisome proliferator activator receptor (PPAR) ligands prevent liver fibrosis, while the role of all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) and its metabolite 9-cis retinoic acid (9-cis RA) is less clear. We have investigated the ability of the combination of PPARγ ligand rosiglitazone (RSG) and of ATRA to prevent liver fibrosis. In vivo treatment with RSG or ATRA reduced fibrotic nodules, spleen weight, and hydroxyproline levels in rat model of thioacetamide-induced liver fibrosis. The combination of ATRA + RSG caused the strongest inhibition, accompanied by decreased expression of collagen I, α-smooth muscle actin, TGFβ1, and TNFα. In vitro studies showed that PPARγ ligand 15-deoxy-Δ12,14-prostaglandinJ(2)[PJ(2)] and RXR ligand 9-cis RA or PJ(2) and ATRA inhibited proliferation of hepatic stellate cells HSC-T6. 9-cis RA inhibited c-jun levels and also inhibited expression of its receptor RXRα in HSC-T6 cells. The combination of PPAR-γ and RAR agonists demonstrated an additive effect in the inhibition of TAA-induced hepatic fibrosis, due to inhibition of HSC proliferation and reduction of profibrotic TGFβ1 and proinflammatory TNFα.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Friedman SL (1999) Cytokines and fibrogenesis. Semin Liver Dis 19:129–140
Friedman SL (1993) Seminars in medicine of the Beth Israel Hospital, Boston: the cellular basis of hepatic fibrosis—mechanisms and treatment strategies. New Engl J Med 328:1828–1833. doi:10.1056/NEJM199306243282508
Bataller R, Brenner DA (2005) Liver fibrosis. J Clin Invest 115:209–218
Imamura M, Ogawa T, Sasaguri Y et al (2005) Suppression of macrophage infiltration inhibits activation of hepatic stellate cells and liver fibrogenesis in rats. Gastroenterology 128:138–146. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2004.10.005
Jiang F, Parsons CJ, Stefanovic B (2006) Gene expression profile of quiescent and activated rat hepatic stellate cells implicates Wnt signaling pathway in activation. J Hepatol 45:401–409. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2006.03.016
Mangelsdorf DJ, Evans RM (1995) The RXR heterodimers and orphan receptors. Cell 83:841–850. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(95)90200-7
Chawla A, Repa JJ, Evans RM et al (2001) Nuclear receptors and lipid physiology: opening the X-files. Science 294:1866–1870. doi:10.1126/science.294.5548.1866
Evans RM (1988) The steroid and thyroid hormone receptor superfamily. Science 240: 889–895. doi:10.1126/science.3283939
Galli A, Crabb DW, Ceni E, Salzano R, Mello T, Svegliati-Baroni G, Ridolfi F, Trozzi L, Surrenti C, Casini A (2002) Antidiabetic thiazolidinediones inhibit collagen synthesis and hepatic stellate cell activation in vivo and in vitro. Gastroenterology 122:1924–1940. doi:10.1053/gast.2002.33666
Marra F, Efsen E, Romanelli RG, Caligiuri A, Pastacaldi S, Batignani G, Bonacchi A, Caporale R, Laffi G, Pinzani M, Gentilini P (2000) Ligands of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma modulate profibrogenic and proinflammatory actions in hepatic stellate cells. Gastroenterology 119:466–478. doi:10.1053/gast.2000.9365
Kon K, Ikejima K, Hirose M, Yoshikawa M, Enomoto N, Kitamura T, Takei Y, Sato N (2002) Pioglitazone prevents early-phase hepatic fibrogenesis caused by carbon tetrachloride. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 291:55–56. doi:10.1006/bbrc.2002.6385
Galli A, Crabb D, Price D, Ceni E, Salzano R, Surrenti C, Casini A (2000) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma transcriptional regulation is involved in platelet-derived growth factor-induced proliferation of human hepatic stellate cells. Hepatology 31:101–108. doi:10.1002/hep.510310117
Miyahara T, Schrum L, Rippe R, Xiong S, Yee HF Jr, Motomura K, Anania FA, Willson TM, Tsukamoto H (2000) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors and hepatic stellate cell activation. J Biol Chem 275:35715–35722. doi:10.1074/jbc.M006577200
Huang GC, Zhang JS, Zhang YE (2000) Effects of retinoic acid on proliferation, phenotype and expression of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors in TGF-beta1-stimulated rat hepatic stellate cells. World J Gastroenterol 6:819–823
McCarroll JA, Phillips PA, Santucci N, Pirola RC, Wilson JS, Apte MV (2006) Vitamin A inhibits pancreatic stellate cell activation: implications for treatment of pancreatic fibrosis. Gut 55:79–89. doi:10.1136/gut.2005.064543
Wang L, Rennie Tankersley L, Tang M, Potter JJ, Mezey E (2002) Regulation of the murine alpha(2)(I) collagen promoter by retinoic acid and retinoid X receptors. Arch Biochem Biophys 401:262–270. doi:10.1016/S0003-9861(02)00058-9
Okuno M, Moriwaki H, Imai S, Muto Y, Kawada N, Suzuki Y, Kojima S (1997) Retinoids exacerbate rat liver fibrosis by inducing the activation of latent TGF-beta in liver stellate cells. Hepatology 26:913–921
Hellemans K, Grinko I, Rombouts K, Schuppan D, Geerts A (1999) All-trans and 9-cis retinoic acid alter rat hepatic stellate cell phenotype differentially. Gut 45:134–142
Shaulian E, Karin M (2002) AP-1 as a regulator of cell life and death. Nat Cell Biol 4:E131–E136. doi:10.1038/ncb0502-e131
Chen A, Davis BH (1999) UV irradiation activates JNK and increases alphaI(I) collagen gene expression in rat hepatic stellate cells. J Biol Chem 274:158–164. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.1.158
Ozeki A, Tsukamoto I (1999) Retinoic acid repressed the expression of c-fos and c-jun and induced apoptosis in regenerating rat liver after partial hepatectomy. Biochim Biophys Acta 1450:308–319. doi:10.1016/S0167-4889(99)00063-4
Konta T, Xu Q, Furusu A, Nakayama K, Kitamura M (2001) Selective roles of retinoic acid receptor and retinoid x receptor in the suppression of apoptosis by all-trans-retinoic acid. J Biol Chem 276:12697–12701. doi:10.1074/jbc.M011000200
Ren X, Ma X, Li Y (2007) All-trans retinoic acid regulates c-jun expression via ERK5 in cardiac myoblasts. J Nutr Biochem (Epub ahead of print)
Muller A, Machnik F, Zimmerman T, Schubert H (1988) Thioacetamide-induced cirrhosis-like lesions in rats—usefulness and reliability of this animal model. Exp Pathol 34:229–236
Woessner JF (1961) The determination of hyroxyproline in tissue and protein samples containing small proportion of this imino acid. Arch Biochem Biophys 93:440–447 doi:10.1016/0003-9861(61)90291-0
Block GD, Locke J, Bowen WC, Petersen BE, Katyal S, Strom SC, Riley T, Howard TA, Michalopoulos GK (1996) Population expansion, clonal growth and specific differentiation patterns in primary cultures of hepatocytes induced by HGF/SF, EGF and TGF α in a chemically defined (HGM) medium. J Cell Biol 132:1133–1149. doi:10.1083/jcb.132.6.1133
Jaster R, Hilgendorf I, Fitzner B, Brock P, Sparmann G, Emmrich J, Liebe S (2003) Regulation of pancreatic stellate cell function in vitro: biological and molecular effects of all-trans retinoic acid. Biochem Pharmacol 66:633–641. doi:10.1016/S0006-2952(03)00390-3
Hellemans K, Verbuyst P, Quartier E, Schuit F, Rombouts K, Chandraratna RA, Schuppan D, Geerts A (2004) Differential modulation of rat hepatic stellate phenotype by natural and synthetic retinoids. Hepatology. 39:97–108. doi:10.1002/hep.20015
Salbert G, Fanjul A, Piedrafita FJ, Lu XP, Kim SJ, Tran P, Pfahl M (1993) Retinoic acid receptors and retinoid X receptor-alpha down-regulate the transforming growth factor-beta 1 promoter by antagonizing AP-1 activity. Mol Endocrinol 7:1347–1356. doi:10.1210/me.7.10.1347
Xu J, Drew PD (2006) 9-Cis-retinoic acid suppresses inflammatory responses of microglia and astrocytes. J Neuroimmunol 171:135–144. doi:10.1016/j.jneuroim.2005.10.004
Wang X, Allen C, Ballow M (2007) Retinoic acid enhances the production of IL-10 while reducing the synthesis of IL-12 and TNF-alpha from LPS-stimulated monocytes/macrophages. J Clin Immunol 27:193–200. doi:10.1007/s10875-006-9068-5
Nozaki Y, Tamaki C, Yamagata T, Sugiyama M, Ikoma S, Kinoshita K, Funauchi M (2006) All-trans-retinoic acid suppresses interferon-gamma and tumor necrosis factor-alpha; a possible therapeutic agent for rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol Int 26:810–817. doi:10.1007/s00296-005-0076-1
Hazra S, Xiong S,Wang J, Rippe RA, Krishna V, Chatterjee K, Tsukamoto H (2004) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma induces a phenotypic switch from activated to quiescent hepatic stellate cells. J Biol Chem 279:11392–11401. doi:10.1074/jbc.M310284200
Li H, Zhang J,Huang G, Zhang N,Chen Q, Zhang X (2002) Effect of retinoid kappa receptor alpha (RXRalpha) transfection on the proliferation and phenotype of rat hepatic stellate cells in vitro. Chin Med J (Engl) 115:928–932
Ohata M, Lin M, Satre M, Tsukamoto H (1997) Diminished retinoic acid signaling in hepatic stellate cells in cholestatic liver fibrosis. Am J Physiol 272:G589–596
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bruck, R., Weiss, S., Aeed, H. et al. Additive Inhibitory Effect of Experimentally Induced Hepatic Cirrhosis by Agonists of Peroxisome Proliferator Activator Receptor γ and Retinoic Acid Receptor. Dig Dis Sci 54, 292–299 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-008-0336-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-008-0336-5