Abstract
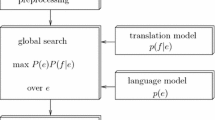
In this work, we present an extension of n-gram-based translation models based on factored language models (FLMs). Translation units employed in the n-gram-based approach to statistical machine translation (SMT) are based on mappings of sequences of raw words, while translation model probabilities are estimated through standard language modeling of such bilingual units. Therefore, similar to other translation model approaches (phrase-based or hierarchical), the sparseness problem of the units being modeled leads to unreliable probability estimates, even under conditions where large bilingual corpora are available. In order to tackle this problem, we extend the n-gram-based approach to SMT by tightly integrating more general word representations, such as lemmas and morphological classes, and we use the flexible framework of FLMs to apply a number of different back-off techniques. In this work, we show that FLMs can also be successfully applied to translation modeling, yielding more robust probability estimates that integrate larger bilingual contexts during the translation process.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bilmes JA, Kirchhoff K (2003) Factored language models and generalized parallel backoff. In: NAACL ’03: Proceedings of the 2003 conference of the North American chapter of the association for computational linguistics on human language technology, pp 4–6
Bod R (2000) Combining semantic and syntactic structure for language modeling. In: Proceedings of the 8th international conference on spoken language processing, ICSLP’00, vol III. Beijing, China, pp 106–109
Charniak E (2001) Immediate-head parsing for language models. In: Proceedings of the 39th annual meeting on association for computational linguistics. Toulouse, France, pp 124–131
Chelba C, Jelinek F (2000) Structured language modeling. Comput Speech Lang 14(4): 283–332
Chiang D (2005) A hierarchical phrase-based model for statistical machine translation. In: Proceedings of the 43rd annual meeting of the association for computational linguistics (ACL’05). Ann Arbor, Michigan, pp 263–270
Crego JM, Mariño JB (2007a) Extending MARIE: an N-gram-based SMT decoder. In: Proceedings of the 45rd annual meeting of the association for computational linguistics (ACL’07). Ann Arbor, Michigan
Crego JM, Mariño JB (2007b) Improving SMT by coupling reordering and decoding. Mach Transl 20(3): 199–215
Habash N, Sadat F (2006) Arabic preprocessing schemes for statistical machine translation. In: NAACL ’06: proceedings of the human language technology conference of the NAACL, Companion Volume: Short Papers on XX, pp 49–52
Katz SM (1987) Estimation of probabilities from sparse data for the language model component of a speech recognizer. IEEE Trans Acoust Speech Signal Process 35(3): 400–401
Kirchhoff K, Bilmes J, Duh K (2008) Factored language models tutorial. Technical report. Deptartment of Electrical Engineering, University of Washington
Kneser R, Ney H (1995) Improved backing-off for m-gram language modeling. In: Proceedings of the international conference on acoustics, speech, and signal processing, ICASSP’95. Detroit, MI, pp 181–184
Koehn P, Hoang H (2007) Factored translation models. In: Proceedings of the 2007 joint conference on empirical methods in natural language processing and computational natural language learning (EMNLP-CoNLL), pp 868–876
Koehn P, Och FJ, Marcu D (2003) Statistical phrase-based translation. In: Proceedings of the human language technology conference of the North American Chapter of the association for computational linguistic. Edmondton, Canada, pp 127–133
Koehn P, Axelrod A, Birch A, Callison-Burch C, Osborne M, Talbot D (2005) Edinburgh system description for the 2005 IWSLT speech translation evaluation. In: Proceedings of the international workshop on spoken language translation, IWSLT’05. Pittsburgh, PA
Koehn P, Hoang H, Birch A, Callison-Burch C, Federico M, Bertoldi N, Cowan B, Shen W, Moran C, Zens R, Dyer C, Bojar O, Constantin A, Herbst E (2007) Moses: open source toolkit for statistical machine translation. In: Proceedings of the annual meeting of the association for computational linguistics (ACL), demonstration session. Prague, Czech Republic
Mariño JB, Banchs RE, Crego JM, de Gispert A, Lambert P, Fonollosa JA, Costa-Jussà MR (2006) N-gram-based machine translation. Comput Linguist 32(4): 527–549
Melamed ID (2004) Statistical machine translation by parsing. In: ACL ’04: Proceedings of the 42nd annual meeting on association for computational linguistics. Morristown, NJ, USA, p 653
Niesler TR (1997) Category-based statistical language models. Ph.D. thesis, University of Cambridge
Nießen S, Ney H (2001) Toward hierarchical models for statistical machine translation of inflected languages. In: Proceedings of the ACL 2001 workshop on data-driven methods in machine translation. Toulouse, France, pp 47–51
Nießen S, Ney H (2004) Statistical machine translation with scarce resources using morpho-syntactic information. Comput Linguist 30(2): 181–204
Och FJ, Ney H (2002) Discriminative training and maximum entropy models for statistical machine translation. In: Proceedings of ACL. Philadelphia, PA, pp 295–302
Och F-J, Tillmann C, Ney H (1999) Improved alignment models for statistical machine translation. In: Proceedings of the joint conference of empirical methods in natural language processing and very large corpora. University of Maryland, College Park, MD, pp 20–28
Papineni K, Roukos S, Ward T, Zhu W-J (2002) Bleu: a method for automatic evaluation of machine translation. In: Proceedings of the annual meeting of the association for computation linguistics. Philadelphia, PA, pp 311–318
Rosenfeld R (1996) A maximum entropy approach to adaptative statistical language modeling. Comput Speech Lang 10: 187–228
Talbot D, Osborne M (2006) Modelling Lexical Redundancy for Machine Translation. In: Proceedings of the 21st international conference on computational linguistics and 44th annual meeting of the association for computational linguistics. Sydney, Australia, pp 969–976
Yang M, Kirchhoff K (2006) Phrase-based backoff models for machine translation of highly inflected languages. In: Proceedings of the European Chapter of the ACL. Trento, Italy, pp 41–48
Zens R, Och FJ, Ney H (2002) Phrase-based statistical machine translation. In: Jarke M, Koehler J, Lakemeyer G (eds) KI-2002: advances in artificial intelligence, vol 2479 of LNAI. pp 18–32
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Crego, J.M., Yvon, F. Factored bilingual n-gram language models for statistical machine translation. Machine Translation 24, 159–175 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10590-010-9082-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10590-010-9082-5