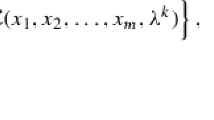Abstract
The augmented Lagrangian method (ALM) provides a benchmark for solving the canonical convex optimization problem with linear constraints. The direct extension of ALM for solving the multiple-block separable convex minimization problem, however, is proved to be not necessarily convergent in the literature. It has thus inspired a number of ALM-variant algorithms with provable convergence. This paper presents a novel parallel splitting method for the multiple-block separable convex optimization problem with linear equality constraints, which enjoys a larger step size compared with the existing parallel splitting methods. We first show that a fully Jacobian decomposition of the regularized ALM can contribute a descent direction yielding the contraction of proximity to the solution set; then, the new iterate is generated via a simple correction step with an ignorable computational cost. We establish the convergence analysis for the proposed method, and then demonstrate its numerical efficiency by solving an application problem arising in statistical learning.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bai, J., Li, J., Xu, F., Zhang, H.: Generalized symmetric ADMM for separable convex optimization. Comput. Optim. Appl. 70(1), 129–170 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10589-017-9971-0
Beck, A.: First-Order Methods in Optimization, vol. 25. SIAM, Philadelphia (2017)
Blum, E., Oettli, W.: Mathematische Optimierung. Grundlagen und Verfahren. Ökonometrie und Unternehmensforschung. Springer, Berlin (1975)
Bose, N., Boo, K.: High-resolution image reconstruction with multisensors. Int. J. Imaging Syst. Technol. 9(4), 294–304 (1998) https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1098-1098(1998)9:4%3c294::AID-IMA11%3e3.0.CO;2-X
Boyd, S., Parikh, N., Chu, E., Peleato, B., Eckstein, J.: Distributed optimization and statistical learning via the alternating direction method of multipliers. Found. Trends Mach. Learn. 3(1), 1–122 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1561/2200000016
Chandrasekaran, V., Parrilo, P.A., Willsky, A.S.: Latent variable graphical model selection via convex optimization. Ann. Stat. 40(4), 1935–1967 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1214/11-AOS949
Chen, C., He, B., Ye, Y., Yuan, X.: The direct extension of ADMM for multi-block convex minimization problems is not necessarily convergent. Math. Program. 155(1–2), 57–79 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10107-014-0826-5
Facchinei, F., Pang, J.S.: Finite-Dimensional Variational Inequalities and Complementarity Problems. Springer Series in Operations Research, vol. I. Springer, New York (2003)
Gabay, D., Mercier, B.: A dual algorithm for the solution of nonlinear variational problems via finite element approximation. Comput. Math. Appl. 2(1), 17–40 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1016/0898-1221(76)90003-1
Glowinski, R.: Numerical Methods for Nonlinear Variational Problems. Springer, Berlin (1984)
Hager, W.W., Zhang, H.: Convergence rates for an inexact ADMM applied to separable convex optimization. Comput. Optim. Appl. 77(3), 729–754 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10589-017-9971-0
He, B.: My 20 years research on alternating directions method of multipliers. Oper. Res. Trans. 22, 1–31 (2018)
He, B.: Study on the splitting methods for separable convex optimization in a unified algorithmic framework. Anal. Theory Appl. 36, 262–282 (2020). https://doi.org/10.4208/ata.OA-SU13
He, B., Hou, L., Yuan, X.: On full Jacobian decomposition of the augmented Lagrangian method for separable convex programming. SIAM J. Optim. 25(4), 2274–2312 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1137/130922793
He, B., Ma, F., Yuan, X.: Optimal proximal augmented Lagrangian method and its application to full Jacobian splitting for multi-block separable convex minimization problems. IMA J. Numer. Anal. 40(2), 1188–1216 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1093/imanum/dry092
He, B., Ma, F., Yuan, X.: Optimally linearizing the alternating direction method of multipliers for convex programming. Comput. Optim. Appl. 75(2), 361–388 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10589-019-00152-3
He, B., Tao, M., Yuan, X.: Alternating direction method with Gaussian back substitution for separable convex programming. SIAM J. Optim. 22(2), 313–340 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1137/110822347
He, B., Tao, M., Yuan, X.: A splitting method for separable convex programming. IMA J. Numer. Anal. 35(1), 394–426 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1093/imanum/drt060
He, B., Tao, M., Yuan, X.: Convergence rate analysis for the alternating direction method of multipliers with a substitution procedure for separable convex programming. Math. Oper. Res. 42(3), 662–691 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1287/moor.2016.0822
He, B., Xu, S., Yuan, J.: Indefinite linearized augmented Lagrangian method for convex optimization with linear inequality constraints. arXiv preprint arXiv:2105.02425 (2021)
He, B., Yuan, X.: Convergence analysis of primal-dual algorithms for a saddle-point problem: from contraction perspective. SIAM J. Imaging Sci. 5(1), 119–149 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1137/100814494
He, B., Yuan, X.: On the \(O(1/n)\) convergence rate of the Douglas–Rachford alternating direction method. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 50(2), 700–709 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1137/110836936
He, B., Yuan, X.: A class of ADMM-based algorithms for three-block separable convex programming. Comput. Optim. Appl. 70(3), 791–826 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10589-018-9994-1
Hestenes, M.R.: Multiplier and gradient methods. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 4(5), 303–320 (1969). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00927673
Kiwiel, K.C., Rosa, C.H., Ruszczynski, A.: Proximal decomposition via alternating linearization. SIAM J. Optim. 9(3), 668–689 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1137/S1052623495288064
Martinet, B.: Régularisation d'inéquations variationnelles par approximations successives. Rev. Fr. Inform. Rech. Oper. 4(R3), 154–158 (1970)
Parikh, N., Boyd, S.: Proximal algorithms. Found. Trends Optim. 1(3), 127–239 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1561/2400000003
Peng, Y., Ganesh, A., Wright, J., Xu, W., Ma, Y.: RASL: robust alignment by sparse and low-rank decomposition for linearly correlated images. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 34(11), 2233–2246 (2012)
Powell, M.J.: A Method for Nonlinear Constraints in Minimization Problems. In: Fletcher, R. (ed.) Optimization, pp. 283–298. Academic Press, New York (1969)
Rockafellar, R.T.: Monotone operators and the proximal point algorithm. SIAM J. Control Optim. 14(5), 877–898 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1137/0314056
Setzer, S., Steidl, G., Teuber, T.: Deblurring Poissonian images by split Bregman techniques. J. Visual Commun. Image Represent. 21(3), 193–199 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvcir.2009.10.006
Tao, M., Yuan, X.: Recovering low-rank and sparse components of matrices from incomplete and noisy observations. SIAM J. Optim. 21(1), 57–81 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1137/100781894
Tibshirani, R., Saunders, M., Rosset, S., Zhu, J., Knight, K.: Sparsity and smoothness via the fused lasso. J. R. Stat. Soc. 67(1), 91–108 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-9868.2005.00490.x
Yuan, J., Bae, E., Tai, X.C.: A study on continuous max-flow and min-cut approaches. In: 2010 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 2217–2224. IEEE (2010)
Yuan, J., Bae, E., Tai, X.C., Boykov, Y.: A continuous max-flow approach to Potts model. In: Computer Vision-ECCV 2010, pp. 379–392. Springer (2010)
Yuan, J., Fenster, A.: Modern convex optimization to medical image analysis. arXiv preprint arXiv:1809.08734 (2018)
Acknowledgements
Funding was provided by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No.11871029).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, S., He, B. A parallel splitting ALM-based algorithm for separable convex programming. Comput Optim Appl 80, 831–851 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10589-021-00321-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10589-021-00321-3
Keywords
- Convex programming
- Augmented Lagrangian method
- Jacobian decomposition
- Parallel computing
- Operator splitting methods