Abstract
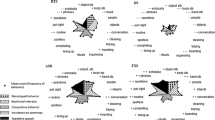
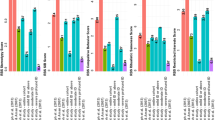
In this study we compared 33 IQ and age matched pairs of individuals with Aspergers Disorder (ASP) and high functioning autism (HFA) on measures of repetitive behavior. On the Repetitive Behavior Scale-Revised (RBS-R), the ASP and HFA groups showed no differences in RBS-R Intensity score (severity) score or Frequency score (number of problems present). This suggests that the two groups are similar with respect to␣the intensity or severity of repetitive behaviors and the presence of repetitive behaviors. At the item level there were no differences on scales typically associated with autism (Stereotyped Behavior) and ASP (Restricted Interests). Similarly, there were no differences between the groups on the Aberrant Behavior Checklist Stereotypy scale. These findings add to the body of literature showing that HFA and ASP fail to differ with respect to repetitive behaviors. The implications of the findings for neurobiologic and genetic studies are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bailey A, Palferman S, Heavey L, Le Couteur A (1998) Autism: the phenotype in relatives. J Autism Dev Disord 28:369–392
Volkmar FR, Klin A, Pauls D (1998) Nosological and genetic aspects of Asperger syndrome. J Autism Dev Disord 28:457–463
Eisenmajer R, Prior M, Leekam S et al (1996) Comparison of clinical symptoms in Autism and Asperger’s disorder. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiat 35:1523–1531
Manjiviona J, Prior M (1995) Comparison of Asperger syndrome and high-functioning autistic children on a test of motor impairment. J Autism Dev Disord 25:23–39
Mayes SD, Calhoun SL, Crites DL (2001) Does DSM-IV Asperger’s disorder exist? J Abnorm Child Psychol 29:263–271
Schopler E (1996) Are Autism and Asperger Syndrome (AS) different labels or different disabilities? J Autism Dev Disord 26:109–110
Szatmari P, Bartolucci G, Bremner R (1989) Asperger’s syndrome and autism: comparison of early history and outcome. Dev Med Child Neurol 31:709–720
Beglinger LJ, Smith TH (2001) A review of subtyping in autism and proposed dimensional classification model. J Autism Dev Disord 31:411–422
Gabriels RL, Cuccaro ML, Hill DE, Ivers BJ, Goldson E (2005) Repetitive behaviors in autism: relationships with associated clinical features. Res Dev Disabil 26:169–181
Militerni R, Bravaccio C, Falco C, Fico C, Palermo MT (2002) Repetitive behaviors in autistic disorder. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry 11:210–218
American Psychiatric Association (1994) Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-IV). American Psychiatric Press, Inc., Washington, DC
Miller JN, Ozonoff S (2000) The external validity of Asperger disorder: lack of evidence from the domain of neuropsychology. J Abnorm Psychol 109:227–238
Woodbury-Smith M, Klin A, Volkmar F (2005) Asperger’s syndrome: a comparison of clinical diagnoses and those made according to the ICD-10 and DSM-IV. J Autism Dev Disord 35:235–240
Volkmar FR, Klin A, Siegel B et al (1994) Field trial for autistic disorder in DSM-IV. Am J Psychiat 151:1361–1367
Gilchrist A, Green J, Cox A, Burton D, Rutter M, Le Couteur A (2001) Development and current functioning in adolescents with Asperger syndrome: a comparative study. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 42:227–240
Starr E, Szatmari P, Bryson S, Zwaigenbaum L (2003) Stability and change among high-functioning children with pervasive developmental disorders: a 2-year outcome study. J Autism Dev Disord 33:15–22
Howlin P (2003) Outcome in high-functioning adults with autism with and without early language delays: implications for the differentiation between autism and Asperger syndrome. J Autism Dev Disord 33:3–13
Szatmari P, Archer L, Fisman S, Streiner DL, WIlson F (1995) Asperger’s syndrome and autism: differences in behavior, cognition, and adaptive functioning. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiat 34:1662–1671
Turner M (1997) Towards an executive dysfunction account of repetitive behavior in autism. In: Russell J (ed) Autism as an executive disorder, Oxford University Press Oxford
South M, Klin A, Ozonoff S (1999) The Yale special interests interview
South M, Ozonoff S, McMahon WM (2005) Repetitive behavior profiles in Asperger syndrome and high-functioning autism. J Autism Dev Disord 35:145–158
Buxbaum JD, Silverman J, Keddache M et al (2004) Linkage analysis for autism in a subset families with obsessive-compulsive behaviors: evidence for an autism susceptibility gene on chromosome 1 and further support for susceptibility genes on chromosome 6 and 19. Mol Psychiatr 9:144–150
McCauley JL, Olson LM, Dowd M et al (2004) Linkage and association analysis at the serotonin transporter (SLC6A4) locus in a rigid-compulsive subset of autism. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet 127B:104–112
Shao Y, Cuccaro ML, Hauser ER et al (2003) Fine mapping of autistic disorder to chromosome 15q11-q13 by use of phenotypic subtypes. Am J Hum Genet 72:539–548
Bodfish JW, Symons F, Lewis M (1999) The Repetitive Behavior Scales: a test manual. Morganton. Western Carolina Center Research Reports, North Carolina
Aman MG, Singh NB (1994) Aberrant Behavior Checklist–community, supplementary manual. East Aurora. Slosson Educational Publications, New York
Rutter M, LeCouteur A, Lord C. (2003) Autism Diagnostic Interview, Revised (ADI-R). Western Psychological Services, Los Angeles, CA
Lord C, Rutter M, Le Couteur A (1994) Autism Diagnostic Interview-Revised: a revised version of a diagnostic interview for caregivers of individuals with possible pervasive developmental disorders. J Autism Dev Disord 24:659–685
American Psychiatric Association (2000) Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-IV), Text Revision. American Psychiatric Press, Inc., Washington, DC
Filipek PA, Accardo PJ, Ashwal S et al (2000) Practice parameter: screening and diagnosis of autism: report of the Quality Standards Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology and the Child Neurology Society. Neurology 55:468–479
Lord C, Rutter M, LeCouteur A (1994) Autism diagnostic interview-revised: A revised version of a diagnostic interview for caregivers of individuals with possible pervasive developmental disorders. J␣Autism Dev Disord 24:659–685
Lord C, Storoschuk S, Rutter M, Pickles A (1993) Using the ADI-R to diagnose autism in preschool children. Infant Ment Health J 14:234–252
Lord C, Pickles A, McLennan J et al (1997) Diagnosing autism: analyses of data from the Autism Diagnostic Interview. J Autism Dev Disord 27:501–517
Bodfish JW, Symons FJ, Parker DE, Lewis MH (2000) Varieties of repetitive behavior in autism: comparisons to mental retardation. J Autism Dev Disord 30:237–243
Bodfish JW, Crawford TW, Powell SB, Parker DE, Golden RN, Lewis MH (1995) Compulsions in adults with mental retardation: prevalence, phenomenology, and comorbidity with stereotypy and self-injury. Am J Ment Retard 100:183–192
Rojahn J, Matson JL, Lott D, Esbensen AJ, Smalls Y (2001) The Behavior Problems Inventory: an instrument for the assessment of self-injury, stereotyped behavior, and aggression/destruction in individuals with developmental disabilities. J Autism Dev Disord 31:577–588
Krug DA, Arick J, Almond P (1980) Behavior checklist for identifying severely handicapped individuals with high levels of autistic behavior. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 21:221–229
Lam KS, Aman MG The Repetitive Behavior Scale – Revised: independent validation in individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorders. J Autism Dev Disord (in press)
Aman MG (2002) The Aberrant Behavior Checklist: an annotated bibliography. Author, Washington, DC
Aman MG, Singh NN, Turbott SH (1987) Reliability of the Aberrant Behavior Checklist and the effect of variations in instructions. Am J Ment Defic 92:237–240
Paclawskyj TR, Matson JL, Bamburg JW, Baglio CS (1997) A comparison of the Diagnostic Assessment for the Severely Handicapped-II (DASH-II) and the Aberrant Behavior Checklist (ABC). Res Dev Disabil 18:289–298
Motulsky HJ (1995) Intuitive biostatistics. Oxord University Press, New York
Agresti A (2002) Categorical data analysis. Hoboken. John Wiley & Sons, New Jersey
Lecavalier L, Aman MG, Hammer D, Stoica W, Mathews GL (2004) Factor analysis of the Nisonger Child Behavior Rating Form in children with autism spectrum disorders. J Autism Dev Disord 34:709–721
Marshburn EC, Aman MG (1992) Factor validity and norms for the aberrant behavior checklist in a community sample of children with mental retardation. J Autism Dev Disord 22:357–373
Newton JT, Sturmey P (1988) The Aberrant Behaviour Checklist: a British replication and extension of its psychometric properties. J Ment Defic Res 32(Pt 2):87–92
Klin A, Pauls D, Schultz R, Volkmar F (2005) Three diagnostic approaches to Asperger syndrome: implications for research. J Autism Dev Disord 35:221–234
Evans DW, Gray FL (2000) Compulsive-like behavior in individuals with Down syndrome: its relation to mental age level, adaptive and maladaptive behavior. Child Dev 71:288–300
Lewis MH, Bodfish JW (1998) Repetitive behavior disorders in autism. Ment Retard Dev Disabil Res Rev 4:80–89
Turner M (1999) Annotation: repetitive behaviour in autism: a review of psychological research. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 40:839–849
Ronald A, Happe F, Plomin R (2005) The genetic relationship between individual differences in social and nonsocial behaviors characteristic of autism. Dev Sci 8:444–458
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cuccaro, M.L., Nations, L., Brinkley, J. et al. A Comparison of Repetitive Behaviors in Aspergers Disorder and High Functioning Autism. Child Psychiatry Hum Dev 37, 347–360 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10578-007-0052-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10578-007-0052-y