Abstract
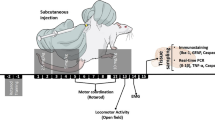
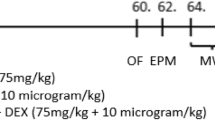
Acute methadone toxicity is a major public health concern which has adverse effects on brain tissue and results in recurrent or delayed respiratory arrest. Our study aimed to investigate the time-dependent changes in several serum biochemical markers of brain damage, spatial working memory, and the brain tissue following acute methadone overdose. Adolescent male rats underwent an intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection of 15 mg/kg methadone. In case of apnea occurrence, resuscitation was performed by a ventilatory pump and administrating naloxone (2 mg/kg; i.p.). The animals were classified into groups of treated rats; methadone and naloxone-Apnea (M/N-Apnea), M/N-Sedate, Methadone, Naloxone, and control (saline) groups. The serum levels of S100B, neuron-specific enolase (NSE), myelin basic protein factors, and (Lactate/Pyruvate) L/P ratio were evaluated at the time-points of 6, 24, and 48 h (h). We found that the alterations of S100B and L/P ratio were considerable in the M/N-Apnea and Methadone groups from the early hours post-methadone overdose, while NSE serum levels elevation was observed only in M/N-Apnea group with a delay at 48 h. Further, we assessed the spatial working memory (Y-maze test), morphological changes, and neuronal loss. The impaired spontaneous alternation behavior was detected in the M/N-Apnea groups on days 5 and 10 post-methadone overdose. The morphological changes of neurons and the neuronal loss were detectable in the CA1, striatum, and cerebellum regions, which were pronounced in both M/N-Apnea and Methadone groups. Together, our findings suggest that alterations in the serum levels of S100B and NSE factors as well as L/P ratio could be induced by methadone overdose with the presence or absence of apnea before the memory impairment and tissue injury in adolescent male rats.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Salam OM, Sleem AA, Youness ER, Omara EA (2019) Identification of biomarkers for the detection of subtle brain injury after cannabis and/or tramadol administration. Egyp J Foren Sci 9(1):58. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41935-019-0165-z
Abdul-Khaliq H, Schubert S, Stoltenburg-Didinger G et al (2000) Protein S-100β in brain and serum after deep hypothermic circulatory arrest in rabbits: relationship to perivascular astrocytic swelling. Clin Chem Lab Med 38:1169–1172. https://doi.org/10.1515/CCLM.2000.180
Abdul-Muneer PM, Chandra N, Haorah J (2015) Interactions of oxidative stress and neurovascular inflammation in the pathogenesis of traumatic brain injury. Mol Neurobiol 51(3):966–979. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-014-8752-3
Ahmad-Molaei L, Hassnian-Moghaddam H, Farnaghi F et al (2018) Delay-dependent impairments in memory and motor functions after acute methadone overdose in rats. Front Pharmacol 9:1023. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2018.01023
Ahn JH, Shin BN, Park JH et al (2016) Long-term observation of neuronal degeneration and microgliosis in the gerbil dentate gyrus after transient cerebral ischemia. J Neurol Sci 363:21–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jns.2016.02.015
Allameh Y, Akrami FS, Mohammadi G, Molavi N, Babakhanian M (2017) Methadone poisoning in children: a systematic review and meta-analysis in Iran. J Pediatr Rev 5(2):1–8. https://doi.org/10.5812/jpr.10133
Alotaibi N, Sammons H, Choonara I (2012) Methadone toxicity in children. Arch Dis Child 97(5):e1–e1. https://doi.org/10.1136/archdischild-2012-301728.2
Ambrožič J, Bunc M, Osredkar J et al (2008) S100B protein in benzodiazepine overdose. Emerg Med J 25:90–92. https://doi.org/10.1136/emj.2006.044222
Anselmo M, Rainho AC, do Carmo Vale M, Estrada J, Valente R, Correia M et al (2006) Methadone intoxication in a child: toxic encephalopathy? J Child Neurol 21(7):618–620. https://doi.org/10.1177/08830738060210071101
Atighi Y, Eizadi-Mood N, Mansourian M, Zamani A, Saffaei A, Sabzghabaee AM (2018) Predictive factors of treatment outcomes for hospital care in children with acute methadone poisoning. J Res Pharmacy Pract 7(4):200. https://doi.org/10.4103/jrpp.JRPP_16_141
Barash JA, Somerville N, DeMaria A (2017) Cluster of an unusual amnestic syndrome—Massachusetts. MMWR Morbid Mortal Weekly Rep 66(3):76
Betts AM, Ritter JL, Kubal WS (2012) Reversible delayed posthypoxic leukoencephalopathy after drug overdose: MRI findings in a collection of patients. Emerg Radiol 19(2):165–173. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10140-011-1013-
Bouvier D, Castellani C, Fournier M, Dauphin JB, Ughetto S, Breton M et al (2011) Reference ranges for serum S100B protein during the first three years of life. Clin Biochem 44(10–11):927–929. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2011.05.004
Böhmer AE, Oses JP, Schmidt AP et al (2011) Neuron-specific enolase, S100B, and glial fibrillary acidic protein levels as outcome predictors in patients with severe traumatic brain injury. Neurosurgery 68:1624–1631. https://doi.org/10.1227/NEU.0b013e318214a81f
Brvar M, Ambrozic J, Osredkar J, Mozina M, Bunc M (2005) S100B protein in heroin overdose: a pilot study. Crit Care 9(1):1–1. https://doi.org/10.1186/cc3353
Brouns R, De Vil B, Cras P et al (2010) Neurobiochemical markers of brain damage in cerebrospinal fluid of acute ischemic stroke patients. Clin Chem 56:451–458. https://doi.org/10.1373/clinchem.2009.134122
Bunten H, Liang WJ, Pounder DJ, Seneviratne C, Osselton D (2011) Interindividual variability in the prevalence of OPRM1 and CYP2B6 gene variations may identify drug-susceptible populations. J Anal Toxicol 35(7):431–437. https://doi.org/10.1093/anatox/35.7.431
Busnello JV, Leke R, Oses JP et al (2006) Acute and chronic electroconvulsive shock in rats: effects on peripheral markers of neuronal injury and glial activity. J Neuroinflammation 78:3013–3017. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2005.11.028
Cardiff RD, Miller CH, Munn RJ (2014) Manual hematoxylin and eosin staining of mouse tissue sections. Cold Spring Harb Proto. https://doi.org/10.1101/pdb.prot073411
Cervos-Navarro J, Diemer NH (1991) Selective vulnerability in brain hypoxia. Crit Rev Neurobiol 6:149–182
Chen C-J, Cheng F-C, Liao S-L et al (2000) Effects of naloxone on lactate, pyruvate metabolism and antioxidant enzyme activity in rat cerebral ischemia/reperfusion. Neurosci Lett 287:113–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-3940(00)01151-4
Cheung R, Hoffman RS, Vlahov D, Manini AF (2018) Prognostic utility of initial lactate in patients with acute drug overdose: a validation cohort. Ann Emerg Med 72(1):16–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.annemergmed.2018.02.022
Chevillard L, Mégarbane B, Risède P et al (2009) Characteristics and comparative severity of respiratory response to toxic doses of fentanyl, methadone, morphine, and buprenorphine in rats. Toxicol Lett 191:327–340. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxlet.2009.09.017
Chiaretti A, Barone G, Riccardi R, Antonelli A, Pezzotti P, Genovese O et al (2009) NGF, DCX, and NSE upregulation correlates with severity and outcome of head trauma in children. Neurology 72(7):609–616. https://doi.org/10.1212/01.wnl.0000342462.51073.06
Corkery JM, Schifano F, Ghodse AH et al (2004) The effects of methadone and its role in fatalities. Hum Psychopharmacol 19:565–576. https://doi.org/10.1002/hup.630
Cummins E, Allen CP, Ricchetti A et al (2012) The effects of acute and chronic steady state methadone on memory retrieval in rats. Psychopharmacology 222:225–235. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-012-2638-8
Darke S, Sims J, McDonald S et al (2000) Cognitive impairment among methadone maintenance patients. J Urban Health 95:687–695. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1360-0443.2000.9556874.x
Doi S, Mori T, Uzawa N et al (2016) Characterization of methadone as a β-arrestin-biased μ-opioid receptor agonist. Mol Pain 12:1744806916654146. https://doi.org/10.1177/1744806916654146
Eap CB, Buclin T, Baumann P (2002) Interindividual variability of the clinical pharmacokinetics of methadone. Clin Pharmacokinet 41(14):1153–1193. https://doi.org/10.2165/00003088-200241140-00003
Ercole A, Thelin EP, Holst A, Bellander BM, Nelson DW (2016) Kinetic modelling of serum S100b after traumatic brain injury. BMC Neurol 16(1):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12883-016-0614-3
Faa A, Senes G, Locci A et al (2012) S100B protein expression in the heart of deceased individuals by overdose: a new forensic marker? Clinics (Sao Paulo) 67:821–826. https://doi.org/10.6061/clinics/2012(07)19
Fan R, Schrott LM, Arnold T, Snelling S, Rao M, Graham D et al (2018) Chronic oxycodone induces axonal degeneration in rat brain. BMC Neurosci 19(1):15. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12868-018-0417-0
Farahmandfar M, Karimian SM, Naghdi N et al (2010) Morphine-induced impairment of spatial memory acquisition reversed by morphine sensitization in rats. Behav Brain Res 211:156–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2010.03.013
Farhadinasab A, Shahidi S, Najafi A et al (2009) Role of naloxone as an exogenous opioid receptor antagonist in spatial learning and memory of female rats during the estrous cycle. Brain Res 1257:65–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2008.12.043
Farid W, Dunlop S, Tait R et al (2008) The effects of maternally administered methadone, buprenorphine and naltrexone on offspring: review of human and animal data. Curr Neuropharmacol 6:125–150. https://doi.org/10.2174/157015908784533842
Finke C, Kopp UA, Prüss H (2011) Cognitive deficits following anti-NMDA receptor encephalitis. Neurol Neurosurg Psychatry 83:195–198. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp-2011-300411
Foster DJ, Somogyi AA, Dyer KR et al (2000) Steady-state pharmacokinetics of (R)-and (S)-methadone in methadone maintenance patients. Br J Clin Pharmacol 50:427–440. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2125.2000.00272.x
Foster DJ, Somogyi AA, White JM et al (2004) Population pharmacokinetics of (R)-,(S)-and rac-methadone in methadone maintenance patients. Br J Clin Pharmacol 57:742–755. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2125.2004.02079.x
Fox LM, Hoffman RS, Vlahov D, Manini AF (2018) Risk factors for severe respiratory depression from prescription opioid overdose. Addiction 113(1):59–66. https://doi.org/10.1111/add.13925
Gaspari RJ, Paydarfar DJN (2007) Pathophysiology of respiratory failure following acute dichlorvos poisoning in a rodent model. NeuroToxicology 28:664–671. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuro.2007.02.002
Gazzolo D, Michetti F, Bruschettini M, Marchese N, Lituania M, Mangraviti S et al (2003) Pediatric concentrations of S100B protein in blood: age-and sex-related changes. Clin Chem 49(6):967–970. https://doi.org/10.1373/49.6.967
Gholami N, Alwasabi F, Farnaghi F (2017) Drug-induced apnea in children admitted to loghman hakim hospital, Tehran. Iran. Iranian J Child Neurol 11(3):15
Gonçalves C-A, Leite MC, Nardin P (2008) Biological and methodological features of the measurement of S100B, a putative marker of brain injury. Clin Biochem 41:755–763. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2008.04.003
González-García S, González-Quevedo A, Fernández-Concepción O et al (2012) Short-term prognostic value of serum neuron specific enolase and S100B in acute stroke patients. Clin Biochem 45:1302–1307. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2012.07.094
Graziani M, Nisticò R (2015) Gender differences in pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of methadone substitution therapy. Front Pharmacol 6:122. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2015.00122
Haghighi-Morad M, Naseri Z, Jamshidi N et al (2020) Methadone-induced encephalopathy: a case series and literature review. BMC Med Imaging 20:6. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12880-020-0410-9
Haque A, Polcyn R, Matzelle D et al (2018) New insights into the role of neuron-specific enolase in neuro-inflammation, neurodegeneration, and neuroprotection. Brain Sci 8:33. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci8020033
Hepner IJ, Homewood J, Taylor AJ (2002) Methadone disrupts performance on the working memory version of the Morris water task. Physiol Behav 76(1):41–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0031-9384(02)00695-9
Herrmann M, Ebert AD, Galazky I et al (2000) Neurobehavioral outcome prediction after cardiac surgery: role of neurobiochemical markers of damage to neuronal and glial brain tissue. Stroke 31:645–650. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.STR.31.3.645
Hyer MM, Phillips LL, Neigh GN (2018) Sex differences in synaptic plasticity: hormones and beyond. Frontiers Mole Neurosci 11:266. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnmol.2018.00266
Jauch EC, Lindsell C, Broderick J et al (2006) Association of serial biochemical markers with acute ischemic stroke: the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke recombinant tissue plasminogen activator Stroke Study. Stroke 37:2508–2513. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.STR.0000242290.01174.9e
Jones JD, Mogali S, Comer SDJD et al (2012) Polydrug abuse: a review of opioid and benzodiazepine combination use. Drug Alcohol Depend 125:8–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2012.07.004
Kantonen T, Karjalainen T, Isojärvi J, Nuutila P, Tuisku J, Rinne J et al (2020) Interindividual variability and lateralization of μ-opioid receptors in the human brain. Neuroimage. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2020.116922
King F, Morris NA, Schmahmann JD (2015) Delayed posthypoxic leukoencephalopathy: improvement with antioxidant therapy. Case Rep Neurol 7(3):242–246. https://doi.org/10.1159/000441892
Klenowski P, Morgan M, Bartlett SE (2015) The role of δ-opioid receptors in learning and memory underlying the development of addiction. Br J Pharmacol 172:297–310. https://doi.org/10.1111/bph.12618
Kozlyuk N, Monteith AJ, Garcia V, Damo SM, Skaar EP, Chazin WJ (2019) S100 proteins in the innate immune response to pathogens. In: Calcium-binding proteins of the EF-hand superfamily. Humana Press, New York, pp 275–290. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-9030-6_18
Kurumatani T, Kudo T, Ikura Y et al (1998) White matter changes in the gerbil brain under chronic cerebral hypoperfusion. Stroke 29:1058–1061. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00227672
Laycock H, Bantel C (2019) Opioid mechanisms and opioid drugs. Anaesth Intens Care Med. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mpaic.2019.05.009
Li W, Li Q, Wang Y et al (2016) Methadone-induced damage to white matter integrity in methadone maintenance patients: a longitudinal self-control DTI study. Sci Rep 6:19662. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep19662
Lupica CR, Proctor WR, Dunwiddie TV (1992) Dissociation of μ and δ opioid receptor-mediated reductions in evoked and spontaneous synaptic inhibition in the rat hippocampus in vitro. Brain Res 593:226–238. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-8993(92)91312-3
Ma M, Chen Y, He J, et al. (2007) Effects of morphine and its withdrawal on Y-maze spatial recognition memory in mice. Neuroscience 147: 1059–1065. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2007.05.020
McCormick CM, Mathews IZ (2010) Adolescent development, hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal function, and programming of adult learning and memory. Prog Neuropsychopharm Biol Psychiatry 34(5):756–765. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnpbp.2009.09.019
Manouchehrifar M, Derakhshandeh N, Shojaee M, Sabzghabaei A, Farnaghi F (2016) An epidemiologic study of pediatric poisoning; a six-month cross-sectional study. Emergency 4(1):21
Mansori K, Soori H, Farnaghi F, Khodakarim S (2016) A case-control study on risk factors for unintentional childhood poisoning in Tehran. Med J Islamic Repub Iran 30:355
Nouri F, Afarinesh MR, Sheibani V, Foroumadi A, Mahani SE, Mahmoudi M, Rohani E (2019) Concomitant abuse of methadone and methamphetamine could impair spatial learning and memory in male rats. Learn Motiv 65:43–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lmot.2019.01.001
Petzold A, Michel P, Stock M et al (2008) Glial and axonal body fluid biomarkers are related to infarct volume, severity, and outcome. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 17:196–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2008.02.002
Raabe, A., Kopetsch, O., Woszczyk, A., Lang, J., Gerlach, R., Zimmermann, M., & Seifert, V. (2003). Serum S-100B protein as a molecular marker in severe traumatic brain injury. Restorative neurology and neuroscience, 21(3, 4), 159–169.
Rady JJ, Portoghese PS, Fujimoto JM (2002) Methadone and heroin antinociception: predominant δ-opioid-receptor responses in methadone-tolerant mice. Jpn J Pharmacol 88:319–331. https://doi.org/10.1254/jjp.88.319
Rapeli P, Fabritius C, Kalska H et al (2009) Memory function in opioid-dependent patients treated with methadone or buprenorphine along with benzodiazepine: longitudinal change in comparison to healthy individuals. Subst Abuse Treat Prev Policy 4:6. https://doi.org/10.1186/1747-597X-4-6
Reisner A, Hayes LL, Holland CM, Wrubel DM, Kebriaei MA, Geller RJ et al (2015) Opioid overdose in a child: case report and discussion with emphasis on neurosurgical implications. J Neurosurg 16(6):752–757. https://doi.org/10.3171/2015.4.PEDS14667
Sahuquillo J, Merino MA, Sanchez-Guerrero A, Arikan F, Vidal-Jorge M, Martínez-Valverde T et al (2014) Lactate and the lactate-to-pyruvate molar ratio cannot be used as independent biomarkers for monitoring brain energetic metabolism: a microdialysis study in patients with traumatic brain injuries. PLoS ONE. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0102540
Salgado RA, Jorens PG, Baar I, Cras P, Hans G, Parizel PM (2010) Methadone-induced toxic leukoencephalopathy: MR imaging and MR proton spectroscopy findings. Am J Neuroradiol 31(3):565–566. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A1889
Sankar R, Shin DH, Wasterlain CG (1997) Serum neuron-specific enolase is a marker for neuronal damage following status epilepticus in the rat. Epilepsy Res 28(2):129–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0920-1211(97)00040-5
Schadrack J, Willoch F, Platzer S et al (1999) Opioid receptors in the human cerebellum: evidence from [11C] diprenorphine PET, mRNA expression and autoradiography. NeuroReport 10:619–624. https://doi.org/10.1097/00001756-199902250-00032
Schaf DV, Tort AB, Fricke D et al (2005) S100B and NSE serum levels in patients with Parkinson's disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 11:39–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2004.07.002
Sengupta P (2013) The laboratory rat: relating its age with human's. Int J Preven Med 4(6):624. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-65722-6
Shahim P, Tegner Y, Wilson DH et al (2014) Blood biomarkers for brain injury in concussed professional ice hockey players. JAMA Neurol 71:684–692. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaneurol.2014.367
Sharma A, Tallchief D, Blood J, Kim T, London A, Kharasch ED (2011) Perioperative pharmacokinetics of methadone in adolescents. Anesthesiology 115(6):1153–1161. https://doi.org/10.1097/ALN.0b013e318238fec5
Shields LB, Hunsaker JC III, Corey TS et al (2007) Methadone toxicity fatalities: a review of medical examiner cases in a large metropolitan area. J Forensic Sci 52:1389–1395. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1556-4029.2007.00565.x
Somerville NJ, O’Donnell J, Gladden RM, Zibbell JE, Green TC, Younkin M et al (2017) Characteristics of fentanyl overdose—Massachusetts, 2014–2016. MMWR Morbid Mortal Weekly Rep 66(14):382
Specka M, Finkbeiner T, Lodemann E et al (2000) Cognitive-motor performance of methadone-maintained patients. Eur Addict Res 6:8–19. https://doi.org/10.1159/000019004
Sternberger NH, Itoyama Y, Kies MW et al (1978) Myelin basic protein demonstrated immunocytochemically in oligodendroglia prior to myelin sheath formation. PNAS. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.75.5.2521
Taheri F, Yaraghi A, Sabzghabaee AM et al (2013) Methadone toxicity in a poisoning referral center. J Res Pharm Pract 2:130. https://doi.org/10.4103/2279-042X.122387
Tanaka Y, Marumo T, Shibuta H, Omura T, Yoshida S (2009) Serum S100B, brain edema, and hematoma formation in a rat model of collagenase-induced hemorrhagic stroke. Brain Res Bull 78(4–5):158–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainresbull.2008.10.012
Thelin EP, Jeppsson E, Frostell A et al (2016) Utility of neuron-specific enolase in traumatic brain injury; relations to S100B levels, outcome, and extracranial injury severity. Critical Care Crit Care 20:285. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13054-016-1450-y
Thigpen JC, Odle BL, Harirforoosh S (2019) Opioids: a review of pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics in neonates, infants, and children. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13318-019-00552-0
Tiong SC, Chieng JSL, Khoo HW, Ng CH (2019) Methadone-induced toxic encephalopathy in pediatric patients: two case reports. J Radiol Case Rep 13(5):1. https://doi.org/10.3941/jrcr.v13i5.3658
Thoresen M, Hallström Å, Whitelaw A et al (1998) Lactate and pyruvate changes in the cerebral gray and white matter during posthypoxic seizures in newborn pigs. Pediatr Res 44:746–754. https://doi.org/10.1203/00006450-199811000-00018
Timofeev I, Carpenter KL, Nortje J et al (2011) Cerebral extracellular chemistry and outcome following traumatic brain injury: a microdialysis study of 223 patients. Brain 134:484–494. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awq353
Tramullas M, Martínez-Cué C, Hurlé MAJP (2007) Chronic methadone treatment and repeated withdrawal impair cognition and increase the expression of apoptosis-related proteins in mouse brain. Psychopharmacology 193:107–120. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-007-0751-x
Van Dorp EL, Yassen A, Dahan AJ (2007) Naloxone treatment in opioid addiction: the risks and benefits. Expert Opin Drug Saf 6:125–132. https://doi.org/10.1517/14740338.6.2.125
Verdejo A, Toribio I, Orozco C et al (2005) Neuropsychological functioning in methadone maintenance patients versus abstinent heroin abusers. Drug Alcohol Depend 78:283–288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2004.11.006
Vestal-Laborde AA, Eschenroeder AC, Bigbee JW et al (2014) The opioid system and brain development: effects of methadone on the oligodendrocyte lineage and the early stages of myelination. Dev Neurosci 36:409–421. https://doi.org/10.1159/000365074
Villegas SC, Thielet N (2020) Methadone prescribing caveats for chronic pain and opioid use disorder. J Nurse Practition 16(3):176–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nurpra.2019.12.017
Wardi G, Brice J, Correia M, Liu D, Self M, Tainter C (2020) Demystifying lactate in the emergency department. Ann Emerg Med 75(2):287–298. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.annemergmed.2019.06.027
Wegener S, Weber R, Ramos-Cabrer P et al (2006) Temporal profile of T 2-weighted MRI distinguishes between pannecrosis and selective neuronal death after transient focal cerebral ischemia in the rat. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 26:38–47. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jcbfm.9600166
Wehner F, Wehner H-D, Schieffer MC et al (2000) Immunohistochemical detection of methadone in the human brain. Front Pharmacol 112:11–16. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2018.01023
Wermeling DP (2015) Review of naloxone safety for opioid overdose: practical considerations for new technology and expanded public access. Therapeut Adv Drug Safety 6(1):20–31. https://doi.org/10.1177/2042098614564776
Winstanley EL, Stover AN (2019) The impact of the opioid epidemic on children and adolescents. Clin Ther 41(9):1655–1662. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinthera.2019.06.003
Woertgen C, Rothoerl RD, Wiesmann M, Missler U, Brawanski A (2002) Glial and neuronal serum markers after controlled cortical impact injury in the rat. In: Intracranial pressure and brain biochemical monitoring. Springer, Vienna, pp 205–207. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-7091-6738-0_53
Wu H-M, Huang S-C, Hattori N et al (2004) Selective metabolic reduction in gray matter acutely following human traumatic brain injury. J Neurotrauma 21:149–161. https://doi.org/10.1089/089771504322778613
Wunderlich M, Wallesch C, Goertler MJ (2006) Release of glial fibrillary acidic protein is related to the neurovascular status in acute ischemic stroke. Eur J Neurol 13:1118–1123. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-1331.2006.01435.x
Yilmaz S, Karakayali O, Kale E et al (2018) Could serum S100B be a predictor of neuronal damage and clinical poor outcomes associated with the use of synthetic cannabinoids? S100B to predict neuronal damage of SC in the ED. Am J Emerg Med 36:435–441. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajem.2017.08.053
Zamani N, Hassanian-Moghaddam H, Bayat AH et al (2015) Reversal of opioid overdose syndrome in morphine-dependent rats using buprenorphine. Toxicol Lett 232:590–594. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxlet.2014.12.007
Žurek J, Fedora M (2012) The usefulness of S100B, NSE, GFAP, NF-H, secretagogin and Hsp70 as a predictive biomarker of outcome in children with traumatic brain injury. Acta Neurochir 154(1):93–103. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-011-1175-2
Acknowledgment
This study was carried out as a part of the Ph.D. thesis and supported by funding from the School of Medicine, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences (Grant No. 70), Tehran, Iran. This work was also supported by the Vice-Chancellor for Research & Technology of Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences (Grant No. 98-21486-1398-11-29). The authors extend appreciation to the Neuroscience Research Center, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran for valuable cooperation.
Funding
This study was supported by funding from the School of Medicine, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences (Grant No. 98-21486-1398-11-29), Tehran, Iran. This funding source had no role in the design of this study, execution, analysis, and interpretation of the data; in the writing of the report; and in the decision to submit the paper for publication.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Abbas Haghparast was responsible for the study concept and design. Leila Ahmad-Molaei and Mahsa Pourhamzeh conducted the working memory test, histological and molecular studies. Abbas Haghparast, Fariba Khodagholi, Reza Ahadi, Hassanian-Moghaddam and Leila Ahmad-Molaei assisted with data analysis and interpretation of findings. Mahsa Pourhamzeh and Leila Ahmad-Molaei drafted the manuscript. All authors critically revised and approved final version for publication.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahmad-Molaei, L., Pourhamzeh, M., Ahadi, R. et al. Time-Dependent Changes in the Serum Levels of Neurobiochemical Factors After Acute Methadone Overdose in Adolescent Male Rat. Cell Mol Neurobiol 41, 1635–1649 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-020-00931-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-020-00931-1