Abstract
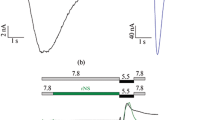
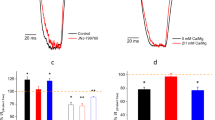
Acid-sensing ion channels (ASICs) are modulated by various classes of ligands, including the recently described hydrophobic monoamines, which inhibit and potentiate ASICs in a subunit-specific manner. In particular, memantine inhibits ASIC1a and potentiates ASIC2a homomers. The aim of the present work was to characterize action mechanism of memantine on recombinant ASIC1a expressed in CHO (Chinese hamster ovary) cells. We have demonstrated that effect of memantine on ASIC1a strongly depends on membrane voltage, conditioning pH value and application protocol. When applied simultaneously with activating acidification at hyperpolarized voltages, memantine caused the strongest inhibition. Surprisingly, application of memantine between ASIC1a activations at zero voltage caused significant potentiation. Analysis of the data suggests that memantine produces two separate effects, voltage-dependent open-channel block and shift of steady-state desensitization curve to more acidic values. Putative binding sites are discussed based on the computer docking of memantine to the acidic pocket and the pore region.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen NJ, Attwell D (2002) Modulation of ASIC channels in rat cerebellar Purkinje neurons by ischaemia-related signals. J Physiol 543:521–529
Askwith CC, Cheng C, Ikuma M, Benson C, Price MP, Welsh MJ (2000) Neuropeptide FF and FMRFamide potentiate acid-evoked currents from sensory neurons and proton-gated DEG/ENaC channels. Neuron 26:133–141
Baconguis I, Gouaux E (2012) Structural plasticity and dynamic selectivity of acid-sensing ion channel-spider toxin complexes. Nature 489:400–405
Baconguis I, Bohlen CJ, Goehring A, Julius D, Gouaux E (2014) X-ray structure of acid-sensing ion channel 1-snake toxin complex reveals open state of a Na(+)-selective channel. Cell 156:717–729
Baron A, Lingueglia E (2015) Pharmacology of acid-sensing ion channels—physiological and therapeutical perspectives. Neuropharmacology 94:19–35
Barygin OI, Gmiro VE, Kim KKh, Magazanik LG, Tikhonov DB (2009) Blockade of NMDA receptor channels by 9-aminoacridine and its derivatives. Neurosci Lett 451:29–33
Beam KG (1976) A voltage-clamp study of the effect of two lidocaine derivatives on the time course of end-plate currents. J Physiol 258:279–300
Benveniste M, Mayer ML (1995) Trapping of glutamate and glycine during open channel block of rat hippocampal neuron NMDA receptors by 9-aminoacridine. J Physiol 483:367–384
Blanpied TA, Boeckman FA, Aizeman E, Johnson JW (1997) Trapping channel block of NMDA-activated responses by amantadine and memantine. J Neurophysiol 77:309–323
Bohlen CJ, Chesler AT, Sharif-Naeini R, Medzihradszky KF, Zhou S, King D, Sánchez EE, Burlingame AL, Basbaum AI, Julius D (2011) A heteromeric Texas coral snake toxin targets acid-sensing ion channels to produce pain. Nature 479:410–414
Boiko N, Kucher V, Eaton BA, Stockand JD (2013) Inhibition of neuronal degenerin/epithelial Na+ channels by the multiple sclerosis drug 4-aminopyridine. J Biol Chem 288:9418–9427
Bolshakov KV, Gmiro VE, Tikhonov DB, Magazanik LG (2003) Determinants of trapping block of N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor channels. J Neurochem 87:56–65
Buta A, Maximyuk O, Kovalskyy D, Sukach V, Vovk M, Ievglevskyi O, Isaeva E, Isaev D, Savotchenko A, Krishtal O (2015) Novel potent orthosteric antagonist of ASIC1a Prevents NMDAR-dependent LTP induction. J Med Chem 58:4449–4461
Chen X, Kalbacher H, Gründer S (2005) The tarantula toxin psalmotoxin 1 inhibits acid-sensing ion channel (ASIC) 1a by increasing its apparent H+ affinity. J Gen Physiol 126:71–79
Chen X, Orser BA, MacDonald JF (2010) Design and screening of ASIC inhibitors based on aromatic diamidines for combating neurological disorders. Eur J Pharmacol 648:15–23
Chu XP, Wemmie JA, Wang WZ, Zhu XM, Saugstad JA, Price MP, Simon RP, Xiong ZG (2004) Subunit-dependent high-affinity zinc inhibition of acid-sensing ion channels. J Neurosci 24:8678–8689
Coryell MW, Wunsch AM, Haenfler JM, Allen JE, Ziemann AE, Cook MN, Dunning JP, Margaret P, Rainier JD, Liu Z, Light AR, Langbehn DR, Wemmie A (2009) Acid-sensing ion channel-1a in the amygdala, a novel therapeutic target in depression-related behavior. J Neurosci 29:5381–5388
De Weille J, Bassilana F (2001) Dependence of the acid-sensitive ion channel, ASIC1a, on extracellular Ca2+ ions. Brain Res 900:277–281
Decher N, Kumar P, Gonzalez T, Pirard B, Sanguinetti MC (2006) Binding site of a novel Kv1.5 blocker: a “foot in the door” against atrial fibrillation. Mol Pharmacol 70:1204–1211
Delaunay A, Gasull X, Salinas M, Noël J, Friend V (2012) Human ASIC3 channel dynamically adapts its activity to sense the extracellular pH in both acidic and alkaline directions. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109:13124–13129
Dewar MJS, Zoebisch EG, Healy EF, Stewart JJP (1985) AM1: a New General Purpose Quantum Mechanical Model. J Am Chem Soc 107:3902–3909
Diochot S, Baron A, Rash LD, Deval E, Escoubas P, Scarzello S, Salinas M, Lazdunski M (2004) A new sea anemone peptide, APETx2, inhibits ASIC3, a major acid-sensitive channel in sensory neurons. EMBO J 23:1516–1525
Dorofeeva NA, Barygin OI, Staruschenko A, Bolshakov KV, Magazanik LG (2008) Mechanisms of non-steroid anti-inflammatory drugs action on ASICs expressed in hippocampal interneurons. J Neurochem 106:429–441
Duan B, Wang YZ, Yang T, Chu XP, Yu Y, Huang Y, Cao H, Hansen J, Simon RP, Zhu MX, Xiong ZG, Xu TL (2011) Extracellular spermine exacerbates ischemic neuronal injury through sensitization of ASIC1a channels to extracellular acidosis. J Neurosci 31:2101–2112
Escoubas P, De Weille JR, Lecoq A, Diochot S, Waldmann R, Champigny G, Moinier D, Ménez A, Lazdunski M (2000) Isolation of a tarantula toxin specific for a class of proton-gated Na+ channels. J Biol Chem 275:25116–25121
Garden DP, Zhorov BS (2010) Docking flexible ligands in proteins with a solvent exposure- and distance-dependent dielectric function. J Comput Aided Mol Des 24:91–105
Garza A, López-Ramírez O, Vega R, Soto E (2010) The aminoglycosides modulate the acid-sensing ionic channel currents in dorsal root ganglion neurons from the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 332:489–499
Gonzales EB, Kawate T, Gouaux E (2009) Pore architecture and ion sites in acid-sensing ion channels and P2X receptors. Nature 460:599–604
Hille B (1977) Local anesthetics: hydrophilic and hydrophobic pathways for the drug-receptor reaction. J Gen Physiol 69:497–515
Jasti J, Furukawa H, Gonzales EB, Gouaux E (2007) Structure of acid-sensing ion channel 1 at 1.9 A resolution and low pH. Nature 449:316–323
Kuduk SD, Chang RK, Wai JMC, Di Marco CN, Cofre V, DiPardo RM, Cook SP, Cato MJ, Jovanovska A, Urban MO, Leitl M, Spencer RH, Kane SA, Hartman GD, Bilodeau MT (2009) Amidine derived inhibitors of acid-sensing ion channel-3 (ASIC3). Bioorg Med Chem Lett 19:4059–4063
Leng T, Lin J, Cottrell JE, Xiong ZG (2013) Subunit and frequency-dependent inhibition of acid sensing ion channels by local anesthetic tetracaine. Mol Pain 9:27–35
Li Z, Scheraga HA (1987) Monte Carlo-minimization approach to the multiple-minima problem in protein folding. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:6611–6615
Li WG, Yu Y, Zhang ZD, Cao H, Xu TL (2010) ASIC3 channels integrate agmatine and multiple inflammatory signals through the nonproton ligand sensing domain. Mol Pain 6:88–98
Li WG, Yu Y, Huang C, Cao H, Xu TL (2011) Nonproton ligand sensing domain is required for paradoxical stimulation of acid-sensing ion channel 3 (ASIC3) channels by amiloride. J Biol Chem 286:42635–42646
Lin J, Chu X, Maysami S, Li M, Si H, Cottrell JE, Simon RP, Xiong Z (2011) Inhibition of acid sensing ion channel currents by lidocaine in cultured mouse cortical neurons. Anesth Analg 112:978–981
Mealing GAR, Lanthorn TH, Small DL, Murray RJ, Mattes KC, Comas TM, Morley P (2001) Structural modifications to an N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonist result in large differences in trapping block. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 297:906–914
Nagaeva EI, Potapieva NN, Tikhonov DB (2015) The effect of hydrophobic monoamines on acid-Sensing ion channels ASIC1B. Acta Nat 7:95–101
Nagaeva EI, Potapieva NN, Nikolaev MV, Gmiro VE, Magazanik LG, Tikhonov DB (2016a) Determinants of action of hydrophobic amines on ASIC1a and ASIC2a. Eur J Pharmacol 788:75–83
Nagaeva EI, Tikhonova TB, Magazanik LG, Tikhonov DB (2016b) Histamine selectively potentiates acid-sensing ion channel 1a. Neurosci Lett 632:136–140
Nikolaev MV, Dorofeeva NA, Komarova MS, Korolkova YV, Andreev YA, Mosharova IV, Grishin EV, Tikhonov DB, Kozlov SA (2017) TRPV1 activation power can switch an action mode for its polypeptide ligands. PLoS ONE 12(5):e0177077
Peper K, Bradley JR, Dreyer F (1982) The acetylcholine receptor at the neuromuscular junction. Physiol Rev 62(4):1271–1340
Price MP, Gong H, Parsons MG, Kundert JR, Reznikov LR, Bernardinelli L, Chaloner K, Buchanan GF, Wemmie JA, Richerson GB, Cassell MD, Welsh MJ (2014) Localization and behaviors in null mice suggest that ASIC1 and ASIC2 modulate responses to aversive stimuli. Genes Brain Behav 13:179–194
Sherwood TW, Askwith CC (2008) Endogenous arginine-phenylalanine-amide-related peptides alter steady-state desensitization of ASIC1a. J Biol Chem 283:1818–1830
Sherwood TW, Lee KG, Gormley MG, Askwith CC (2011) Heteromeric ASIC channels composed of ASIC2b and ASIC1a display novel channel properties and contribute to acidosis-induced neuronal death. J Neurosci 31(26):9723–9734
Sobolevsky AI, Yelshansky MV (2000) The trapping block of NMDA receptor channels in acutely isolated rat hippocampal neurones. J Physiol 526:493–506
Staruschenko A, Dorofeeva NA, Bolshakov KV, Stockand JD (2007) Subunit-dependent cadmium and nickel inhibition of acid-sensing ion channels. Dev Neurobiol 67:97–107
Tikhonov DB, Zhorov BS (2012) Architecture and pore block of eukaryotic voltage-gated sodium channels in view of NavAb bacterial sodium channel structure. Mol Pharmacol 82:97–104
Tikhonova TB, Nagaeva EI, Barygin OI, Potapieva NN, Bolshakov KV, Tikhonov DB (2015) Monoamine NMDA receptor channel blockers inhibit and potentiate native and recombinant proton-gated ion channels. Neuropharmacology 89:1–10
Voilley N (2004) Acid-sensing ion channels (ASICs): new targets for the analgesic effects of non-steroid anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Curr Drug Targets Inflamm Allergy 3:71–79
Waldmann R, Champigny G, Bassilana F, Heurteaux C, Lazdunski M (1997) A proton-gated cation channel involved in acid-sensing. Nature 386:173–177
Weiner SJ, Kollman PA, Case DA, Singh UC, Chio C, Alagona G, Profeta S, Weiner PK (1984) A new force field for molecular mechanical simulation of nucleic acids and proteins. J Am Chem Soc 106:765–784
Weiner SJ, Kollman PA, Nguyen DT, Case DA (1986) An all atom force-field for simulations of proteins and nucleic-acids. J Comput Chem 7:230–252
Wemmie JA, Askwith CC, Lamani E, Cassell MD, Freeman JH, Welsh MJ (2003) Acid-sensing ion channel 1 is localized in brain regions with high synaptic density and contributes to fear conditioning. J Neurosci 23:5496–5502
Woodhull AM (1973) Ionic blockage of sodium channels in nerve. J Gen Physiol 61:687–708
Yu Y, Chen Z, Li W, Cao H, Feng E, Yu F, Liu H, Jiang H, Xu T (2010) A nonproton ligand sensor in the acid-sensing ion channel. Neuron 68:61–72
Yu Y, Li WG, Chen Z, Cao H, Yang H, Jiang H, Xu TL (2011) Atomic level characterization of the nonproton ligand-sensing domain of ASIC3 channels. J Biol Chem 286:24996–25006
Acknowledgements
The work is supported by Russian Science Foundation Grant 16-14-00122.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
V.Y.S. and T.B.T performed experiments. V.S.K. performed modeling. D.B.T. designed the project and drafted the manuscript. All the authors discussed the results and commented the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shteinikov, V.Y., Tikhonova, T.B., Korkosh, V.S. et al. Potentiation and Block of ASIC1a by Memantine. Cell Mol Neurobiol 38, 869–881 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-017-0561-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-017-0561-6