Abstract
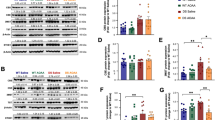
Mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) is a key regulator of metabolism, cell growth, and protein synthesis. Since decreased mTOR activity has been found to slow aging in many species, the aim of this study was to examine the activity of mTOR and its phosphorylated form in in vitro and in vivo models mimicking Alzheimer’s disease (AD), and investigate the potential pathway of PGC-1β in regulating mTOR expression. Primary neurons and N2a cells were treated with Aβ25–35, while untreated cells served as controls. The expression of mTOR, p-mTOR (Ser2448), and PGC-1β was determined with Western blotting and RT-PCR assay, and the translocation of mTOR was detected using confocal microscopy. Aβ25–35 treatment stimulated the translocation of mTOR from cytoplasm to nucleus, and resulted in elevated expression of mTOR and p-mTOR (Ser2448) and reduced PGC-1β expression. In addition, overexpression of PGC-1β was found to decrease mTOR expression. The results of this study demonstrate that Aβ increases the expression of mTOR and p-mTOR at the site of Ser2448, and the stimulation of Aβ is likely to depend on sirtuin 1, PPARγ, and PGC-1β pathway in regulating mTOR expression.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguirre-Rueda D, Guerra-Ojeda S, Aldasoro M, Iradi A, Obrador E, Ortega A, Mauricio MD, Vila JM, Valles SL (2015) Astrocytes protect neurons from Aβ1-42 peptide-induced neurotoxicity increasing TFAM and PGC-1 and decreasing PPAR-γ and SIRT-1. Int J Med Sci 12(1):48–56. doi:10.7150/ijms.10035
Alonso A, Zaidi T, Novak M, Grundke-Iqbal I, Iqbal K (2001) Hyperphosphorylation induces self-assembly of tau into tangles of paired helical filaments/straight filaments. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98(12):6923–6928. doi:10.1073/pnas.121119298
Alzheimer’s Association (2015) 2015 Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimers dement 11:332–384. doi:10.1016/j.jalz.2015.02.003
Caccamo A, Majumder S, Richardson A, Strong R, Oddo S (2010) Molecular interplay between mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR), amyloid-beta, and tau: effects on cognitive impairments. J Biol Chem 285(17):13107–13120. doi:10.1074/jbc.M110.100420
Cai Z, Chen G, He W, Xiao M, Yan LJ (2015) Activation of mTOR: a culprit of Alzheimer’s disease? Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat 11:1015–1030. doi:10.2147/NDT.S75717
Camacho A, Rodriguez-Cuenca S, Blount M, Prieur X, Barbarroja N, Fuller M, Hardingham GE, Vidal-Puig A (2012) Ablation of PGC1 beta prevents mTOR dependent endoplasmic reticulum stress response. Exp Neurol 237(2):396–406. doi:10.1016/j.expneurol.2012.06.031
Chaturvedi RK, Flint Beal M (2013) Mitochondrial diseases of the brain. Free Radic Biol Med 63:1–29. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2013.03.018
Chiang GG, Abraham RT (2005) Phosphorylation of mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) at Ser-2448 is mediated by p70S6 kinase. J Biol Chem 280(27):25485–25490. doi:10.1074/jbc.M501707200
Deshpande A, Mina E, Glabe C, Busciglio J (2006) Different conformations of amyloid beta induce neurotoxicity by distinct mechanisms in human cortical neurons. J Neurosci 26(22):6011–6018. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1189-06.2006
Dries DR, Yu G, Herz J (2012) Extracting β-amyloid from Alzheimer’s disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109(9):3199–3200. doi:10.1073/pnas.1121560109
Ferreira ST, Lourenco MV, Oliveira MM, De Felice FG (2015) Soluble amyloid-β oligomers as synaptotoxins leading to cognitive impairment in Alzheimer’s disease. Front Cell Neurosci 9:191. doi:10.3389/fncel.2015.00191
Gaubitz C, Oliveira TM, Prouteau M, Leitner A, Karuppasamy M, Konstantinidou G, Rispal D, Eltschinger S, Robinson GC, Thore S, Aebersold R, Schaffitzel C, Loewith R (2015) Molecular basis of the rapamycin insensitivity of target of rapamycin complex 2. Mol Cell 58(6):977–988. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2015.04.031
Ghosh HS, McBurney M, Robbins PD (2010) SIRT1 negatively regulates the mammalian target of rapamycin. PLoS One 5(2):e9199. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0009199
Harrison DE, Strong R, Sharp ZD, Nelson JF, Astle CM, Flurkey K, Nadon NL, Wilkinson JE, Frenkel K, Carter CS, Pahor M, Javors MA, Fernandez E, Miller RA (2009) Rapamycin fed late in life extends lifespan in genetically heterogeneous mice. Nature 460(7253):392–395. doi:10.1038/nature08221
Hayashi Y, Yoshida M, Yamato M, Ide T, Wu Z, Ochi-Shindou M, Kanki T, Kang D, Sunagawa K, Tsutsui H, Nakanishi H (2008) Reverse of age-dependent memory impairment and mitochondrial DNA damage in microglia by an overexpression of human mitochondrial transcription factor in mice. J Neurosci 28(34):8624–8634. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1957-08.2008
Ikeuchi M, Matsusaka H, Kang D, Matsushima S, Ide T, Kubota T, Fujiwara T, Hamasaki N, Takeshita A, Sunagawa K, Tsutsui H (2005) Overexpression of mitochondrial transcription factor A ameliorates mitochondrial deficencies and cardiac failure after myocardial infarction. Circulation 112(5):683–690. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.104.524835
Johnson SC, Yanos ME, Kayser EB, Quintana A, Sangesland M, Castanza A, Uhde L, Hui J, Wall VZ, GagnidzeA OhK, Wasko BM, Ramos FJ, Palmiter RD, Rabinovitch PS, Morgan PG, Sedensky MM, Kaeberlein M (2013) mTOR inhibition alleviates mitochondrial disease in a mouse model of leigh syndrome. Science 342:1524–1528. doi:10.1126/science.1244360
Kelly TJ, Lerin C, Haas W, Gygi SP, Puigserver P (2009) GCN5-mediated transcriptional control of the metabolic coactivator PGC-1beta through lysine acetylation. J Biol Chem 284(30):19945–19952. doi:10.1074/jbc.M109.015164
Kim JE, Chen J (2000) Cytoplasmic-nuclear shuttling of FKBP12- rapamycin associated protein is involved in rapamycin-sensitive signaling and translation initiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97(27):14340–14345. doi:10.1073/pnas.011511898
Kumar R, Chaterjee P, Sharma PK, Singh AK, Gupta A, Gill K, Tripathi M, Dey AB, Dey S (2013) Sirtuin1: a promising serum protein marker for early detection of Alzheimer’s disease. PLoS One 8(4):e61560. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0061560
Li X, Alafuzoff I, Soininen H, Winblad B, Pei JJ (2005) Levels of mTOR and its downstream targets 4E-BP1, eEF2, and eEF2 kinase in relationships with tau in Alzheimer’s disease brain. Febs J 272(16):4211–4220. doi:10.1111/j.1742-4658.2005.04833.x
Loewith R, Jacinto E, Wullschleger S, Lorberg A, Crespo JL, Bonenfant D, Oppliger W, Jenoe P, Hall MN (2002) Two TOR complexes, only one of which is rapamycin sensitive, have distinct roles in cell growth control. Mol Cell 10(3):457–468. doi:10.1016/S1097-2765(02)00636-6
Ma T, Zhao Y, Kwak YD, Yang Z, Thompson R, Luo Z, Xu H, Liao FF (2009) Statin’s excitoprotection is mediated by sAPP and the subsequent attenuation of calpain-induced truncation events, likely via rho-ROCK signaling. J Neurosci 29(36):11226–11236. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.6150-08.2009
Mudò G, Mäkelä J, Di Liberto V, Tselykh TV, Olivieri M, Piepponen P, Eriksson O, Mälkiä A, Bonomo A, Kairisalo M, Aguirre JA, Korhonen L, Belluardo N, Lindholm D (2012) Transgenic expression and activation of PGC-1α protect dopaminergic neurons in the MPTP mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Cell Mol Life Sci 69(7):1153–1165. doi:10.1007/s00018-011-0850-z
Pei JJ, Hugon J (2008) mTOR-dependent signalling in Alzheimer’s disease. J Cell Mol Med 12(6B):2525–2532. doi:10.1111/j.1582-4934.2008.00509.x
Qiang L, Wang L, Kon N, Zhao W, Lee S, Zhang Y, Rosenbaum M, Zhao Y, Gu W, Farmer SR, Accili D (2012) Brown remodeling of white adipose tissue by SirT1-dependent deacetylation of pparγ. Cell 150(3):620–632. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2012.06.027
Qin W, Haroutunian V, Katsel P, Cardozo CP, Ho L, Buxbaum JD, Pasinetti GM (2009) PGC-1alpha expression decreases in the Alzheimer disease brain as a function of dementia. Arch Neurol 66(3):352–361. doi:10.1001/archneurol.2008.588
Querfurth HW, LaFerla FM (2010) Alzheimer’s disease. N Engl J Med 362(4):329–344. doi:10.1056/NEJMra0909142
Richardson A, Galvan V, Lin AL, Oddo S (2015) How longevity research can lead to therapies for Alzheimer’s disease: the rapamycin story. Exp Gerontol 68:51–58. doi:10.1016/j.exger.2014.12.002
Siman R, Cocca R, Dong Y (2015) The mTOR inhibitor rapamycin mitigates perforant pathway neurodegeneration and synapse loss in a mouse model of early-stage Alzheimer-type tauopathy. PLoS One 10(11):e0142340. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0142340
Sloane PD, Zimmerman S, Suchindran C, Reed P, Wang L, Boustani M, Sudha S (2002) The public health impact of Alzheimer’s disease, 2000–2050: potential implication of treatment advances. Annu Rev Public Health 23:213–231. doi:10.1146/annurev.publhealth.23.100901.140525
Spilman P, Podlutskaya N, Hart MJ, Debnath J, Gorostiza O, Bredesen D, Richardson A, Strong R, Galvan V (2010) Inhibition of mTOR by rapamycin abolishes cognitive deficits and reduces amyloid-beta levels in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. PLoS One 5(4):e9979. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0009979
St-Pierre J, Drori S, Uldry M, Silvaggi JM, Rhee J, Jager S, Handschin C, Zheng K, Lin J, Yang W, Simon DK, Bachoo R, Spiegelman BM (2006) Suppression of reactive oxygen species and neurodegeneration by the PGC-1 transcriptional coactivators. Cell 127(2):397–408. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2006.09.024
Trushina E, McMurray CT (2007) Oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction in neurodegenerative diseases. Neuroscience 145(4):1233–1248. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2006.10.056
Vallés SL, Borrás C, Gambini J, Furriol J, Ortega A, Sastre J, Pallardó FV, Viña J (2008) Oestradiol or genistein rescues neurons from amyloid beta-induced cell death by inhibiting activation of p38. Aging Cell 7(1):112–118. doi:10.1111/j.1474-9726.2007.00356.x
Villena JA (2015) New insights into PGC-1 coactivators: redefining their role in the regulation of mitochondrial function and beyond. Febs J 282(4):647–672. doi:10.1111/febs.13175
Viola KL, Klein WL (2015) Amyloid β oligomers in Alzheimer’s disease pathogenesis, treatment, and diagnosis. Acta Neuropathol 129(2):183–206. doi:10.1007/s00401-015-1386-3
Wang R, Li JJ, Diao S, Kwak YD, Liu L, Zhi L, Büeler H, Bhat NR, Williams RW, Park EA, Liao FF (2013) Metabolic stress modulates Alzheimer’s β-secretase gene transcription via SIRT1-PPARγ-PGC-1 in neurons. Cell Metab 17(5):685–694. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2013.03.016
Wareski P, Vaarmann A, Choubey V, Safiulina D, Liiv J, Kuum M, Kaasik A (2009) PGC-1{alpha} and PGC-1{beta} regulate mitochondrial density in neurons. J Biol Chem 284(32):21379–21385. doi:10.1074/jbc.M109.018911
Yuan Y, Wang Y, Hu FF, Jiang CY, Zhang YJ, Yang JL, Zhao SW, Gu JH, Liu XZ, Bian JC, Liu ZP (2016) Cadmium activates reactive oxygen species-dependent AKT/mTOR and mitochondrial apoptotic pathways in neuronal cells. Biomed Environ Sci 29(2):117–126. doi:10.3967/bes2016.013
Zahs KR, Ashe KH (2013) β-Amyloid oligomers in aging and Alzheimer’s disease. Front Aging Neurosci 5:28. doi:10.3389/fnagi.2013.00028
Zhang X, Shu L, Hosoi H, Murti GK, Houghton PJ (2002) Predominant nuclear localization of mammalian target of rapamycin in normal and malignant cells in culture. J Biol Chem 277(31):28127–28134. doi:10.1074/jbc.M202625200
Zheng X, Boyer L, Jin M, Kim Y, Fan W, Bardy C, Berggren T, Evans RM, Gage FH, Hunter T (2016) Alleviation of neuronal energy deficiency by mTOR inhibition as a treatment for mitochondria-related neurodegeneration. Elife 5:e13378. doi:10.7554/eLife13378
Acknowledgments
We would like to express our sincere thanks to Dr. Francesca-Fang Liao from University of Tennessee Health Science Center for kindly providing us pcDNA-PPARγ.WT, pcDNA-PPARγ.K268T/K293T, pcDNA-SIRT1.WT, and its mutant SIRT1.H355A. This study was supported by the Grants from the Academic Development Funds for the Professors of Fujian Medical University (Grant No. JS/14002) and the Doctoral Starting-up Foundation of Fujian Medical University (Grant No. 2009bs002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, YC., Gao, XX., Zhang, ZG. et al. PPAR Gamma Coactivator 1 Beta (PGC-1β) Reduces Mammalian Target of Rapamycin (mTOR) Expression via a SIRT1-Dependent Mechanism in Neurons. Cell Mol Neurobiol 37, 879–887 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-016-0425-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-016-0425-5