Abstract
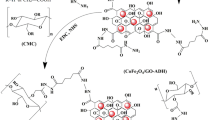
In this study, a magnetically enhanced drug delivery composite was synthesized by co-precipitating magnetite nanoparticle (MNP) with 2,3-dialdehyde cellulose-6-phosphate (DACP) and investigated for ampyrone drug loading and controlled delivery. The magnetic core containing Fe3O4 was synthesized through the intramolecular Cannizzaro reaction during the in situ preparation of MNPs in the presence of sodium hydroxide solution, producing hydroxyl acid cellulose phosphate (HACP). The prepared magnetite nanocomposite MNP/HACP was characterized using FT-IR, SEM–EDX, XRD, TEM, VSM and TGA. The release profiles of ampyrone loaded on MNP/HACP showed a continuous release rate of more than 95% after 50 h, compared to the lower release rate of DACP, where only 60% of the loaded ampyrone was released after 50 h. These results show that MNP/HACP nanocomposites present an enhanced loading-release system with the potential to act as a magnetically enhanced drug delivery system.














Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
18 December 2019
In the original publication of the article, one of the co-authors name was mistakenly missed out. It has been updated in this correction.
References
Aguilera G, Berry C, West R, Gonzalez-Monterrubio E, Angulo-Molina A, Arias-Carri´on O, Angel M´endez-Rojas M (2019) Carboxymethyl cellulose coated magnetic nanoparticle transport across a human lung microvascular endothelial cell model of the blood–brain barrier. Nanoscale Adv 1:671–685
Alam MS, Choi JH, Lee D (2012) Synthesis of novel Schiff base analogues of 4-amino-1, 5-dimethyl-2-phenylpyrazol-3-one and their evaluation for antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activity. Bioorg Med Chem 20(13):4103–4108
Allia P, Barrera G, Tiberto P, Nardi T, Leterrier Y, Sangermano M (2014) Fe3O4 nanoparticle and nanocomposites with potential application in biomedicine and in communication technologies: nanoparticle aggregation, interaction, and effective magnetic anisotropy. J Appl Phys 116(11):113903
Dias F, Duarte C (2013) Cellulose and its derivatives use in the pharmaceutical compounding practice. In: Van De Ven TGM (ed) Cellulose–medical pharmaceutical and electronic applications. In Tech Open, Croatia, pp 141–162
Edgar KJ (2004) Cellulose esters, organic. In: Korschwitz J (ed) Encyclopedia of polymer science and technology, 3rd edn. pp 131–133. Wiley, New York
Edgar KJ (2007) Cellulose esters in drug delivery. Cellulose 14:49–64
El-kott A, Syef AF, Alshehri MA, Al Dosage S, Keshk SMAS (2019) Suppression efficacy of lignosulfonate/mercerized cotton composite against cancer cell’s activities. Adv Compos Lett 28:1–9
Fernandes VJ Jr, Araujo AS, Fonseca VM, Fernandes NS, Silva DR (2002) Thermogarvimetric evaluation of polyester/sisal flame retarded composite. Thermochem Acta 392–393:71–77
Francesca U, Giuseppe R, Agnese M, Fabiana Q, Maria R (2006) Cyclodextrins in the production of large porous particles: development of dry powders for the sustained release of insulin to the lungs. Eur J Pharm Sci 28:423–432
Fricain JC, Granja PL, Barbosa MA, de Jeso B, Barthe N, Baquey C (2001) Cellulose phosphates as biomaterials. In vivo biocompatibility studies. Biomaterials 23:971–980
Frisch MJ, Trucks GW, Schlegel HB et al. (2009) Gaussian-09, Revision A.1, 483 Gaussian, Inc., Wallingford, CT
Godwin A, Bolina K, Clochard M, Dinand E, Rankin S, Simic S, Brocchini S (2001) New strategies for polymer development in pharmaceutical science- a short review. J Pharm Pharmacol 53:1175–1184
Gomez-Lopera SA, Plaza RC, Delgado AV (2001) Synthesis and characterization of spherical magnetite/biodegradable polymer composite particles. J Colloid Interface Sci 240(1):40–47
Heinze T, Liebert TF, Pfeiffer KS, Hussain MA (2003) Unconventional cellulose esters: synthesis, characterization and structure-property relations. Cellulose 10:283–296
Irfan A, Chaudhry AR et al (2017) Exploring the charge transfer nature and electro-optical properties of anthracene-based sensitizers @TiO2 cluster. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 80(Supplement C):239–246
Jiang W, Yang HC, Yang SY, Horng HE, Hung JC, Chen YC, Hong CY (2004) Preparation and properties of superparamagnetic nanoparticle with narrow size distribution and biocompatible. J Magn Magn Mater 283:210–215
Kayal S, Ramanujan RV (2010a) Doxorubicin loaded PVA coated iron oxide nanoparticle for targeted drug delivery. Mater Sci Eng C 30:484–490
Kayal S, Ramanujan RV (2010b) Doxorubicin loaded PVA coated iron oxide nanoparticle for targeted drug delivery. Mater Sci Eng C 30(3):484–490
Keshk SMAS, Salah M (2014) Bacterial cellulose and its phosphoric dichloride for efficient removal of metal ions. Amer J Polym Sci 4:10–16
Keshk SMA, Gouda M (2017) Natural biodegradable medical polymers: cellulose. In: Xiang Z (ed) Science and principles of biodegradable and bioresorbable medical polymers-materials and properties, pp 279–294. Elsevier, ISBN: 978-0-08-100372-5
Keshk SMAS, Bondock S, El-Zahhar A, Abu Haija M (2019a) Synthesis and characterization of novel Schiff’s bases derived from cellulose phosphate 2,3-dialdehyde. Cellulose 26:3703–3712
Keshk SMAS, Bondock S, Youssef AMS, El-Zahhar A (2019b) Novel synthesis of flame-retardant magnetic nanoparticle/hydroxyl acid cellulose-6-phosphate composite. Mater Res Express 6(8):085310
Keshk SMAS, El-Zahhar A, Al-Sehemi AG, Irfan A, Bondock S (2019c) Synthesis and physicochemical characterization of a magnetic nanoparticle/dialdehyde cellulose composite as a flame retardant. Mater Res Express 6(2):025312
Kim S, Kim JH, Jeon O, Kwon IC, Park K (2008) Engineered polymers for advanced drug delivery. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 71:420–430
Koksharov YA (2009) Magnetism of nanoparticle: effects of size, shape, and interactions. In: Gubin SP (ed) Magnetic nanoparticle. Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim, pp 197–254
Leone G, Torricelli P, Giardino R, Barbucci R (2008) New phosphorylated derivatives of carboxymethylcellulose with osteogenic activity. Polym Adv Technol 19:824–830
Liechty WB, Kryscio DR, Slaughter BV, Peppas NA (2010) Polymers for drug delivery systems. Annu Rev Chem Biomol Eng 1:149–173
Longzhang Z, Jingwei M, Nengqin J, Yu Z, Hebai S (2009) Chitosan-coated magnetic nanoparticle as carriers of 5-fluorouracil: preparation, characterization and cytotoxicity studies. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 68:1–6
Nardi T, Sangermano M, Leterrier Y, Allia P, Tiberto P, Månson JAE (2013) UV-cured transparent magnetic polymer nanocomposites. Polymer 54:4472–4479
Patitsa M, Karathanou K, Kanaki Z, Tzioga L, Pippa N, Demetzos C, Verganelakis D, Cournia Z, Klinakis A (2017) Magnetic nanoparticle coated with polyarabic acid demonstrate enhanced drug delivery and imaging properties for cancer theranostic applications. Sci Rep 7:775–782
Pham XN, Nguyen TP, Pham TN, Nga TT (2010) Synthesis and characterization of chitosan coated magnetite nanoparticle and their application in curcumin drug delivery. Adv Nat Sci Nanosci Nanotechnol 7:045010
Qu J-B, Shao H-H, Jing G-L, Huang F (2013) PEG-chitosan coated iron oxide nanoparticle with high saturated magnetization as carriers of 10-hydroxycamptothecin: preparation, characterization and cytotoxicity studies. Colloids Surf B 102:37–44
Radi S, Toubi Y, Hamdani I, Hakkou A, Souna F, Himri I, Bouakka M (2012) Synthesis, antibacterial and antifungal activities of some new bipyrazolic tripodal derivatives. Res J Chem Sci 2(4):40–44
Shokri J, Adibki K (2013) Application of cellulose and cellulose derivatives in pharmaceutical industries. In: Van De Ven TGM (ed) Cellulose–medical, pharmaceutical and electronic applications. In Tech Open, Croatia, pp 47–66
Urquiza E, Cardona F, Duarte C, Cole B, Wu B, Méndez-Rojas M, Cherr G (2017) Facilitation of trace metal uptake in cells by inulin coating of metallic nanoparticle. R Soc Open Sci 4:170480
Volkert B, Wolf B, Fischer S, Li N, Lou C (2009) Application of modified bead cellulose as a carrier of active ingredients. Macromol Symp 280:130–135
Yao Y, Miao S, Yu S, Ping Ma L, Sun H, Wang S (2012) Fabrication of Fe3O4/SiO2 core/shell nanoparticle attached to graphene oxide and its use as an adsorbent. J Colloid Interface Sci 379:20–26
Zhang WF, Zhang YH, Jiang Q, Zhao WJ, Yu AJ, Chang H, Lu XM, Xie FW, Ye BX, Zhang SS (2016) Tetraazacalix [2] arence [2] triazine coated Fe3O4/SiO2 magnetic nanoparticle for simultaneous dispersive solid phase extraction and determination of trace multitarget analytes. Anal Chem 88:10523–10532
Acknowledgments
The authors extend their appreciation to the Deanship of Scientific Research at King Khalid University for funding this work through research groups program under Grant Number R.G.P. 1/19/40. Thomas Heinze acknowledged financially supported by the DFG-funded Collaborative Research Centre PolyTarget (SFB 1278, Project A02).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Keshk, S.M.A.S., El-Zahhar, A.A., Alsulami, Q.A. et al. Synthesis, characterization and ampyrone drug release behavior of magnetite nanoparticle/2,3-dialdehyde cellulose-6-phosphate composite. Cellulose 27, 1603–1618 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-019-02887-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-019-02887-y