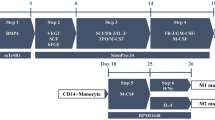
Abstract
Microcystin-leucine-arginine (MC-LR) was produced by toxic cyanobacteria, which has been shown to have potent hepatotoxicity. Our previous study has proved that MC-LR were able to promote intrahepatic biliary epithelial cell excessive proliferation. However, the underlying mechanism is not yet entirely clarified. Herein, mice were fed with different concentrations (1, 7.5, 15, or 30 μg/L) of MC-LR by drinking water for 6 months. As the concentration of MC-LR increased, a growing number of macrophages were evaluated in the portal area of the mouse liver. Next, we built a co-culture system to explore the interaction between macrophages (THP-1 cells) and human intrahepatic biliary epithelial cells (HiBECs) in the presence of MC-LR. Under the exposure of MC-LR, HiBECs secreted a large amount of inflammatory factors (IL-6, IL-8, IL-1β, COX-2, XCL-1) and chemokine (MCP-1), which produced a huge chemotactic effect on THP-1 cells and induced elevation of the surface M2-subtype biomarkers (IL-10, CD163, CCL22, and Arg-1). In turn, high content of IL-6 in the medium activated JAK2/STAT3, MEK/ERK, and PI3K/AKT pathways in HiBECs, inducing HiBEC abnormal proliferation and migration. Together, these results suggested that MC-LR-mediated interaction between HiBECs and macrophages induced the M2-type polarization of macrophages, and activated IL-6/JAK2/STAT3, MEK/ERK, and PI3K/AKT pathways in HiBECs, further enhanced cell proliferation, improved cell migration, and hindered cell apoptosis by activating p-STAT3.
Graphical abstract

MC-LR stimulates HiBECs to produce various inflammatory factors, recruiting a large number of macrophages and promoting the differentiation of macrophages into M2-type. In turn, the M2 macrophages could also produce amounts of IL-6 and activate STAT3 through JAK2/STAT3, MEK/ERK, and PI3K/AKT pathways in HiBECs, resulting in the promotion of cell proliferation, inhibition of apoptosis, and enhancement of migration.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- MC-LR:
-
Microcystin-leucine-arginine
- HiBECs:
-
Human intrahepatic biliary epithelial cells
- MCs:
-
Microcystins
- CCA:
-
Cholangiocarcinoma
- IL-6:
-
Interleukin-6
- MCP-1:
-
Myeloid cell leukemia-1
- BCL-2:
-
B cell lymphoma-2
- JAK:
-
Janus kinase
- STAT3:
-
Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3
- TFF3:
-
Trefoil factor family 3
- MAPK:
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase
- PI3K:
-
Phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase
- ERK:
-
Extracellular signal-regulated kinase
References
Aggarwal BB, Kunnumakkara AB, Harikumar KB, Gupta SR, Tharakan ST, Koca C, et al. Signal transducer and activator of transcription-3, inflammation, and cancer: how intimate is the relationship? Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2009;1171:59–76. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1749-6632.2009.04911.x.
Baeck C, Wehr A, Karlmark KR, Heymann F, Vucur M, Gassler N, et al. Pharmacological inhibition of the chemokine CCL2 (MCP-1) diminishes liver macrophage infiltration and steatohepatitis in chronic hepatic injury. Gut. 2012;61(3):416–26. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2011-300304.
Bojadzija Savic G, Edwards C, Briand E, Lawton L, Wiegand C, Bormans M. Daphnia magna exudates impact physiological and metabolic changes in Microcystis aeruginosa. Toxins (Basel). 2019;11(7). https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11070421.
Chen J, Xie P, Li L, Xu J. First identification of the hepatotoxic microcystins in the serum of a chronically exposed human population together with indication of hepatocellular damage. Toxicol Sci. 2009;108(1):81–9. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfp009.
Chen Y, Wang J, Chen X, Li D, Han X. Microcystin-leucine arginine mediates apoptosis and engulfment of Leydig cell by testicular macrophages resulting in reduced serum testosterone levels. Aquat Toxicol. 2018;199:116–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2018.03.018.
Chen Y, Wang J, Zhang Q, Xiang Z, Li D, Han X. Microcystin-leucine arginine exhibits immunomodulatory roles in testicular cells resulting in orchitis. Environ Pollut. 2017;229:964–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.07.081.
Chen Y, Zhou Y, Wang J, Wang L, Xiang Z, Li D, et al. Microcystin-leucine arginine causes cytotoxic effects in Sertoli cells resulting in reproductive dysfunction in male mice. Sci Rep. 2016;6:39238. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep39238.
Corbel S, Mougin C, Nelieu S, Delarue G, Bouaicha N. Evaluation of the transfer and the accumulation of microcystins in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum cultivar MicroTom) tissues using a cyanobacterial extract containing microcystins and the radiolabeled microcystin-LR ((14)C-MC-LR). Sci Total Environ. 2016;541:1052–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.10.004.
Dahm-Kahler P, Ghahremani M, Lind AK, Sundfeldt K, Brannstrom M. Monocyte chemotactic protein-1 (MCP-1), its receptor, and macrophages in the perifollicular stroma during the human ovulatory process. Fertil Steril. 2009;91(1):231–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fertnstert.2007.07.1330.
Demetris AJ, Fontes P, Lunz JG, Specht S, Murase N, Marcos A. Wound healing in the biliary tree of liver allografts. Cell Transplant. 2006;15:S57–65.
Dong N, Shi X, Wang S, Gao Y, Kuang Z, Xie Q, et al. M2 macrophages mediate sorafenib resistance by secreting HGF in a feed-forward manner in hepatocellular carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 2019;121(1):22–33. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41416-019-0482-x.
Falconer IR, Humpage AR. Health risk assessment of cyanobacterial (blue-green algal) toxins in drinking water. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2005;2(1):43–50. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph2005010043.
He L, Huang Y, Guo Q, Zeng H, Zheng C, Wang J, et al. Chronic microcystin-LR exposure induces hepatocarcinogenesis via increased gankyrin in vitro and in vivo. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;49(4):1420–30. https://doi.org/10.1159/000493446.
Heinrich PC, Behrmann I, Haan S, Hermanns HM, Muller-Newen G, Schaper F. Principles of interleukin (IL)-6-type cytokine signalling and its regulation. Biochem J. 2003;374(Pt 1):1–20. https://doi.org/10.1042/BJ20030407.
Heymann F, Trautwein C, Tacke F. Monocytes and macrophages as cellular targets in liver fibrosis. Inflamm Allergy Drug Targets. 2009;8(4):307–18. https://doi.org/10.2174/187152809789352230.
Hin Tang JJ, Hao Thng DK, Lim JJ, Toh TB. JAK/STAT signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepat Oncol. 2020;7(1):HEP18. https://doi.org/10.2217/hep-2020-0001.
Hogaboam CM, Bone-Larson CL, Steinhauser ML, Matsukawa A, Gosling J, Boring L, et al. Exaggerated hepatic injury due to acetaminophen challenge in mice lacking C-C chemokine receptor 2. Am J Pathol. 2000;156(4):1245–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0002-9440(10)64995-4.
Holland A, Kinnear S. Interpreting the possible ecological role(s) of cyanotoxins: compounds for competitive advantage and/or physiological aide? Mar Drugs. 2013;11(7):2239–58. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11072239.
Honkanen RE, Zwiller J, Moore RE, Daily SL, Khatra BS, Dukelow M, et al. Characterization of microcystin-LR, a potent inhibitor of type 1 and type 2A protein phosphatases. J Biol Chem. 1990;265(32):19401–4.
Isse K, Harada K, Nakanuma Y. IL-8 expression by biliary epithelial cells is associated with neutrophilic infiltration and reactive bile ductules. Liver Int. 2007;27(5):672–80. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1478-3231.2007.01465.x.
Jiang GX, Zhong XY, Cui YF, Liu W, Tai S, Wang ZD, et al. IL-6/STAT3/TFF3 signaling regulates human biliary epithelial cell migration and wound healing in vitro. Mol Biol Rep. 2010;37(8):3813–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-010-0036-z.
Jiang Q, Li Q, Chen H, Shen A, Cai Q, Lin J, et al. Scutellaria barbata D. Don inhibits growth and induces apoptosis by suppressing IL-6-inducible STAT3 pathway activation in human colorectal cancer cells. Exp Ther Med. 2015;10(4):1602–8. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2015.2692.
Kakinuma Y, Kimura T, Watanabe Y. Possible involvement of liver resident macrophages (Kupffer cells) in the pathogenesis of both intrahepatic and extrahepatic inflammation. Can J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017;2017:2896809–10. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/2896809.
Kitagawa M, Liao PJ, Lee KH, Wong J, Shang SC, Minami N, et al. Dual blockade of the lipid kinase PIP4Ks and mitotic pathways leads to cancer-selective lethality. Nat Commun. 2017;8(1):2200. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-017-02287-5.
Kiu H, Nicholson SE. Biology and significance of the JAK/STAT signalling pathways. Growth Factors. 2012;30(2):88–106. https://doi.org/10.3109/08977194.2012.660936.
Kong L, Zhou Y, Bu H, Lv T, Shi Y, Yang J. Deletion of interleukin-6 in monocytes/macrophages suppresses the initiation of hepatocellular carcinoma in mice. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2016;35(1):131. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-016-0412-1.
Landskron G, De la Fuente M, Thuwajit P, Thuwajit C, Hermoso MA. Chronic inflammation and cytokines in the tumor microenvironment. J Immunol Res. 2014;2014:149185–19. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/149185.
Lee JJ, Kim HJ, Yang CS, Kyeong HH, Choi JM, Hwang DE, et al. A high-affinity protein binder that blocks the IL-6/STAT3 signaling pathway effectively suppresses non-small cell lung cancer. Mol Ther. 2014;22(7):1254–65. https://doi.org/10.1038/mt.2014.59.
Li X, Zhao Q, Zhou W, Xu L, Wang Y. Effects of chronic exposure to microcystin-LR on hepatocyte mitochondrial DNA replication in mice. Environ Sci Technol. 2015;49(7):4665–72. https://doi.org/10.1021/es5059132.
Li XY, Li J, Meng FX, Yao L. Hepatotoxicity and immunotoxicity of MC-LR on silver carp. Ecotox Environ Safe. 2019;169:28–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.10.110.
Li Y, Guo G, Song J, Cai Z, Yang J, Chen Z, et al. B7-H3 promotes the migration and invasion of human bladder cancer cells via the PI3K/Akt/STAT3 signaling pathway. J Cancer. 2017;8(5):816–24. https://doi.org/10.7150/jca.17759.
Liu J, Sun Y. The role of PP2A-associated proteins and signal pathways in microcystin-LR toxicity. Toxicol Lett. 2015;236(1):1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxlet.2015.04.010.
Liu X, Cao X, Liu C, Cao Y, Zhao Q, Tan X, et al. MTERFD1 promotes cell growth and irradiation resistance in colorectal cancer by upregulating interleukin-6 and interleukin-11. Int J Biol Sci. 2019;15(12):2750–62. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijbs.36916.
Ma J, Li Y, Duan H, Sivakumar R, Li X. Chronic exposure of nanomolar MC-LR caused oxidative stress and inflammatory responses in HepG2 cells. Chemosphere. 2018;192:305–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.10.158.
Meng X, Peng H, Ding Y, Zhang L, Yang J, Han X. A transcriptomic regulatory network among miRNAs, piRNAs, circRNAs, lncRNAs and mRNAs regulates microcystin-leucine arginine (MC-LR)-induced male reproductive toxicity. Sci Total Environ. 2019;667:563–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.02.393.
Mowe MAD, Mitrovic SM, Lim RP, Furey A, Yeo DCJ. Tropical cyanobacterial blooms: a review of prevalence, problem taxa, toxins and influencing environmental factors. J Limnol. 2015;74(2):205–24. https://doi.org/10.4081/jlimnol.2014.1005.
O’Shea JJ, Pesu M, Borie DC, Changelian PS. A new modality for immunosuppression: targeting the JAK/STAT pathway. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2004;3(7):555–64. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd1441.
Pan C, Chen Y, Xu T, Wang J, Li D, Han X. Chronic exposure to microcystin-leucine-arginine promoted proliferation of prostate epithelial cells resulting in benign prostatic hyperplasia. Environ Pollut. 2018;242(Pt B):1535–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.08.024.
Papadimitriou T, Kagalou I, Stalikas C, Pilidis G, Leonardos ID. Assessment of microcystin distribution and biomagnification in tissues of aquatic food web compartments from a shallow lake and evaluation of potential risks to public health. Ecotoxicology. 2012;21(4):1155–66. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-012-0870-y.
Pompura SL, Dominguez-Villar M. The PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in regulatory T-cell development, stability, and function. J Leukoc Biol. 2018;103:1065–76. https://doi.org/10.1002/JLB.2MIR0817-349R.
Rizvi S, Gores GJ. Molecular pathogenesis of cholangiocarcinoma. Dig Dis. 2014;32(5):564–9. https://doi.org/10.1159/000360502.
Rong GH, Yang GX, Ando Y, Zhang W, He XS, Leung PS, et al. Human intrahepatic biliary epithelial cells engulf blebs from their apoptotic peers. Clin Exp Immunol. 2013;172(1):95–103. https://doi.org/10.1111/cei.12046.
Sakaguchi M, Oka M, Iwasaki T, Fukami Y, Nishigori C. Role and regulation of STAT3 phosphorylation at Ser727 in melanocytes and melanoma cells. J Invest Dermatol. 2012;132(7):1877–85. https://doi.org/10.1038/jid.2012.45.
Schaper F, Rose-John S. Interleukin-6: biology, signaling and strategies of blockade. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2015;26(5):475–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cytogfr.2015.07.004.
Sgrignani J, Garofalo M, Matkovic M, Merulla J, Catapano CV, Cavalli A. Structural biology of STAT3 and its implications for anticancer therapies development. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(6). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19061591.
Strazzabosco M, Fabris L. Development of the bile ducts: essentials for the clinical hepatologist. J Hepatol. 2012;56(5):1159–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2011.09.022.
Suzuki T, Yoshinaga N, Tanabe S. Interleukin-6 (IL-6) regulates claudin-2 expression and tight junction permeability in intestinal epithelium. J Biol Chem. 2011;286(36):31263–71. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M111.238147.
Wang CX, Xiong HF, Wang S, Wang J, Nie X, Guo Q, et al. Overexpression of TEM8 promotes ovarian cancer progression via Rac1/Cdc42/JNK and MEK/ERK/STAT3 signaling pathways. Am J Transl Res. 2020;12(7):3557–76.
Wang J, Zhang C, Zhu J, Ding J, Chen Y, Han X. Blood-brain barrier disruption and inflammation reaction in mice after chronic exposure to microcystin-LR. Sci Total Environ. 2019;689:662–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.06.387.
Wynn TA, Chawla A, Pollard JW. Macrophage biology in development, homeostasis and disease. Nature. 2013;496(7446):445–55. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature12034.
Yan M, Shen G, Zhou Y, Meng X, Han X. The role of ERK-RSK signaling in the proliferation of intrahepatic biliary epithelial cells exposed to microcystin-leucine arginine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020;521(2):492–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.10.143.
Yin Z, Ma TT, Lin Y, Lu X, Zhang CZ, Chen S, et al. IL-6/STAT3 pathway intermediates M1/M2 macrophage polarization during the development of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cell Biochem. 2018;119(11):9419–32. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.27259.
Yokomuro S, Tsuji H, Lunz JG, Sakamoto T, Ezure T, Murase N, et al. Growth control of human biliary epithelial cells by interleukin 6, hepatocyte growth factor, transforming growth factor beta 1, and activin A: comparison of a cholangiocarcinoma cell line with primary cultures of non-neoplastic biliary epithelial cells. Hepatology. 2000;32(1):26–35. https://doi.org/10.1053/jhep.2000.8535.
Zegeye MM, Lindkvist M, Falker K, Kumawat AK, Paramel G, Grenegard M, et al. Activation of the JAK/STAT3 and PI3K/AKT pathways are crucial for IL-6 trans-signaling-mediated pro-inflammatory response in human vascular endothelial cells. Cell Commun Signal. 2018;16(1):55. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12964-018-0268-4.
Zheng C, Zeng H, Lin H, Wang J, Feng X, Qiu Z, et al. Serum microcystin levels positively linked with risk of hepatocellular carcinoma: a case-control study in southwest China. Hepatology. 2017;66(5):1519–28. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.29310.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31870492, 31901182, 31670519, and 31971517), the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province of China (BK20190316), and Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (0214-14380438 and 0214-14380471).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
MC-LR causes an inflammatory response in biliary epithelial cells resulting in recruitment of macrophages and its M2-subtype polarization.
MC-LR-mediated cell interaction between macrophage and biliary epithelial cells promotes the proliferation and migration of biliary epithelial cells.
MC-LR promotes HiBEC proliferation by inducing phosphorylation level of STAT3 by activating IL-6/JAK2, MEK/ERK, and PI3K/AKT pathways.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(DOCX 1240 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, M., Gu, S., Pan, C. et al. MC-LR-induced interaction between M2 macrophage and biliary epithelial cell promotes biliary epithelial cell proliferation and migration through regulating STAT3. Cell Biol Toxicol 37, 935–949 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10565-020-09575-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10565-020-09575-9