Abstract
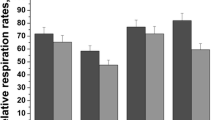
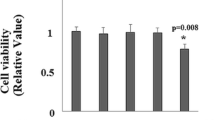
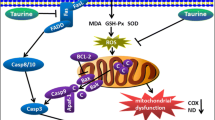
Acetaldehyde (Ac), the main metabolite of ethanol oxidation, is a very reactive compound involved in alcohol-induced liver damage. In the present work, we studied the effect of Ac in mitochondria functionality. Mitochondria from Wistar rats were isolated and treated with Ac. Ac decreased respiratory control by 50% which was associated with a decrease in adenosine triphosphate content (28.5%). These results suggested that Ac could be inducing changes in cell redox status. We determined protein oxidation, superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity, and glutathione ratio, indicating that Ac induced an enhanced oxidation of proteins and a decrease in SOD activity (90%) and glutathione/oxidized GSH ratio (36%). The data suggested that Ac-induced oxidative stress mediated by mitochondria dysfunction can lead to cell sensitization and to a second oxidative challenge. We pretreated hepatocytes with Ac followed by treatment with antimycin A, and this experiment revealed a noticeable decrease in cell viability, determined by neutral red assay, in comparison with cells treated with Ac alone. Our data demonstrate that Ac impairs mitochondria functionality generating oxidative stress that sensitizes cells to a second damaging signal contributing to the development of alcoholic liver disease.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albano E. Alcohol, oxidative stress and free radical damage. Proc Nutr Soc. 2006;65:278–90. doi:10.1079/PNS2006496.
Anni H, Israel Y. Characterization of adducts of ethanol metabolites with cytochrome c. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1999;23:26–37.
Borenfreund E, Puerner JA. Cytotoxicity of metals, metal–metal and metal–chelator combinations assayed in vitro. Toxicology. 1986;39:121–34. doi:10.1016/0300-483X(86)90130-7.
Brooks PJ, Theruvathu JA. DNA adducts from acetaldehyde: implications for alcohol-related carcinogenesis. Alcohol. 2005;35:187–93. doi:10.1016/j.alcohol.2005.03.009.
Cahill A, Cunningham CC. Effects of chronic ethanol feeding on the protein composition of mitochondrial ribosomes. Electrophoresis. 2000;21:3420–6. doi:10.1002/1522-2683(20001001)21:16<3420::AID-ELPS3420>3.0.CO;2-Q.
Colell A, Garcia-Ruiz C, Mari M, Fernandez-Checa JC. Mitochondrial permeability transition induced by reactive oxygen species is independent of cholesterol-regulated membrane fluidity. FEBS Lett. 2004;560:63–8. doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(04)00071-7.
Cunningham CC, Coleman WB, Spach PI. The effects of chronic ethanol consumption on hepatic mitochondrial energy metabolism. Alcohol Alcohol. 1990;25:127–36.
Fariss MW, Reed DJ. High-performance liquid chromatography of thiols and disulfides: dinitrophenol derivatives. Methods Enzymol. 1987;143:101–9. doi:10.1016/0076-6879(87)43018-8.
Flores-Herrera O, Uribe A, Pardo JP, Rendon JL, Martinez F. A novel ATP-diphosphohydrolase from human term placental mitochondria. Placenta. 1999;20:475–84. doi:10.1053/plac.1999.0401.
Garcia-Ruiz C, Morales A, Ballesta A, Rodes J, Kaplowitz N, Fernandez-Checa JC. Effect of chronic ethanol feeding on glutathione and functional integrity of mitochondria in periportal and perivenous rat hepatocytes. J Clin Invest. 1994;94:193–201. doi:10.1172/JCI117306.
Gomez-Quiroz L, Bucio L, Souza V, Escobar C, Farfan B, Hernandez E, Konigsberg M, Vargas-Vorackova F, Kershenobich D, Gutierrez-Ruiz MC. Interleukin 8 response and oxidative stress in HepG2 cells treated with ethanol, acetaldehyde or lipopolysaccharide. Hepatol Res. 2003;26:134–41. doi:10.1016/S1386-6346(03)00010-X.
Gomez-Quiroz LE, Paris R, Lluis JM, Bucio L, Souza V, Hernandez E, Gutierrez M, Santiago M, Garcia-Ruiz C, Fernandez-Checa JC, Kershenobich D, Gutierrez-Ruiz MC. Differential modulation of interleukin 8 by interleukin 4 and interleukin 10 in HepG2 cells treated with acetaldehyde. Liver Int. 2005;25:122–30. doi:10.1111/j.1478-3231.2005.01005.x.
Gomez-Quiroz LE, Factor VM, Kaposi-Novak P, Coulouarn C, Conner EA, Thorgeirsson SS. Hepatocyte-specific c-Met deletion disrupts redox homeostasis and sensitizes to Fas-mediated apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 2008;283:14581–9.
Gutierrez-Ruiz MC, Gomez Quiroz LE, Hernandez E, Bucio L, Souza V, Llorente L, Kershenobich D. Cytokine response and oxidative stress produced by ethanol, acetaldehyde and endotoxin treatment in HepG2 cells. Isr Med Assoc J. 2001;3:131–6.
Hasumura Y, Teschke R, Lieber CS. Characteristics of acetaldehyde oxidation in rat liver mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 1976;251:4908–13.
Hoek JB, Cahill A, Pastorino JG. Alcohol and mitochondria: a dysfunctional relationship. Gastroenterology. 2002;122:2049–63. doi:10.1053/gast.2002.33613.
Johnson RM. Swelling studies on liver mitochondria from essential fatty acid deficient rats. Exp Cell Res. 1963;32:118–29. doi:10.1016/0014-4827(63)90073-9.
Jung TW, Lee JY, Shim WS, Kang ES, Kim JS, Ahn CW, Lee HC, Cha BS. Adiponectin protects human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells against acetaldehyde-induced cytotoxicity. Biochem Pharmacol. 2006;72:616–23. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2006.05.013.
Koch OR, Pani G, Borrello S, Colavitti R, Cravero A, Farre S, Galeotti T. Oxidative stress and antioxidant defenses in ethanol-induced cell injury. Mol Aspects Med. 2004;25:191–8. doi:10.1016/j.mam.2004.02.019.
Konigsberg M, López-Diazguerrero N, Bucio L, Gutierrez-Ruiz M. Uncoupling effect of mercuric chloride on mitochondria isolated from an hepatic cell line. J Appl Toxicol. 2001;21:323–9. doi:10.1002/jat.763.
Kono H, Rusyn I, Yin M, Gabele E, Yamashina S, Dikalova A, Kadiiska MB, Connor HD, Mason RP, Segal BH, Bradford BU, Holland SM, Thurman RG. NADPH oxidase-derived free radicals are key oxidants in alcohol-induced liver disease. J Clin Invest. 2000;106:867–72. doi:10.1172/JCI9020.
Kroemer G, Dallaporta B, Resche-Rigon M. The mitochondrial death/life regulator in apoptosis and necrosis. Annu Rev Physiol. 1998;60:619–42. doi:10.1146/annurev.physiol.60.1.619.
Lanzetta PA, Alvarez LJ, Reinach PS, Candia OA. An improved assay for nanomole amounts of inorganic phosphate. Anal Biochem. 1979;100:95–7. doi:10.1016/0003-2697(79)90115-5.
Lyamzaev KG, Nepryakhina OK, Saprunova VB, Bakeeva LE, Pletjushkina OY, Chernyak BV, Skulachev VP. Novel mechanism of elimination of malfunctioning mitochondria (mitoptosis): formation of mitoptotic bodies and extrusion of mitochondrial material from the cell. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008;1777:817–25. doi:10.1016/j.bbabio.2008.03.027.
Lluis JM, Colell A, Garcia-Ruiz C, Kaplowitz N, Fernandez-Checa JC. Acetaldehyde impairs mitochondrial glutathione transport in HepG2 cells through endoplasmic reticulum stress. Gastroenterology. 2003;124:708–24. doi:10.1053/gast.2003.50089.
Mosmann T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods. 1983;65:55–63. doi:10.1016/0022-1759(83)90303-4.
Ni R, Leo MA, Zhao J, Lieber CS. Toxicity of beta-carotene and its exacerbation by acetaldehyde in HepG2 cells. Alcohol Alcohol. 2001;36:281–5. doi:10.1093/alcalc/36.4.281.
Olivares IP, Bucio L, Souza V, Carabez A, Gutierrez-Ruiz MC. Comparative study of the damage produced by acute ethanol and acetaldehyde treatment in a human fetal hepatic cell line. Toxicology. 1997;120:133–44. doi:10.1016/S0300-483X(97)03650-0.
Patel VB, Worrall S, Emery PW, Preedy VR. Protein adduct species in muscle and liver of rats following acute ethanol administration. Alcohol Alcohol. 2005;40:485–93. doi:10.1093/alcalc/agh196.
Roman J, Colell A, Blasco C, Caballeria J, Pares A, Rodes J, Fernandez-Checa JC. Differential role of ethanol and acetaldehyde in the induction of oxidative stress in HEP G2 cells: effect on transcription factors AP-1 and NF-kappaB. Hepatology. 1999;30:1473–80. doi:10.1002/hep.510300623.
Santiago-Lomeli M, Gomez-Quiroz LE, Ortiz-Ortega VM, Kershenobich D, Gutierrez-Ruiz MC. Differential effect of interleukin-10 on hepatocyte apoptosis. Life Sci. 2005;76:2569–79. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2004.10.048.
Signorini-Allibe N, Gonthier B, Lamarche F, Eysseric H, Barret L. Chronic consumption of ethanol leads to substantial cell damage in cultured rat astrocytes in conditions promoting acetaldehyde accumulation. Alcohol Alcohol. 2005;40:163–71. doi:10.1093/alcalc/agh097.
Tuma DJ. Role of malondialdehyde–acetaldehyde adducts in liver injury. Free Radic Biol Med. 2002;32:303–8. doi:10.1016/S0891-5849(01)00742-0.
Wenzel P, Muller J, Zurmeyer S, Schuhmacher S, Schulz E, Oelze M, Pautz A, Kawamoto T, Wojnowski L, Kleinert H, Munzel T, Daiber A. ALDH-2 deficiency increases cardiovascular oxidative stress—evidence for indirect antioxidative properties. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008;367:137–43. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2007.12.089.
Winterbourn CC, Hawkins RE, Brian M, Carrell RW. The estimation of red cell superoxide dismutase activity. J Lab Clin Med. 1975;85:337–41.
Acknowledgments
This work was partially funded by grants from the Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnología (CONACYT: 45921 and 61544), Secretaría de Educación Pública (PIFI2006-35-129-346/CA 142006-35-40), and the Universidad Autónoma Metropolitana-Iztapalapa.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Farfán Labonne, B.E., Gutiérrez, M., Gómez-Quiroz, L.E. et al. Acetaldehyde-induced mitochondrial dysfunction sensitizes hepatocytes to oxidative damage. Cell Biol Toxicol 25, 599–609 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10565-008-9115-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10565-008-9115-5