Abstract
Recent studies of organizational behavior have witnessed a growing interest in unethical leadership, leading to the development of abusive supervision research. Given the increasing interest in the causes of abusive supervision, this study proposes an organizing framework for its antecedents and tests it using meta analysis. Based on an analysis of effect sizes drawn from 74 studies, comprising 30,063 participants, the relationship between abusive supervision and different antecedent categories are examined. The results generally support expected relationships across the four categories of abusive antecedents, including: supervisor related antecedents, organization related antecedents, subordinate related antecedents, and demographic characteristics of both supervisors and subordinates. In addition, possible moderators that can also influence the relationships between abusive supervision and its antecedents are also examined. The significance and implications of different level factors in explaining abusive supervision are discussed.


Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Schyns and Schilling (2013) conducted a meta-analysis on destructive leadership, which contains abusive supervision as one type of destructive leadership.
A summary of studies and sample characteristics can be provided by the corresponding author upon request.
One coder is the author of this paper. The other coder is an expert in organizational behavior researcher who has sufficient knowledge of abusive supervision.
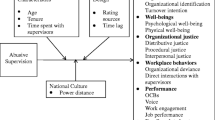
Five demographic variables in Fig. 2 are excluded because they are normally considered as control variables in the extant literature.
References
Aquino, K., & Thau, S. (2009). Workplace victimization: Aggression from the target’s perspective. Annual Review of Psychology, 60(1), 717–741.
Bamberger, P. A., & Bacharach, S. B. (2006). Abusive supervision and subordinate problem drinking: Taking resistance, stress and subordinate personality into account. Human Relations, 59(6), 723–752.
Bandura, A. (1973). Aggression: A social learning analysis. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall PTR.
Barling, J., Dupre, K. E., & Kelloway, E. K. (2009). Predicting workplace aggression and violence. Annual Review of Psychology, 60, 671–692.
Borenstein, M., Hedges, L. V., Higgins, J. P. T., & Rothstein, H. R. (2011). Introduction to meta-analysis. Chichester, UK: Wiley.
Bowling, N. A., & Beehr, T. A. (2006). Workplace harassment from the victim’s perspective: A theoretical model and meta-analysis. Journal of Applied Psychology, 91(5), 998–1012.
Colbert, A. E., Judge, T. A., Choi, D., & Wang, G. (2012). Assessing the trait theory of leadership using self and observer ratings of personality: The mediating role of contributions to group success. The Leadership Quarterly, 23(4), 670–685.
Colquitt, J. A., Conlon, D. E., Wesson, M. J., Porter, C. O. L. H., & Ng, K. Y. (2001). Justice at the millennium: A meta-analytic review of 25 years of organizational justice research. Journal of Applied Psychology, 86(3), 425.
Colquitt, J. A., Scott, B. A., Rodell, J. B., Long, D. M., Zapata, C. P., Conlon, D. E., & Wesson, M. J. (2013). Justice at the millennium, a decade later: A meta-analytic test of social exchange and affect-based perspectives. Journal of Applied Psychology, 98(2), 199–236.
Conger, J. A. (1998). Qualitative research as the cornerstone methodology for understanding leadership. The Leadership Quarterly, 9(1), 107–121.
Conway, N., & Coyle-Shapiro, J. A. M. (2012). The reciprocal relationship between psychological contract fulfilment and employee performance and the moderating role of perceived organizational support and tenure. Journal of Occupational and Organizational Psychology, 85(2), 277–299.
Dekker, I., & Barling, J. (1998). Personal and organizational predictors of workplace sexual harassment of women by men. Journal of Occupational Health Psychology, 3(1), 7–18.
DeRue, D. S., Nahrgang, J. D., Wellman, N., & Humphrey, S. E. (2011). Trait and behavioral theories of leadership: An integration and meta-analytic test of their relative validity. Personnel Psychology, 64(1), 7–52.
Felson, R. B. (1992). Kick’em when they’re down. The Sociological Quarterly, 33(1), 1–16.
Ferris, G. R., Davidson, S. L., & Perrewe, P. L. (2010). Political skill at work: Impact on work effectiveness. Boston: Nicholas Brealey.
Gerstner, C. R., & Day, D. V. (1997). Meta-analytic review of leader–member exchange theory: Correlates and construct issues. Journal of Applied Psychology, 82(6), 827–844.
Grandy, G., & Starratt, A. (2010). Making sense of abusive leadership the experiences of young workers. Charlotte, NC: Information Age-IAP.
Gross, J. J., Carstensen, L. L., Pasupathi, M., Tsai, J., Skorpen, C. G., & Hsu, A. Y. C. (1997). Emotion and aging: Experience, expression, and control. Psychology and Aging, 12(4), 590–599.
Harrell-Cook, G., Ferris, G. R., & Dulebohn, J. H. (1999). Political behaviors as moderators of the perceptions of organizational politics–work outcomes relationships. Journal of Organizational Behavior, 20(7), 1093–1105.
Harris, K. J., Kacmar, K. M., & Boonthanum, R. (2005) The interrelationship between abusive supervision, leader–member exchange, and various outcomes. Paper presented at Annual Meeting of the Society for Industrial–Organizational Psychology, Los Angeles, CA.
Harris, K. J., Kacmar, K. M., & Zivnuska, S. (2007). An investigation of abusive supervision as a predictor of performance and the meaning of work as a moderator of the relationship. The Leadership Quarterly, 18(3), 252–263.
Harvey, P., Stoner, J., Hochwarter, W., & Kacmar, C. (2007). Coping with abusive supervision: The neutralizing effects of ingratiation and positive affect on negative employee outcomes. The Leadership Quarterly, 18(3), 264–280.
Hogan, R., & Kaiser, R. B. (2005). What we know about leadership. Review of General Psychology, 9(2), 169–180.
Hunter, J. E., & Schmidt, F. L. (2004). Methods of meta-analysis: Correcting error and bias in research findings. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Johnson, H. A. M., & Spector, P. E. (2007). Service with a smile: Do emotional intelligence, gender, and autonomy moderate the emotional labor process? Journal of Occupational Health Psychology, 12(4), 319–333.
Landis, R. S. (2013). Successfully combining meta-analysis and structural equation modeling: Recommendations and strategies. Journal of Business and Psychology, 28(3), 251–261.
Lowe, Kevin B., Kroeck, K. Galen, & Sivasubramaniam, Nagaraj. (1996). Effectiveness correlates of transformational and transactional leadership: A meta-analytic review of the MLQ literature. The Leadership Quarterly, 7(3), 385–425.
Martinko, M. J., Harvey, P., Brees, J. R., & Mackey, J. (2013). A review of abusive supervision research. Journal of Organizational Behavior, 34(S1), S120–S137.
Ng, S. B. C., & Chen, G. Z. X. (2012). Abusive supervision, silence climate and silence behaviors: A multi-level examination of the mediating processes in China. Paper presented at the Iternational Association for Chinese Management Research (IACMR) conference, Hongkong.
Ng, S. B. C., Chen, Z. X., & Aryee, S. (2012). Abusive supervision in Chinese work settings. Cheltenham, UK: Edward Elgar.
Nickerson, R. S. (1998). Confirmation bias: A ubiquitous phenomenon in many guises. Review of General Psychology, 2(2), 175.
Olafsson, R. F., & Johannsdottir, H. L. (2004). Coping with bullying in the workplace: The effect of gender, age and type of bullying. British Journal of Guidance and Counselling, 32(3), 319–333.
Podsakoff, P. M., MacKenzie, S. B., Jeong-Yeon, L., & Podsakoff, N. P. (2003). Common method biases in behavioral research: A critical review of the literature and recommended remedies. Journal of Applied Psychology, 88(5), 879.
Richardson, H. A., Simmering, M. J., & Sturman, M. C. (2009). A tale of three perspectives examining post hoc statistical techniques for detection and correction of common method variance. Organizational Research Methods, 12(4), 762–800.
Rothstein, H. R., & Hopewell, S. (2009). Grey literature. In H. Cooper, L. V. Hedges, & J. C. Valentine (Eds.), The handbook of research synthesis and meta-analysis (pp. 103–125). New York: Russell Sage Foundation.
Schat, A. C., Frone, M. R., & Kelloway, E. K. (2006). Prevalence of workplace aggression in the US workforce: Findings from a national study. In E. K. Kelloway, J. Barling, & J. J. Hurrell Jr. (Eds.), Handbook of workplace violence (pp. 47–90). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Schyns, B., & Schilling, J. (2013). How bad are the effects of bad leaders? A meta-analysis of destructive leadership and its outcomes. The Leadership Quarterly, 24(1), 138–158.
Smith, P. K., Shu, S., & Madsen, K. (2001). Characteristics of victims of school bullying: developmental changes in coping strategies and skills. In J. Juvonen & S. Graham (Eds.), Peer harassment at school: The plight of the vulnerable and victimised (pp. 332–352). New York: Guildford.
Tepper, B. J. (2000). Consequences of abusive supervision. Academy of Management Journal, 43(2), 178–190.
Tepper, B. J. (2007). Abusive supervision in work organizations: Review, synthesis, and research agenda. Journal of Management, 33(3), 261–289.
Tepper, B. J., Duffy, M. K., & Shaw, J. D. (2001). Personality moderators of the relationship between abusive supervision and subordinates’ resistance. Journal of Applied Psychology, 86(5), 974–983.
Tepper, B. J., Moss, S. E., Lockhart, D. E., & Carr, J. C. (2007). Abusive supervision, upward maintenance communication, and subordinates’ psychological distress. Academy of Management Journal, 50(5), 1169–1180.
Watson, D., Pennebaker, J. W., & Folger, R. (1987). Beyond negative affectivity: Measuring stress and satisfaction in the workplace. Journal of Organizational Behavior Management, 8(2), 141–158.
Williams, L. J., & Anderson, S. E. (1994). An alternative approach to method effects by using latent-variable models: Applications in organizational-behavior research. Journal of Applied Psychology, 79(3), 323–331.
Wong, C.-S., & Law, K. S. (2002). The effects of leader and follower emotional intelligence on performance and attitude: An exploratory study. The Leadership Quarterly, 13(3), 243–274.
Wu, L. Z., Kwan, H. K., Liu, J., & Resick, C. J. (2012). Work-to-family spillover effects of abusive supervision. Journal of Managerial Psychology, 27(7), 714–731.
Yukl, G. A. (2006). Leadership in organizations. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson–Prentice Hall.
References: studies included in the meta-analysis.
Alexander, K. (2012). Abusive supervision as a predictor of deviance and health outcomes: The exacerbating role of narcissism and social support. Dissertation Abstracts International: Section B: The Sciences and Engineering, 72(12-B), 7731.
Aryee, S., Chen, Z. X., Sun, L. Y., & Debrah, Y. A. (2007). Antecedents and outcomes of abusive supervision: Test of a trickle-down model. Journal of Applied Psychology, 92(1), 191–201.
Aryee, S., Sun, L. Y., Chen, Z. X. G., & Debrah, Y. A. (2008). Abusive supervision and contextual performance: The mediating role of emotional exhaustion and the moderating role of work unit structure. Management and Organization Review, 4(3), 393–411.
Bardes, M. (2009). Aspects of goals and rewards systems as antecedents of abusive supervision: The mediating effect of hindrance stress. Florida, USA: University of Central Florida.
Biron, M. (2010). Negative reciprocity and the association between perceived organizational ethical values and organizational deviance. Human Relations, 63(6), 875–897.
Bowling, N. A., & Michel, J. S. (2011). Why do you treat me badly? The role of attributions regarding the cause of abuse in subordinates’ responses to abusive supervision. Work and Stress, 25(4), 309–320.
Breaux, D. M., Perrewé, P. L., Hall, A. T., Frink, D. D., & Hochwarter, W. A. (2008). Time to try a little tenderness? The detrimental effects of accountability when coupled with abusive supervision. Journal of Leadership and Organizational Studies, 15(2), 111–122. (Sage).
Brown, M. E., Trevino, L. K., & Harrison, D. A. (2005). Ethical leadership: A social learning perspective for construct development and testing. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes, 97(2), 117–134.
Burris, E. R., Detert, J. R., & Chiaburu, D. S. (2008). Quitting before leaving: The mediating effects of psychological attachment and detachment on voice. Journal of Applied Psychology, 93(4), 912–922.
Burton, J. P., & Hoobler, J. M. (2011). Aggressive reactions to abusive supervision: The role of interactional justice and narcissism. Scandinavian Journal of Psychology, 52(4), 389–398.
Burton, J. P., Hoobler, J. M., & Scheuer, M. L. (2012). Supervisor workplace stress and abusive supervision: The buffering effect of exercise. Journal of Business and Psychology, 27(3), 271–279.
Camps, J., Decoster, S., & Stouten, J. (2012). My share is fair, so i don’t care the moderating role of distributive justice in the perception of leaders’ self-serving behavior. Journal of Personnel Psychology, 11(1), 49–59.
Carlson, D., Ferguson, M., Hunter, E., & Whitten, D. (2012). Abusive supervision and work–family conflict: The path through emotional labor and burnout. The Leadership Quarterly, 23(5), 849–859.
Chi, S.-C. S., & Liang, S.-G. (2013). When do subordinates’ emotion-regulation strategies matter? Abusive supervision, subordinates’ emotional exhaustion, and work withdrawal. The Leadership Quarterly, 24(1), 125.
Decoster, S., Camps, J., Stouten, J., Vandevyvere, L., & Tripp, T. M. (2013). Standing by your organization: The impact of organizational identification and abusive supervision on followers’ perceived cohesion and tendency to gossip. Journal of Business Ethics, 118(3), 623–634.
Detert, J. R., Trevino, L. K., Burris, E. R., & Andiappan, M. (2007). Managerial modes of influence and counterproductivity in organizations: A longitudinal business-unit-level investigation. Journal of Applied Psychology, 92(4), 993–1005.
Ding, X. Q., Tian, K., Yang, C. S., & Gong, S. F. (2012). Abusive supervision and LMX: Leaders’ emotional intelligence as antecedent variable and trust as consequence variable. Chinese Management Studies, 6(2), 258–271.
Duffy, M. K., & Ferrier, W. J. (2003). Birds of a feather…? How supervisor-subordinate dissimilarity moderates the influence of supervisor behaviors on workplace attitudes. Group and Organization Management, 28(2), 217–248.
Dupre, K. E. (2005). Beating up the boss: The prediction and prevention of interpersonal aggression targeting workplace supervisors. Dissertation Abstracts International Section A: Humanities and Social Sciences, 63(3-A), 669.
Dupre, K. E., Inness, M., Connelly, C. E., Barling, J., & Hoption, C. (2006). Workplace aggression in teenage part-time employees. Journal of Applied Psychology, 91(5), 987–997.
Haggard, D. L., Robert, C., & Rose, A. J. (2011). Co-rumination in the workplace: Adjustment trade-offs for men and women who engage in excessive discussions of workplace problems. Journal of Business and Psychology, 26(1), 27–40.
Harris, K. J., Harvey, P., & Kacmar, K. M. (2011). Abusive supervisory reactions to coworker relationship conflict. The Leadership Quarterly, 22(5), 1010–1023.
Harris, K. J., Harvey, P., Harris, R. B., & Cast, M. (2013). An investigation of abusive supervision, vicarious abusive supervision, and their joint impacts. Journal of Social Psychology, 153(1), 38–50.
Hobman, E. V., Restubog, S. L. D., Bordia, P., & Tang, R. L. (2009). Abusive supervision in advising relationships: Investigating the role of social support. Applied Psychology—an International Review (Psychologie Appliquee—Revue Internationale), 58(2), 233–256.
Hoobler, J. M., & Brass, D. J. (2006). Abusive supervision and family undermining as displaced aggression. Journal of Applied Psychology, 91(5), 1125–1133.
Hoobler, J. M., & Hu, J. (2013). A model of injustice, abusive supervision, and negative affect. The Leadership Quarterly, 24(1), 256–269.
Inness, M., Barling, J., & Tumer, N. (2005). Understanding supervisor-targeted aggression: A within-person, between-jobs design. Journal of Applied Psychology, 90(4), 731–739.
Jian, Z. Q., Kwan, H. K., Qiu, Q., Liu, Z. Q., & Yim, F. H. K. (2012). Abusive supervision and frontline employees’ service performance. Service Industries Journal, 32(5), 683–698.
Kernan, M. C., Watson, S., Chen, F. F., & Kim, T. G. (2011). How cultural values affect the impact of abusive supervision on worker attitudes. Cross Cultural Management—an International Journal, 18(4), 464–484.
Kiazad, K., Restubog, S. L. D., Zagenczyk, T. J., Kiewitz, C., & Tang, R. L. (2010). In pursuit of power: The role of authoritarian leadership in the relationship between supervisors’ machiavellianism and subordinates’ perceptions of abusive supervisory behavior. Journal of Research in Personality, 44(4), 512–519.
Kiewitz, C., Restubog, S. L. D., Zagenczyk, T. J., Scott, K. D., Garcia, P., & Tang, R. L. (2012). Sins of the parents: Self-control as a buffer between supervisors’ previous experience of family undermining and subordinates’ perceptions of abusive supervision. The Leadership Quarterly, 23(5), 869–882.
Lian, H. W., Ferris, D. L., & Brown, D. J. (2012a). Does power distance exacerbate or mitigate the effects of abusive supervision? It depends on the outcome. Journal of Applied Psychology, 97(1), 107–123.
Lian, H. W., Ferris, D. L., & Brown, D. J. (2012b). Does taking the good with the bad make things worse? How abusive supervision and leader-member exchange interact to impact need satisfaction and organizational deviance. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes, 117(1), 41–52.
Lian, H., Brown, D., Ferris, D. L., Liang, L., Keeping, L., & Morrison, R. (2013). Abusive supervision and retaliation: A self-control framework. Academy of Management Journal, 57, 116–139.
Lin, W. P., Wang, L., & Chen, S. T. (2013). Abusive supervision and employee well-being: The moderating effect of power distance orientation. Applied Psychology—an International Review (Psychologie Appliquee—Revue Internationale), 62(2), 308–329.
Liu, J., Kwan, H. K., Wu, L. Z., & Wu, W. K. (2010). Abusive supervision and subordinate supervisor-directed deviance: The moderating role of traditional values and the mediating role of revenge cognitions. Journal of Occupational and Organizational Psychology, 83(4), 835–856.
Liu, D., Liao, H., & Loi, R. (2012). The dark side of leadership: A three-level investigation of the cascading effect of abusive supervision on employee creativity. Academy of Management Journal, 55(5), 1187–1212.
Liu, C., Yang, L. Q., & Nauta, M. M. (2013). Examining the mediating effect of supervisor conflict on procedural injustice–job strain relations: The function of power distance. Journal of Occupational Health Psychology, 18(1), 64–74.
Martinko, M. J., Harvey, P., Sikora, D., & Douglas, S. C. (2011). Perceptions of abusive supervision: The role of subordinates’ attribution styles. Leadership Quarterly, 22(4), 751–764.
Mawritz, M. B., Mayer, D. M., Hoobler, J. M., Wayne, S. J., & Marinova, S. V. (2012). A trickle-down model of abusive supervision. Personnel Psychology, 65(2), 325–357.
Mayer, D. M., Thau, S., Workman, K. M., Van Dijke, M., & De Cremer, D. (2012). Leader mistreatment, employee hostility, and deviant behaviors: Integrating self-uncertainty and thwarted needs perspectives on deviance. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes, 117(1), 24–40.
Mitchell, M. S., & Ambrose, M. L. (2007). Abusive supervision and workplace deviance and the moderating effects of negative reciprocity beliefs. Journal of Applied Psychology, 92(4), 1159–1168.
Mitchell, M. S., & Ambrose, M. L. (2012). Employees’ behavioral reactions to supervisor aggression: An examination of individual and situational factors. Journal of Applied Psychology, 97(6), 1148–1170.
Nelson, R. J. (1998). Abusive supervision and subordinates’ coping strategies (p. 88). Kentucky, USA: University of Kentucky.
Ogunfowora, B. (2009). The consequences of ethical leadership: Comparisons with transformational leadership and abusive supervision. Calgary, Canada: University of Calgary.
Palanski, M., Avey, J. B., & Jiraporn, N. (2014). The effects of ethical leadership and abusive supervision on job search behaviors in the turnover process. Journal of Business Ethics, 121(1), 135–146.
Pyc, L. S. (2012). The moderating effects of workplace ambiguity and perceived job control on the relations between abusive supervision and employees’ behavioral, psychological, and physical strains. Dissertation Abstracts International Section A: Humanities and Social Sciences, 72(8-A), 2986.
Rafferty, A. E., & Restubog, S. L. D. (2011). The influence of abusive supervisors on followers’ organizational citizenship behaviours: The hidden costs of abusive supervision. British Journal of Management, 22(2), 270–285.
Rafferty, A. E., Restubog, S. L. D., & Jimmieson, N. L. (2010). Losing sleep: Examining the cascading effects of supervisors’ experience of injustice on subordinates’ psychological health. Work and Stress, 24(1), 36–55.
Restubog, S. L. D., Scott, K. L., & Zagenczyk, T. J. (2011). When distress hits home: The role of contextual factors and psychological distress in predicting employees’ responses to abusive supervision. Journal of Applied Psychology, 96(4), 713–729.
Shao, P., Resick, C. J., & Hargis, M. B. (2011). Helping and harming others in the workplace: The roles of personal values and abusive supervision. Human Relations, 64(8), 1051–1078.
Shoss, M. K., Eisenberger, R., Restubog, S. L. D., & Zagenczyk, T. J. (2013). Blaming the organization for abusive supervision: The roles of perceived organizational support and supervisor’s organizational embodiment. Journal of Applied Psychology, 98(1), 158–168.
Sulea, C., Filipescu, R., Horga, A., Ortan, C., & Fischmann, G. (2012). Interpersonal mistreatment at work and burnout among teachers. Cognition, Brain, Behavior: An Interdisciplinary Journal, 16(4), 553–570.
Tepper, B. J., Duffy, M. K., Hoobler, J., & Ensley, M. D. (2004). Moderators of the relationships between coworkers’ organizational citizenship behavior and fellow employees’ attitudes. Journal of Applied Psychology, 89(3), 455–465.
Tepper, B. J., Duffy, M. K., Henle, C. A., & Lambert, L. S. (2006). Procedural injustice, victim precipitation, and abusive supervision. Personnel Psychology, 59(1), 101–123.
Tepper, B. J., Lambert, L. S., Henle, C. A., Giacalone, R. A., & Duffy, M. K. (2008). Abusive supervision and subordinates’ organization deviance. Journal of Applied Psychology, 93(4), 721–732.
Tepper, B. J., Carr, J. C., Breaux, D. M., Geider, S., Hu, C. Y., & Hua, W. (2009). Abusive supervision, intentions to quit, and employees’ workplace deviance: A power/dependence analysis. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes, 109(2), 156–167.
Tepper, B. J., Moss, S. E., & Duffy, M. K. (2011). Predictors of abusive supervision: Supervisor perceptions of deep-level dissimilarity, relationship conflict, and subordinate performance. Academy of Management Journal, 54(2), 279–294.
Thau, S., & Mitchell, M. S. (2010). Self-gain or self-regulation impairment? Tests of competing explanations of the supervisor abuse and employee deviance relationship through perceptions of distributive justice. Journal of Applied Psychology, 95(6), 1009–1031.
Thau, S., Bennett, R. J., Mitchell, M. S., & Marrs, M. B. (2009). How management style moderates the relationship between abusive supervision and workplace deviance: An uncertainty management theory perspective. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes, 108(1), 79–92.
Thoroughgood, C. N., Tate, B. W., Sawyer, K. B., & Jacobs, R. (2012). Bad to the bone: Empirically defining and measuring destructive leader behavior. Journal of Leadership and Organizational Studies, 19(2), 230–255.
Thun, B., & Kelloway, E. K. (2011). Virtuous leaders: Assessing character strengths in the workplace. Canadian Journal of Administrative Sciences (Revue Canadienne Des Sciences De L Administration), 28(3), 270–283.
Wang, W., Mao, J. Y., Wu, W. K., & Liu, J. (2012). Abusive supervision and workplace deviance: The mediating role of interactional justice and the moderating role of power distance. Asia Pacific Journal of Human Resources, 50(1), 43–60.
Whitman, M. V., Halbesleben, J. R. B., & Shanine, K. K. (2013). Psychological entitlement and abusive supervision: Political skill as a self-regulatory mechanism. Health Care Management Review, 38(3), 248–257.
Whitman, M. V., Halbeslebe, J. R. B., & Holmes, O. (2014). Abusive supervision and feedback avoidance: The mediating role of emotional exhaustion. Journal of Organizational Behavior, 35(1), 38–53.
Wu, T.-Y. (2008). Abusive supervision and emotional exhaustion: The mediating effects of subordinate justice perception and emotional labor. Chinese Journal of Psychology, 50(2), 201–221.
Wu, T. Y., & Hu, C. Y. (2009). Abusive supervision and employee emotional exhaustion dispositional antecedents and boundaries. Group and Organization Management, 34(2), 143–169.
Wu, L.-Z., Liu, J., & Liu, G. (2009). Abusive supervision and employee performance: Mechanisms of traditionality and trust. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 41(6), 510–518.
*Wu, W. K., Wang, W. & Liu, J. (2010) Abusive supervision and team effectiveness: The mediating role of team efficacy. Paper presented at 2010 IEEE International Conference on Management Science and Engineering.
Xu, E., Huang, X., Lam, C. K., & Miao, Q. (2012). Abusive supervision and work behaviors: The mediating role of LMX. Journal of Organizational Behavior, 33(4), 531–543.
Yagil, D. (2006). The relationship of abusive and supportive workplace supervision to employee burnout and upward influence tactics. Journal of Emotional Abuse, 6(1), 49–65.
Yagil, D., Ben-Zur, H., & Tamir, I. (2011). Do employees cope effectively with abusive supervision at work? An exploratory study. International Journal of Stress Management, 18(1), 5–23.
Zellars, K. L., Tepper, B. J., & Duffy, M. K. (2002). Abusive supervision and subordinates’ organizational citizenship behavior. Journal of Applied Psychology, 87(6), 1068–1076.
Zhao, H. D., Peng, Z. L., Han, Y., Sheard, G., & Hudson, A. (2013). Psychological mechanism linking abusive supervision and compulsory citizenship behavior: A moderated mediation study. Journal of Psychology, 147(2), 177–195.
Acknowledgments
Thanks to Yumeng Yue for research assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Bednall, T.C. Antecedents of Abusive Supervision: a Meta-analytic Review. J Bus Ethics 139, 455–471 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10551-015-2657-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10551-015-2657-6