Abstract
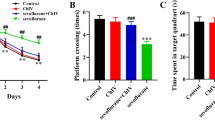
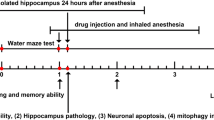
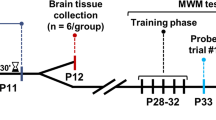
Neurocognition is a severe, neurological challenge caused due to sevoflurane application for induction of anaesthesia. The plan of this study is to investigate the effect of fingolimod loaded niosomes on the cognitive impairment induced by sevoflurane. Span 40 and cholesterol were used in reverse phase evaporation techniques for the preparation of fingolimod -loaded niosomes. The positively charged niosomes were obtained by using chloride salts of 1,2-dioleoyl-3-trimethylammonium-propane (DOTAP). The Fingolimod loaded niosomes has average particle size of 223.5 nm and the surface charge measured as + 8.7 ± 1.2 mV in presence of DOTAP. The Fingolimod loaded niosomes formulation shows higher entrapment efficiency. Fingolimod loaded positively charged niosomes were efficiently retained drug and increase the sustain release property. Fingolimod niosomes increases the spontaneous alternation in Y maze and reduces the escape latency in the Morris water maze test, which leads to significant (p < 0.01) improvement in spatial short-term and long-term memory. The neuronal death in the hippocampus due to the sevoflurane exposure was attenuated by fingolimod loaded niosomes, which was proved by histopathological study. It could be defined that fingolimod loaded niosomes attenuates the sevoflurane induced cognitive impairment.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
C. Boz, M. Terzi, B. Ozer, R. Turkoglu, R. Karabudak, H. Efendi et al., Comparative analysis of fingolimod versus teriflunomide in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 36, 101376 (2019)
C.M. Bye, N.S. Hong, K. Moore, S.H. Deibel, R.J. McDonald, The Effects of Pool Shape Manipulations on Rat Spatial Memory Acquired in the Morris Water Maze. 47(1), 29–37 (2018)
T. Di Maira, E.C. Little, M. Berenguer, Immuno suppression in liver transplant. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 46–47 (2020)
B. Drexler, B. Antkowiak, H. Thiermann, C. Grasshoff, Atropine increases sevoflurane potency in cortical but not spinal networks during cholinergic overstimulation. Toxicology 268(1–2), 98–103 (2010)
C. Grasshoff, B. Drexler, H. Hentschke, H. Thiermann, B. Antkowiak, Cholinergic Modulation of Sevoflurane Potency in Cortical and Spinal Networks In Vitro. Anesthesiology 106, 1147–1155 (2007)
L. Elhampour, M.A. Azarbayjani, M. Nasehi, M. Peeri, Concurrent Effects of Exercise and Curcumin on Spatial Learning and Memory in Sensitized Male Mice Following Morphine Administration. Galen Medical Journal 8(1072), 1–5 (2019)
G.L. Ellman, Tissue sulfhydryl groups. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 82, 70–77 (1959)
A. Ennaceur, J. Delacour, A new one-trial test for neurobiological studies of memory in rats: I. Behavioral Data. Behav. Brain Res. 31, 47–59 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1016/0166-4328(88)90157-X
Z. Hajat, N. Ahmad, J. Andrzejowski, The role and limitations of EEG-based depth of anaesthesia monitoring in theatres and intensive care. Anaesthesia 72(Suppl 1), 38–47 (2021)
A.A. Hasan, H. Madkor, S. Wageh, Formulation and evaluation of metformin hydrochloride-loaded niosomes as controlled release drug delivery system. Drug. Deliv. 20(3–4), 120–6 (2013)
A. Huwiler, U. Zangemeister-Wittke, The sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor modulator fingolimod as a therapeutic agent: Recent findings and new perspectives. Pharmacol. Ther. 185, 34–49 (2018)
A. Katrolia, S.B. Chauhan, V.K. Shukla, Formulation and evaluation of Metformin Hydrochloride-loaded Curcumin-Lycopene Niosomes. SN Applied Sciences. 1(1703), 1–4 (2019)
Y. Konishi, L.A. Evered, D.A. Scott, B.S. Silbert, Postoperative cognitive dysfunction after sevoflurane or propofol general anaesthesia in combination with spinal anaesthesia for hip arthroplasty. Anaesth Intensive Care. 46(6), 596–600 (2018)
S. Kratzer, C. Mattusch, P.S. Garcia, S. Schmid, E. Kochs, Propofol and Sevoflurane Differentially Modulate Cortical Depolarization following Electric Stimulation of the Ventrobasal Thalamus. Front Comput. Neurosci. 11(109), 11–12 (2017)
L. La Mantia, I. Tramacere, B. Firwana, I. Pacchetti, R. Palumbo, G. Filippini, Fingolimod for relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 19, 4 (2016)
J.H. Lee, Y. Yeo, Controlled Drug Release from Pharmaceutical Nanocarriers. Chem. Eng. Sci. 24(125), 75–84 (2015)
J. Liang, Q. Wang, J.Q. Li, T. Guo, D. Yu, Long non-coding RNA MEG3 promotes cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury through increasing pyroptosis by targeting miR-485/AIM2 axis. Exp. Neurol. 325, 113–139 (2020)
K. Mali, G. Sutar, O. Devade, R. Dias, Evaluation of Nootropic Activity of Limonia acidissima Against Scopolamine-induced Amnesia in Rats. Turk. J. Pharm. Sci. 18(1), 3–9 (2021)
Y. Mao, J. Wang, Y. Zhao, Y. Wu, K.J. Kwak, C.S. Chen et al., A novel liposomal formulation of FTY720 (Fingolimod) for promising enhanced targeted delivery. Nanomedicine 10(2), 393–400 (2014)
C. Mohanty, S. Acharya, A.K. Mohanty, F. Dilnawaz, S.K. Sahoo, Curcumin-encapsulated MePEG/PCL diblock copolymeric micelles: a novel controlled delivery vehicle for cancer therapy. Nanomedicine (lond). 5(3), 433–449 (2010)
A.K. Mohanty, G.P. Mohanta, Dual anticancer drug loaded methoxy poly (ethylene glycol)-poly (ε-caprolactone) block copolymeric micelles as novel drug carriers. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 6(9), 328–332 (2014)
N. Morales-Delgado, N. Popović, E. Cruz-Sánchez, M. Caballero Bleda, M. Popović, Time-of-Day and Age Impact on Memory in Elevated Plus-Maze Test in Rats. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 12(304), 1–4 (2018)
M. Marius, T. Gonzal, A. Gilbert, N. William, D.B. Francis, Analgesic, anti-inflammatory and anti-arthritic properties of aqueous and methanolic stem bark extracts from Nauclea pobeguinii (Rubiacee) in rats. J. Complement. Integr. Med. 15(4), 2017–2140 (2018)
I.A. Osman, E.B. Basalious, Method Development and Validation for Fingolimod by HPLC/UV in Immediate-Release Oral Capsule and Study the Effect of Excipients on Solubility and Dissolution Behavior. J. Analy. Pharma. Res. 2(1), 12–14 (2016)
B.J.A. Palanca, M.S. Avidan, G.A. Mashour, Human neural correlates of sevoflurane-induced unconsciousness. Br. J. Anaesth. 119(4), 573–582 (2017)
J.K. Patra, G. Das, L.F. Fraceto, E.V. Ramos Campos, M.P. Rodriguez-Torres, L.S. Acosta-Torres, Nano based drug delivery systems: recent developments and future prospects. J. Nanobiotechnol. 16(71), 2–33 (2018)
M. Pohanka, M. Hrabinova, K. Kuca, J. Simonato, Assessment of Acetylcholinesterase Activity Using Indoxylacetate and Comparison with the Standard Ellman’s Method. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 12(4), 2631–2640 (2011)
R. Rajendran, D.B. Ambikar, R.A. Khandare, V.D. Sannapuri, N.S. Vyawahare, P. Clayton, Nootropic activity of Caralluma fimbriata extract in mice. Food Nutr. Sci. 05, 147–152 (2014). https://doi.org/10.4236/fns.2014.52019
A. Shaked, M.R. DesMarais, H. Kopetskie, S. Feng, J.D. Punch, J. Levitsky et al., Outcomes of immune suppression minimization and withdrawal early after liver transplantation. Am. J. Transplant. 19(5), 1397–1409 (2019)
E. Swallow, O. Patterson-Lomba, L. Yin, R. Mehta, C. Pelletier, D. Kao et al., Comparative safety and efficacy of ozanimod versus fingolimod for relapsing multiple sclerosis. J. Comp. Eff. Res. 9(4), 275–285 (2020)
H.T. Ton, L. Yang, Z. Xie, Sevoflurane increases locomotion activity in mice. PLoS One. 14(5) (2019)
A. Walf, C. Frye, The use of the elevated plus maze as an assay of anxiety-related behavior in rodents. Nat. Protoc. 2(2), 322–328 (2007)
A.A. Yetisgin, S. Cetinel, M. Zuvin, A. Kosar, O. Kutlu, Therapeutic Nanoparticles and Their Targeted Delivery Applications. Molecules 25(9), 2193 (2020)
J. Yin, X. Zhao, L. Wang, X. Xie, H. Geng, X. Zhan, J. Teng, Sevoflurane-induced inflammation development: involvement of cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway. Behav. Pharmacol. 30(8), 730–737 (2019)
Y. Zhang, G.J. Shan, Y.X. Zhang, S.J. Cao, S.N. Zhu, H.J. Li et al., Propofol compared with sevoflurane general anaesthesia is associated with decreased delayed neurocognitive recovery in older adults. Br. J. Anaesth. 121(3), 595–604 (2018)
Acknowledgements
XingDa Li is extremely thankful to Department of Anesthesiology, Linyi Central Hospital, Linyi, China for providing desired facility to carry out the research activity and other relevant supports.
Funding
This study didn’t receive any specific grant/fund from any funding agencies in the public, commercial, or nonprofits sector.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HW and XL are associated in planning the work. The experiments were carried out by XL and YR whereas HW, YR and XL were involved in data handling and processing. All the authors contributed equally in preparing the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Weng, H., Liu, X., Ren, Y. et al. Fingolimod loaded niosomes attenuates sevoflurane induced cognitive impairments. Biomed Microdevices 24, 5 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-021-00603-x
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-021-00603-x