Abstract
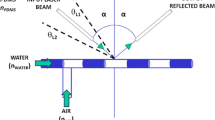
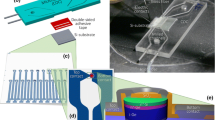
In this work, it is presented a micro-optofluidic flow detector used for on-chip biological and chemical samples investigation. It is made in Poly-dimethyl-siloxane using a master-slave approach based on the 3D-Printing techniques. The micro-optofluidic device is made by assembling a microfluidic T-junction with a micro-optical section that consists of two optical fiber insertions and a PDMS gold-spattered micro-waveguide. The working principle in the detection is based on a different light transmission correlated to the fluid interfering with the laser beam in a micro-channel section. The proposed solution allows to realize a PDMS micro-device taking the advantage of 3D- Printing and goes beyond the restriction in the material selection. The device’s performances were tested in the fluids detection and in the evaluation of the cell concentrations. Additionally, the micro-device was used as a real-time two-phase fluids flow detector. The two-phases flows were successfully monitored in different experimental conditions, varying both hydrodynamic and optical external stimuli.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
A.K. Au, W. Huynh, L.F. Horowitz, A. Folch, 3D-printed microfluidics. Angew. Chem. Int. 55(12), 3862–3881 (2016)
N. Bhattacharjee, A. Urrios, S. Kanga, A. Folch, The upcoming 3D-printing revolution in microfluidics. Lab on a Chip. 16(10), 1720–1742 (2016)
H. Becker, L.E. Locascio, Polymer microfluidics devices. Talanta. 56(2), 267–287 (2002)
M. Brammer, T. Mappes, Modular platforms for optofluidic systems. Optofluidics. 1(1), 1–10 (2010)
M. Bucolo, J. Guo, M. Intaglietta, W. Coltro, Special issue on microfluidics engineering for point-of-care diagnostics. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circ. Syst. 11(6), 1488–1499 (2017)
F. Cairone, S. Gagliano, D. Carbone, G. Recca, M. Bucolo, Micro-optofluidic switch realized by 3D printing technology. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 20(4), 1–10 (2016a)
F. Cairone, S. Gagliano, M. Bucolo, Experimental study on the slug flow in a serpentine microchannel. Int. J. Exp. Thermal Fluid Sci. 76, 34–44 (2016b)
F. Cairone, D. Mirabella, P.J. Cabrales, M. Intaglietta, M. Bucolo, Quantitative analysis of spatial irregularities in RBCs flows. Chaos Solitons and Fractals. 115, 349–355 (2018a)
F. Cairone, D. Ortiz, P.J. Cabrales, M. Intaglietta, M. Bucolo, Emergent behaviors in RBCs flows in micro-channels using digital particle image velocimetry. Microvasc. Res. 116, 77–86 (2018b)
S. Camou, H. Fujita, T. Fujii, PDMS 2D optical lens integrated with microfluidic channels: principle and characterization. Lab Chip. 3, 40–45 (2003)
H.N. Chan, Y. Chen, Y. Shu, Y. Chen, Q. Tian, H. Wu, Direct, one-step molding of 3D-printed structures for convenient fabrication of truly 3D PDMS microfluidic chips. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 19(1), 9–18 (2015)
H.N. Chan, M.J.A. Tan, H. Wu, Point-of-care testing: Applications of 3D printing. Lab Chip. 17(16), 2713–2739 (2017)
D.A. Chang-Yen, R.K. Eich, B.K. Gale, A monolithic PDMS waveguide system fabricated using soft-lithography techniques. J. Lightwave Technol. 23(6), 2088–2093 (2005)
H. Cong, F.C. Loo, J. Chen, Y. Wang, S.K. Kong, H.P. Ho, Target trapping and in situ single-cell genetic marker detection with a focused optical beam. Biosens Bioelectron. 133, 236–242 (2019)
A. Cossarizza, H.D. Chang, A. Radbruch, M. Akdis, I. Andrä, F. Annunziato, Guidelines for the use of flow cytometry and cell sorting in immunological studies. Eur. J. Immunol. 47(10), 1584–1797 (2017)
S. Gagliano, G. Stella, M. Bucolo, Real-time detection of slug velocity in microchannels. Micromachines. 11(3), 241 (2020)
P.C.H. Li, Microfluidics Lab-on-a-Chip for Chemical and Biological Analysis and Discovery, p. 94. CRC Taylor and Francis (2006)
A. Llobera, R. Wilke, S. Buttgenbach, Enhancement of the response of poly(dimethylsiloxane) hollow prisms through air mirrors for absorbance-based sensing. Talanta. 75(2), 473–479 (2008)
J.C. McDonald, G.M. Whitesides, Poly(dimethylsiloxane) as a material for fabricating microfluidic devices. Acc. Chem. Res. 35(7), 491–499 (2002)
N.P. Macdonald, J.M. Cabot, P. Smejkal, R.M. Guijt, B. Paull, M.C. Breadmore, Comparing microfluidic perfomance of three-dimensional (3D) printing platform. Anal. Chem. 89(7), 3858–3866 (2017)
P. Minzioni, R. Osellame, C. Sada, S. Zhao, F.G. Omenetto, K.B. Gylfason, T. Haraldsson, Y. Zhang, A. Ozcan, A. Wax, Roadmap for optofluidics. J. Optic, 19(9) (2017)
J.M. Ng, I. Gitlin, A.D. Stroock, G.M. Whitesides, Components for integrated poly (dimethylsiloxane) microfluidic systems. Electrophoresis. 23(20), 3461–3473 (2007)
F. Sapuppo, A. Llobera, F. Schembri, M. Intaglietta, V.J. Cadarso, M. Bucolo, A polymeric micro-optical interface for flow monitoring in biomicrofluidics. Biomicrofluidics. 4(2), 6258 (2010)
F. Sapuppo, F. Schembri, L. Fortuna, A. Llobera, M. Bucolo, A polymeric micro-optical system for the spatial monitoring in two-phase microfluidics. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 12, 165 (2012)
D.I. Walsh, D.S. Kong, S.K. Murthy, P.A. Carr, Enabling microfluidics: From clean rooms to makerspaces. Trends Biotechnol. 35(5), 383–392 (2017)
G. Weisgrab, A. Ovsianikov, P.F. Costa, Functional 3D printing for microfluidic chips. Adv. Mater. Technol. 4(10), 1900275 (2019)
A. Yamaguchi, T. Fukuoka, K. Kuroda, R. Hara, Y. Utsumi, Dielectrophoresis-enabled surface enhanced Raman scattering of glycine modified on Au-nanoparticle-decorated polystyrene beads in micro-optofluidic devices. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 507, 118–123 (2016)
A.A. Yazdi, A. Popma, W. Wong, T. Nguyen, Y. Pan, J. Xu, 3D printing: An emerging tool for novel microfluidics and lab-on-a-chip applications. Microfluidics and Nanofluidics. 20(3), 50 (2016)
F. Yeshaiahu, L.P. Lee, D. Psaltis, C. Yang, Optofluidics Fundamentals. Devices and Application. McGraw-Hill (2010)
H.T. Zhaoa, Y. Zhang, P.Y. Liu, P.H. Yap, W. Ser, A.Q. Liu, Chemical reaction monitoring via the light focusing in optofluidic. Waveguides. 280, 16–23 (2019)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cairone, F., Davi, S., Stella, G. et al. 3D-Printed micro-optofluidic device for chemical fluids and cells detection. Biomed Microdevices 22, 37 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-020-00487-3
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-020-00487-3