Abstract
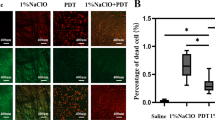
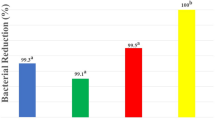
Enterococcus faecalis(E. faecalis) is a common microorganism could be isolated from the infected canals, especially in the case of refractory apical periodontitis. Due to its ability to invade the dentinal tubules and highly resistant to antimicrobial strategies, the thorough debridement of E.faecalis is hard to achieve. And that may be one of the reasons to cause reinfection and therapeutic failure. According to the anatomy of dentinal tubules published before and the results of our team previous work, we designed six types of microtubes with different sizes. By using the method of centrifugation and incubation, a standard infected model mimicking dentinal tubules was established. Sodium hypochlorite (NaClO) is the most popular irrigant applied in root canal treatment. We used three different concentrations with four distinct irrigation duration to observe the antibacterial process of E. faecalis colonies within microtubes dynamically. We concluded that the role of NaClO in the microtubes is concentration dependent and duration dependent. And the interpretation of the results has a certain reference value for clinicians.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Ardizzoni, L. Generali, E. Righi, et al., Differential efficacy of endodontic obturation procedures: An ex vivo study. Odontology 102(2), 223–231 (2014)
V.B. Berber, B.P. Gomes, N.T. Sena, et al., Efficacy of various concentrations of NaOCl and instrumentation techniques in reducing enterococcus faecalis within root canals and dentinal tubules. Int. Endod. J. 39(1), 10–17 (2006)
G. Bryce, D. O'Donnell, D. Ready, et al., Contemporary root canal irrigants are able to disrupt and eradicate single- and dual-species biofilms. J. Endod. 35(9), 1243–1248 (2009)
N.P. Chau, N.H. Chung, J.G. Jeon, Relationships between the antibacterial activity of sodium hypochlorite and treatment time and biofilm age in early enterococcus faecalis biofilms. Int. Endod. J. 48(8), 782–789 (2015)
P. Chivatxaranukul, S.G. Dashper, H.H. Messer, Dentinal tubule invasion and adherence by enterococcus faecalis. Int. Endod. J. 41(10), 873–882 (2008)
J.K. Cullen, J.A. Wealleans, T.C. Kirkpatrick, et al., The effect of 8.25% sodium hypochlorite on dental pulp dissolution and dentin flexural strength and modulus. J. Endod. 41(6), 920–924 (2015)
T. Du, Z. Wang, Y. Shen, et al., Effect of long-term exposure to endodontic disinfecting solutions on young and old enterococcus faecalis biofilms in dentin canals. J. Endod. 40(4), 509–514 (2014)
S.A. Farook, V. Shah, D. Lenouvel, et al., Guidelines for management of sodium hypochlorite extrusion injuries. Br. Dent. J. 217(12), 679–684 (2014)
D. Figdor, J.K. Davies, G. Sundqvist, Starvation survival, growth and recovery of enterococcus faecalis in human serum. Oral Microbiol. Immunol. 18(4), 234–239 (2003)
J.M. Guerreiro-Tanomaru, N.B. de Faria-Junior, M.A. Duarte, et al., Comparative analysis of enterococcus faecalis biofilm formation on different substrates. J. Endod. 39(3), 346–350 (2013)
T.A. Krause, F.R. Liewehr, C.L. Hahn, The antimicrobial effect of MTAD, sodium hypochlorite, doxycycline, and citric acid on enterococcus faecalis. J. Endod. 33(1), 28–30 (2007)
R.M. Love, Invasion of dentinal tubules by root canal bacteria. Endod. Topics. 9(1), 52–65 (2010)
J. Ma, Z. Wang, Y. Shen, M. Haapasalo, A new noninvasive model to study the effectiveness of dentin disinfection by using confocal laser scanning microscopy. J. Endod. 37(10), 1380–1385 (2011)
S.A. Mohmmed, M.E. Vianna, M.R. Penny, et al., The effect of sodium hypochlorite concentration and irrigation needle extension on biofilm removal from a simulated root canal model. Aust. Endod. J. 43(3), 102–109 (2017a)
S.A. Mohmmed, M.E. Vianna, M.R. Penny, et al., Confocal laser scanning, scanning electron, and transmission electron microscopy investigation of enterococcus faecalis biofilm degradation using passive and active sodium hypochlorite irrigation within a simulated root canal model. Microbiology 6(4) (2017b)
W.R. Moorer, P.R. Wesselink, Factors promoting the tissue dissolving capability of sodium hypochlorite. Int. Endod. J. 15(4), 187–196 (1982)
M. Nourzadeh, A. Amini, F. Fakoor, et al., Comparative antimicrobial efficacy of Eucalyptus Galbie and Myrtus Communis L. extracts, chlorhexidine and sodium hypochlorite against enterococcus Faecalis. Iran. Endod. J. 12(2), 205–210 (2017)
F. Palazzi, A. Blasi, Z. Mohammadi, et al., Penetration of sodium hypochlorite modified with surfactants into root canal dentin. Braz. Dent. J. 27(2), 208–216 (2016)
E.T. Pinheiro, B.P. Gomes, C.C. Ferraz, et al., Microorganisms from canals of root-filled teeth with periapical lesions. Int. Endod. J. 36(1), 1–11 (2003)
S. Ran, J. Wang, W. Jiang, et al., Assessment of dentinal tubule invasion capacity of enterococcus faecalis under stress conditions ex vivo. Int. Endod. J. 48(4), 362–372 (2015)
B. Retamozo, S. Shabahang, N. Johnson, et al., Minimum contact time and concentration of sodium hypochlorite required to eliminate enterococcus faecalis. J. Endod. 36(3), 520–523 (2010)
G. Rossi-Fedele, J.A. Figueiredo, L. Steier, et al., Evaluation of the antimicrobial effect of super-oxidized water (Sterilox(R)) and sodium hypochlorite against enterococcus faecalis in a bovine root canal model. J. Appl. Oral Sci. 18(5), 498–502 (2010)
M.M. Shirazi, O. Abouali, H. Emdad, et al., Numerical and analytical investigation of irrigant penetration into dentinal microtubules. Comput. Biol. Med. 89, 1–17 (2017)
B.W. Sigusch, S. Kranz, S. Klein, et al., Colonization of enterococcus faecalis in a new SiO/SiO(2)-microtube in vitro model system as a function of tubule diameter. Dent. Mater. 30(6), 661–668 (2014)
T.P. Sim, J.C. Knowles, Y.L. Ng, et al., Effect of sodium hypochlorite on mechanical properties of dentine and tooth surface strain. Int. Endod. J. 34(2), 120–132 (2001)
J.J. Siqueira, I.N. Rocas, Polymerase chain reaction-based analysis of microorganisms associated with failed endodontic treatment. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 97(1), 85–94 (2004)
S. Stojicic, S. Zivkovic, W. Qian, et al., Tissue dissolution by sodium hypochlorite: Effect of concentration, temperature, agitation, and surfactant. J. Endod. 36(9), 1558–1562 (2010)
S. Stojicic, Y. Shen, M. Haapasalo, Effect of the source of biofilm bacteria, level of biofilm maturation, and type of disinfecting agent on the susceptibility of biofilm bacteria to antibacterial agents. J. Endod. 39(4), 473–477 (2013)
X. Sun, S. Wang, Y. Yang, et al., Study of invasion and colonization of E. faecalis in microtubes by a novel device. Biomed. MIcrodevices 18(5), 82 (2016)
S. Taschieri, F.M. Del, L. Samaranayake, et al., Microbial invasion of dentinal tubules: A literature review and a new perspective. J. Investig. Clin. Dent. 5(3), 163–170 (2014)
D.T. Wong, G.S. Cheung, Extension of bactericidal effect of sodium hypochlorite into dentinal tubules. J. Endod. 40(6), 825–829 (2014)
M. Zehnder, Root canal irrigants. J. Endod. 32(5), 389–398 (2006)
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the NSF of China (11674010, 11434001, 81170952) and Science and Technology Project of Dongcheng District, Beijing 2017-3-004.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, X., Li, S., Wang, S. et al. The evaluation of E. faecalis colonies dissolution ability of sodium hypochlorite in microenvironment by a novel device. Biomed Microdevices 20, 36 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-018-0279-3
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-018-0279-3