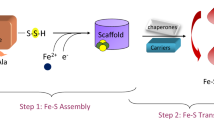
Abstract
A key element in eukaryotic immune defenses against invading microbes is the production of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species. One of the main targets of these species are the iron–sulfur clusters, which are essential prosthetic groups that confer to proteins the ability to perform crucial roles in biological processes. Microbes have developed sophisticated systems to eliminate nitrosative and oxidative species and promote the repair of the damages inflicted. The Ric (Repair of Iron Centers) proteins constitute a novel family of microbial di-iron proteins with a widespread distribution among microbes, including Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, protozoa and fungi. The Ric proteins are encoded by genes that are up-regulated by nitric oxide and hydrogen peroxide. Recent studies have shown that the active di-iron center is involved in the restoration of Fe–S clusters damaged by exposure to nitric oxide and hydrogen peroxide.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DNIC:
-
Dinitrosyl iron complexes
- E. :
-
Escherichia
- EXAFS:
-
Extended X-ray absorption fine structure
- Fe–S:
-
Iron–sulfur
- N. :
-
Neisseria
- NO:
-
Nitric oxide
- P. :
-
Pseudomonas
- R. :
-
Ralstonia
- Ric:
-
Repair of iron centers proteins
- RNS:
-
Reactive nitrogen species
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- S. :
-
Staphylococcus
- sp.:
-
Species
- XAS:
-
X-ray absorption spectroscopy
References
Almeida CC, Romão CV, Lindley PF, Teixeira M, Saraiva LM (2006) The role of the hybrid cluster protein in oxidative stress defense. J Biol Chem 281:32445–32450
Angelini S, Gerez C, Ollagnier-de Choudens S, Sanakis Y, Fontecave M, Barras F, Py B (2008) NfuA, a new factor required for maturing Fe/S proteins in Escherichia coli under oxidative stress and iron starvation conditions. J Biol Chem 283:14084–14091. doi:10.1074/jbc.M709405200
Angelo M, Hausladen A, Singel DJ, Stamler JS (2008) Interactions of NO with hemoglobin: from microbes to man. Methods Enzymol 436:131–168
Ayala-Castro C, Saini A, Outten FW (2008) Fe–S cluster assembly pathways in bacteria. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 72:110–125. doi:10.1128/MMBR.00034-07
Bandyopadhyay S, Naik SG, O’Carroll IP, Huynh BH, Dean DR, Johnson MK, Dos Santos PC (2008) A proposed role for the Azotobacter vinelandii NfuA protein as an intermediate iron–sulfur cluster carrier. J Biol Chem 283:14092–14099. doi:10.1074/jbc.M709161200
Beinert H, Holm RH, Munck E (1997) Iron–sulfur clusters: nature’s modular, multipurpose structures. Science 277:653–659. doi:10.1126/science.277.5326.653
Bodenmiller DM, Spiro S (2006) The yjeB (nsrR) gene of Escherichia coli encodes a nitric oxide-sensitive transcriptional regulator. J Bacteriol 188:874–881. doi:10.1128/JB.188.3.874-881.2006
Brunskill EW, de Jonge BL, Bayles KW (1997) The Staphylococcus aureus scdA gene: a novel locus that affects cell division and morphogenesis. Microbiology 143:2877–2882
Chang W, Small DA, Toghrol F, Bentley WE (2006) Global transcriptome analysis of Staphylococcus aureus response to hydrogen peroxide. J Bacteriol 188:1648–1659. doi:10.1128/JB.188.4.1648-1659.2006
Chow ED, Liu OW, O’Brien S, Madhani HD (2007) Exploration of whole-genome responses of the human AIDS-associated yeast pathogen Cryptococcus neoformans var grubii: nitric oxide stress and body temperature. Curr Genet 52:137–148. doi:10.1007/s00294-007-0147-9
Constantinidou C, Hobman JL, Griffiths L, Patel MD, Penn CW, Cole JA, Overton TW (2006) A reassessment of the FNR regulon and transcriptomic analysis of the effects of nitrate, nitrite, NarXL, and NarQP as Escherichia coli K12 adapts from aerobic to anaerobic growth. J Biol Chem 281:4802–4815. doi:10.1074/jbc.M512312200
Djaman O, Outten FW, Imlay JA (2004) Repair of oxidized iron–sulfur clusters in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem 279:44590–44599. doi:10.1074/jbc.M406487200
Drapier JC (1997) Interplay between NO and [Fe–S] clusters: relevance to biological systems. Methods 11:319–329. doi:10.1006/meth.1996.0426
Eriksson S, Lucchini S, Thompson A, Rhen M, Hinton JC (2003) Unravelling the biology of macrophage infection by gene expression profiling of intracellular Salmonella enterica. Mol Microbiol 47:103–118. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2958.2003.03313.x
Filenko N, Spiro S, Browning DF, Squire D, Overton TW, Cole J, Constantinidou C (2007) The NsrR regulon of Escherichia coli K-12 includes genes encoding the hybrid cluster protein and the periplasmic, respiratory nitrite reductase. J Bacteriol 189:4410–4417. doi:10.1128/JB.00080-07
Flatley J, Barrett J, Pullan ST, Hughes MN, Green J, Poole RK (2005) Transcriptional responses of Escherichia coli to S-nitrosoglutathione under defined chemostat conditions reveal major changes in methionine biosynthesis. J Biol Chem 280:10065–10072. doi:10.1074/jbc.M410393200
Fontecave M, Ollagnier-de-Choudens S (2008) Iron–sulfur cluster biosynthesis in bacteria: mechanisms of cluster assembly and transfer. Arch Biochem Biophys 474:226–237. doi:10.1016/j.abb.2007.12.014
Fontecave M, Choudens SO, Py B, Barras F (2005) Mechanisms of iron–sulfur cluster assembly: the SUF machinery. J Biol Inorg Chem 10:713–721. doi:10.1007/s00775-005-0025-1
Heurlier K, Thomson MJ, Aziz N, Moir JW (2008) The nitric oxide (NO)-sensing repressor NsrR of Neisseria meningitidis has a compact regulon of genes involved in NO synthesis and detoxification. J Bacteriol 190:2488–2495. doi:10.1128/JB.01869-07
Imlay JA (2006) Iron–sulphur clusters and the problem with oxygen. Mol Microbiol 59:1073–1082. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2958.2006.05028.x
Johnson DC, Dean DR, Smith AD, Johnson MK (2005) Structure, function, and formation of biological iron–sulfur clusters. Annu Rev Biochem 74:247–281. doi:10.1146/annurev.biochem.74.082803.133518
Justino MC, Vicente JB, Teixeira M, Saraiva LM (2005) New genes implicated in the protection of anaerobically grown Escherichia coli against nitric oxide. J Biol Chem 280:2636–2643. doi:10.1074/jbc.M411070200
Justino MC, Almeida CC, Goncalves VL, Teixeira M, Saraiva LM (2006) Escherichia coli YtfE is a di-iron protein with an important function in assembly of iron–sulphur clusters. FEMS Microbiol Lett 257:278–284. doi:10.1111/j.1574-6968.2006.00179.x
Justino MC, Almeida CC, Teixeira M, Saraiva LM (2007) Escherichia coli di-iron YtfE protein is necessary for the repair of stress-damaged iron–sulfur clusters. J Biol Chem 282:10352–10359. doi:10.1074/jbc.M610656200
Kiley PJ, Beinert H (2003) The role of Fe–S proteins in sensing and regulation in bacteria. Curr Opin Microbiol 6:181–185. doi:10.1016/S1369-5274(03)00039-0
Kim CC, Monack D, Falkow S (2003) Modulation of virulence by two acidified nitrite-responsive loci of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. Infect Immun 71:3196–3205. doi:10.1128/IAI.71.6.3196-3205.2003
Kurtz DM Jr (1997) Structural similarity and functional diversity in diiron-oxo proteins. J Biol Inorg Chem 2:159–167. doi:10.1007/s007750050120
Lill R, Muhlenhoff U (2008) Maturation of iron–sulfur proteins in eukaryotes: mechanisms, connected processes, and diseases. Annu Rev Biochem 77:669–700. doi:10.1146/annurev.biochem.76.052705.162653
Meyer J (2008) Iron–sulfur protein folds, iron–sulfur chemistry, and evolution. J Biol Inorg Chem 13:157–170. doi:10.1007/s00775-007-0318-7
Mukhopadhyay P, Zheng M, Bedzyk LA, LaRossa RA, Storz G (2004) Prominent roles of the NorR and Fur regulators in the Escherichia coli transcriptional response to reactive nitrogen species. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:745–750. doi:10.1073/pnas.0307741100
Nakano MM, Geng H, Nakano S, Kobayashi K (2006) The nitric oxide-responsive regulator NsrR controls ResDE-dependent gene expression. J Bacteriol 188:5878–5887. doi:10.1128/JB.00486-06
Outten FW, Djaman O, Storz G (2004) A suf operon requirement for Fe–S cluster assembly during iron starvation in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol 52:861–872. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2958.2004.04025.x
Overton TW, Whitehead R, Li Y, Snyder LA, Saunders NJ, Smith H, Cole JA (2006) Coordinated regulation of the Neisseria gonorrhoeae-truncated denitrification pathway by the nitric oxide-sensitive repressor, NsrR, and nitrite-insensitive NarQ-NarP. J Biol Chem 281:33115–33126. doi:10.1074/jbc.M607056200
Overton TW, Justino MC, Li Y, Baptista JM, Melo AM, Cole JA, Saraiva LM (2008) Widespread distribution in pathogenic bacteria of di-iron proteins that repair oxidative and nitrosative damage to iron–sulfur centers. J Bacteriol 190:2004–2013. doi:10.1128/JB.01733-07
Pilon M, Abdel-Ghany SE, Van Hoewyk D, Ye H, Pilon-Smits EA (2006) Biogenesis of iron–sulfur cluster proteins in plastids. Genet Eng (N Y) 27:101–117. doi:10.1007/0-387-25856-6_7
Pohlmann A, Cramm R, Schmelz K, Friedrich B (2000) A novel NO-responding regulator controls the reduction of nitric oxide in Ralstonia eutropha. Mol Microbiol 38:626–638. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2958.2000.02157.x
Pullan ST, Gidley MD, Jones RA, Barrett J, Stevanin TM, Read RC, Green J, Poole RK (2007) Nitric oxide in chemostat-cultured Escherichia coli is sensed by Fnr and other global regulators: unaltered methionine biosynthesis indicates lack of S nitrosation. J Bacteriol 189:1845–1855. doi:10.1128/JB.01354-06
Richmond CS, Glasner JD, Mau R, Jin H, Blattner FR (1999) Genome-wide expression profiling in Escherichia coli K-12. Nucleic Acids Res 27:3821–3835. doi:10.1093/nar/27.19.3821
Rodionov DA, Dubchak IL, Arkin AP, Alm EJ, Gelfand MS (2005) Dissimilatory metabolism of nitrogen oxides in bacteria: comparative reconstruction of transcriptional networks. PLoS Comput Biol 1:0415–0431
Rogers PA, Eide L, Klungland A, Ding H (2003) Reversible inactivation of E. coli endonuclease III via modification of its [4Fe–4S] cluster by nitric oxide. DNA Repair (Amst) 2:809–817. doi:10.1016/S1568-7864(03)00065-X
Saraiva LM, Vicente JB, Teixeira M (2004) The role of the flavodiiron proteins in microbial nitric oxide detoxification. Adv Microb Physiol 49:77–129. doi:10.1016/S0065-2911(04)49002-X
Sebbane F, Lemaitre N, Sturdevant DE, Rebeil R, Virtaneva K, Porcella SF, Hinnebusch BJ (2006) Adaptive response of Yersinia pestis to extracellular effectors of innate immunity during bubonic plague. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:11766–11771. doi:10.1073/pnas.0601182103
Strube K, de Vries S, Cramm R (2007) Formation of a dinitrosyl iron complex by NorA, a nitric oxide-binding di-iron protein from Ralstonia eutropha H16. J Biol Chem 282:20292–20300. doi:10.1074/jbc.M702003200
Takahashi Y, Tokumoto U (2002) A third bacterial system for the assembly of iron–sulfur clusters with homologs in archaea and plastids. J Biol Chem 277:28380–28383. doi:10.1074/jbc.C200365200
Todorovic S, Justino MC, Wellenreuther G, Hildebrandt P, Murgida DH, Meyer-Klaucke W, Saraiva LM (2008) Iron–sulfur repair YtfE protein from Escherichia coli: structural characterization of the di-iron center. J Biol Inorg Chem 13:765–770. doi:10.1007/s00775-008-0362-y
Vicente JB, Justino MC, Goncalves VL, Saraiva LM, Teixeira M (2008) Biochemical, spectroscopic, and thermodynamic properties of flavodiiron proteins. Methods Enzymol 437:21–45. doi:10.1016/S0076-6879(07)37002-X
Vollack KU, Zumft WG (2001) Nitric oxide signaling and transcriptional control of denitrification genes in Pseudomonas stutzeri. J Bacteriol 183:2516–2526. doi:10.1128/JB.183.8.2516-2526.2001
Yang W, Rogers PA, Ding H (2002) Repair of nitric oxide-modified ferredoxin [2Fe–2S] cluster by cysteine desulfurase (IscS). J Biol Chem 277:12868–12873. doi:10.1074/jbc.M109485200
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by FCT project POCI/SAU-IMI/56088/2004. MCJ is recipient of the SFRH/BPD/43172/2008 grant and JMB is recipient of the SFRH/BD/41209/2007 grant from FCT.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Justino, M.C., Baptista, J.M. & Saraiva, L.M. Di-iron proteins of the Ric family are involved in iron–sulfur cluster repair. Biometals 22, 99–108 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-008-9191-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-008-9191-2