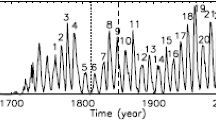Abstract
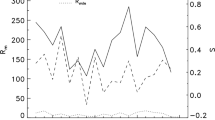
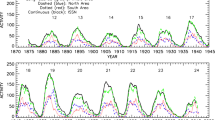
Motivated by a successful prediction on the peak of solar cycle 24 (81.7, comparable to the observed 81.9, Du in Astrophys. Space Sci. 338:9, 2012), based on the logarithmic relationship between the maximum amplitude (\(R_{ \mathrm{m}}\)) of a solar cycle and the preceding minimum \(aa\) geomagnetic index (\(aa_{\mathrm{min}}\)), we perform a prediction on the peak of the upcoming cycle 25 using the sunspot number of the new version instead. If the suggested error in \(aa\) (3 nT) before 1957 is corrected, the correlation between \(\ln R_{\mathrm{m}}\) and \(\ln aa_{\mathrm{min}}\) (\(r=0.92\)) is stronger than that not corrected (\(r=0.86\)). Based on this relationship, the peak value of cycle 25 is predicted to be \(R_{\mathrm{m}}(25)\simeq 151.1\pm 16.9\), about 30% stronger than cycle 24. Employing the ‘Waldmeier effect’ that the rise time of a cycle is well anti-correlated to its amplitude, we estimated the rise time, \(T_{\mathrm{a}}(25)=4.3\pm 0.2\pm 0.6\), and the peak time of cycle 25, \(2024.1 \pm 0.8 \) (years), which is during April 2023 and November 2024.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Babcock, H.W.: Astrophys. J. 133, 572 (1961)
Brown, G.M., Williams, W.R.: Planet. Space Sci. 17, 455 (1969)
Cameron, R.H.: Highlights of astronomy. In: Montmerle, T. (ed.) 16, XXVIIIth IAU General Assembly (2012)
Choudhuri, A.R., Chatterjee, P., Jiang, J.: Phys. Rev. Lett. 98, 131103 (2007)
Chowdhury, P., Kilcik, A., Yurchyshyn, V., Obridko, V.N., Rozelot, J.P.: Sol. Phys. 294, 142 (2019)
Clette, F., Lefèvre, L.: Sol. Phys. 291, 2629 (2016)
Clette, F., Cliver, E., Lefèvre, L., Svalgaard, L., Vaquero, J., Leibacher, J.: Sol. Phys. 219, 2479 (2016)
Clilverd, M.A., Clarke, E., Ulich, T., Linthe, J., Rishbeth, H.: Geophys. Res. Lett. 110, A07205 (2005)
Dikpati, M., de Toma, G., Gilman, P.A.: Geophys. Res. Lett. 33, L05102 (2006)
Dmitrieva, I.V., Kuzanyan, K.M., Obridko, V.N.: Sol. Phys. 195, 209 (2000)
Du, Z.L.: Ann. Geophys. 29, 1005 (2011)
Du, Z.L.: Astrophys. Space Sci. 338, 9 (2012)
Du, Z.L., Wang, H.N.: Res. Astron. Astrophys. 11, 1482 (2011)
Du, Z.L., Wang, H.N., Zhang, L.Y.: Chin. J. Astron. Astrophys. 8, 477 (2008)
Du, Z.L., Wang, H.N., Zhang, L.Y.: Sol. Phys. 255, 179 (2009a)
Du, Z.L., Li, R., Wang, H.N.: Astron. J. 138, 1998 (2009b)
Han, Y.B., Wang, J.L.: Chin. Astron. Astrophys. 23, 139 (1999)
Han, Y.B., Yin, Z.Q.: Sol. Phys. 294, 107 (2019)
Hathaway, D.H., Wilson, R.M.: Geophys. Res. Lett. 33, 18101 (2006)
Hathaway, D.H., Wilson, R.M., Reichmann, E.J.: Sol. Phys. 151, 177 (1994)
Javaraiah, J.: New Astron. 34, 54 (2015)
Jiang, J., Wang, J.-X., Jiao, Q.-R., Cao, J.-B.: Astrophys. J. 863, 159 (2018)
Kane, R.P.: Ann. Geophys. 28, 1463 (2010)
Li, K.J., Feng, W., Li, F.Y.: J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 135, 72 (2015)
Li, F.Y., Kong, D.F., Xie, J.L., Xiang, N.B., Xu, J.C.: J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 181, 110 (2018)
Lockwood, M., Stamper, R., Wild, M.N.: Nature 399, 437 (1999)
Lukianova, R., Alekseev, G., Mursula, K.: J. Geophys. Res. 114, A02105 (2009)
Martini, D., Mursula, K.: Ann. Geophys. 24, 3411 (2006)
Mininni, P.D., Gomez, D.O., Mindlin, G.B.: Sol. Phys. 208, 167 (2002)
Mursula, K., Martini, D.: J. Geophys. Res. 111, A08209 (2006)
Mursula, K., Martini, D.: Geophys. Res. Lett. 34, L22107 (2007)
Nevanlinna, H.: Ann. Geophys. 22, 1691 (2004)
Nevanlinna, H., Kataja, E.: Geophys. Res. Lett. 20, 2703 (1993)
Ohl, A.I.: Soln. Dannye 12, 84 (1966)
Parker, E.N.: Astrophys. J. 122, 293 (1955)
Petrovay, K.: Living Rev. Sol. Phys. 7, 6 (2010)
Petrovay, K.: Living Rev. Sol. Phys. 17, 2 (2020)
Ramesh, K.B., Lakshmi, N.B.: Sol. Phys. 276, 395 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-011-9866-7. arXiv:1109.2700v1
Schatten, K.H.: Geophys. Res. Lett. 32, 21105 (2005)
Schatten, K.H., Sofia, S.: Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 14, 632–635 (1987)
Schatten, K.H., Scherrer, P.H., Svalgaard, L., Wilcox, J.M.: Geophys. Res. Lett. 5, 411 (1978)
Schatten, K., Myers, D.J., Sofia, S.: Geophys. Res. Lett. 23, 605 (1996)
Singh, P.R., Tiwari, C.M., Saxena, A.K., Agrawal, S.L.: Phys. Scr. 94, 105005 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1088/1402-4896/ab10b6
Svalgaard, L., Cliver, E.W.: J. Geophys. Res. 112, A10111 (2007)
Svalgaard, L., Cliver, E.W., Le Sager, P.: Adv. Space Res. 34, 436 (2004)
Tlatov, A.G.: Astrophys. Space Sci. 323, 221 (2009)
Tlatov, A.G.: Adv. Space Res. 55, 851 (2015)
Upton, L.A., Hathaway, D.H.: Geophys. Res. Lett. 45, 8091 (2018)
Waldmeier, M.: Astron. Mitt. (Zür.) 14, 439 (1939)
Wang, J.L., Han, Y.B.: Astrophys. Rep. 1(Suppl), 76 (1997)
Wang, Y.M., Sheeley, N.R.: Astrophys. J. 694, L11 (2009)
Wilson, R.M.: Sol. Phys. 125, 143 (1990)
Yoshida, A., Yamagishi, H.: Ann. Geophys. 28, 417 (2010)
Acknowledgements
A lot of thanks to the Royal Observatory of Belgium, the National Geophysical Data Center, the International Service of Geomagnetic Indices, and Helsinki, Finland for providing the related data. This work is supported by the National Science Foundation of China (NSFC) through grants 11973058 and 11603040.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Du, Z.L. The solar cycle: predicting the peak of solar cycle 25. Astrophys Space Sci 365, 104 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10509-020-03818-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10509-020-03818-1