Abstract
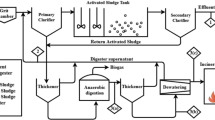
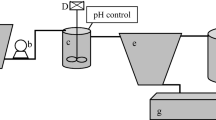
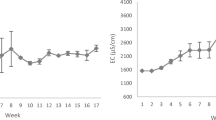
Recirculating aquaculture systems (RAS) can emit total phosphorus (TP) concentrations in their discharge water, which exceed environmentally tolerated restrictions. A compact phosphorus (P) elimination module has been developed and its performance has been tested using the discharge water from a commercial scale freshwater RAS for pike perch (Sander lucioperca) production. To enable its widespread and easy use in practical conditions, the standard principle of chemical-physical phosphorus elimination was adapted to the conditions prevalent in RAS operations. The effect of different precipitants and flocculants in RAS discharge water was studied in laboratory trials. When it came to the TP-elimination performance and the environmental impact, the combination of iron(III) chloride and calcium hydroxide proved highly suitable as the precipitation and flocculation agents. Based on the results that were obtained, a commercial scale P-elimination module was designed. The module was equipped with a 500-L hopper-bottomed reaction tank, dosing units for the precipitation and flocculation agents and valves for the automatic discharge of sludge and cleared water. The TP-elimination potential in different operational modes and retention times was examined. The amounts of excess sludge and cleared water quality were evaluated. The designed 500 L P-elimination module works in automatic batch mode and enables operators to eliminate approx. 95% of the phosphorus emissions from the discharge water from a RAS for annual fish production of about 20 to 25 t. It was possible to achieve TP concentrations of below 1 mg L−1 in the module’s cleared water discharge.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bai S, Zhu Y, Zhang X et al (2010) Enhanced phosphorus removal from municipal wastewater by coagulation with alum and iron salts. In: Paper presented at the 4th International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedical Engineering, Chengdu, 21–23 June 2010
Besaratinia A, Pfeifer GP (2007) A review of mechanisms of acrylamide carcinogenicity. Carcinogenesis 28:519–528
Chen S, Coffin DE, Malone RF (1997) Sludge production and management for recirculating aquacultural systems. J World Aquacult Soc 28:303–315
Ebeling JM, Sibrell PL, Ogden SR, Summerfelt ST (2003) Evaluation of chemical coagulation–flocculation aids for the removal of suspended solids and phosphorus from intensive recirculating aquaculture effluent discharge. Aquac Eng 29:23–42
Galvin RM (1996) Occurrence of metals in water: an overview. Water SA 22:7–18
Grundl T, Delwiche J (1993) Kinetics of ferric oxyhydroxide precipitation. J Contam Hydrol 14:71–97
Hosang W, Bischof W (1998) Abwassertechnik. Teubner, Stuttgart
LfL (2006) Landwirtschaftliche Verwertung von Klärschlamm. LfL-Information. Aviable at https://www.lfl.bayern.de/mam/cms07/publikationen/daten/informationen/p_21327.pdf. Cited 20 Oct 2017
Li T, Wang H, Dong W, Liu T, Ouyang F, Zhang Q (2014) Phosphate removal during Fe(II) oxidation in the presence of Cu(II): characteristics and application for electro-plating wastewater treatment. Sep Purif Technol 132:388–395
Martins CIM, Eding EH, Verdegem MCJ, Heinsbroek LTN, Schneider O, Blancheton JP, d’Orbcastel ER, Verreth JAJ (2010) New developments in recirculating aquaculture systems in Europe: a perspective on environmental sustainability. Aquac Eng 43:83–93
Metcalf, Eddy Inc. (2003) Wastewater engineering: treatment and reuse. McGraw-Hill, New York
Müller-Belecke A, Zienert S, Thürmer C, Kaufhold S, Spranger U (2013) The “self cleaning inherent gas denitrification-reactor” for nitrate elimination in RAS for pike perch (Sander lucioperca) production. Aquac Eng 57:18–23
NASTAQ (2014) Nationaler Strategieplan Aquakultur für Deutschland. Aviable via https://www.portal-fischerei.de/fileadmin/redaktion/dokumente/fischerei/Bund/Nationaler_Strategieplan_Aquakultur_Deutschland.pdf. Cited 20 Oct 2017
Orihel DM, Baulch HM, Casson NJ, North RL, Parsons CT, Seckar DCM, Venkiteswaran JJ (2017) Internal phosphorus loading in Canadian fresh waters: a critical review and data analysis. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 74:2005–2029
Qian JW, Xiang XJ, Yang WY, Wang M, Zheng BQ (2004) Flocculation performance of different polyacrylamide and the relation between optimal dose and critical concentration. Eur Polym J 40:1699–1704
Rümmler F (2010) Kreislauftechnik – Wasseraufbereitung und Wiederverwendung. In: Schmidt-Puckhaber (ed) Fisch vom Hof?! Fischerzeugung in standortunabhängigen Kreislaufanlagen. DLG-Verlag, Frankfurt, p 41
Schreckenbach K, Knösche R, Ebert K (2001) Nutrient and energy content of freshwater fishes. J Appl Ichthyol 17:142–144
Suhr KI, Pedersen LF, Nielsen JL (2014) End-of-pipe single-sludge denitrification in pilot-scale recirculating aquaculture systems. Aquac Eng 62:28–35
van Bussel C, Mahlmann L, Kroeckel S et al (2013) The effect of high ortho-phosphate water levels on growth, feed intake, nutrient utilization and health status of juvenile turbot (Psetta maxima) reared in intensive RAS. Aquac Eng 57:63–70
van Rijn J, Tal Y, Schreier HJ (2006) Denitrification in recirculating systems: theory and applications. Aquac Eng 34:364–376
Weston DP, Lentz RD, Cahn MD, Ogle RS, Rothert AK, Lydy MJ (2009) Toxicity of anionic polyacrylamide formulations when used for erosion control in agriculture. J Environ Qual 38:238–247
Zhang X, Hu J, Spanjers H, van Lier JB (2014) Performance of inorganic coagulants in treatment of backwash waters from a brackish aquaculture recirculation system and digestibility of salty sludge. Aquacult Eng 61:9–16
Funding
The joint project was funded under the trade mark 2817501711 with resources provided by the German Federal Ministry of Food and Agriculture, following a decision by the German Bundestag. Duration: 1 November 2013–31 October 2015.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Müller-Belecke, A., von Plessen, S., Schmidt, G. et al. Design and practical test of a compact phosphorus elimination module for freshwater RAS discharge water. Aquacult Int 26, 1135–1145 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-018-0273-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-018-0273-z