Abstract
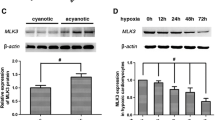
KLF11 is a Krüppel-like factor (KLF) family member, which plays a central role in cardiac hypertrophy and cerebrovascular protection during ischemic insults. However, the roles of KLF11 in hypoxia/reoxygenation (H/R) injury of rat cardiomyocytes H9c2 have not been elucidated. The aim of this study was to evaluate the effects of KLF11 on H/R injury and investigate the molecular mechanisms involved. Here, we found that KLF11 was increased following H/R and reached the highest level with 24 h hypoxia followed by 12 h reoxygenation. Moreover, we found that inhibition of KLF11 by small RNA suppressed cell apoptosis, the activity of caspase3, the expression of cleaved-caspase3 and cytochrome C in the cytoplasm and the damage of mitochondrial membrane induced by H/R in H9c2, suggesting that KLF11 silencing protects against H/R injury. In addition, we observed that knockdown of KLF11 elevated the expression of p-JAK2 and p-STAT3 in H9c2, and AG490, a selective inhibitor of JAK2/STAT3 abrogated the potential roles of KLF11 in cell apoptosis and mitochondrial damage. In aggregates, our results showed that depletion of KLF11 protected H9c2 against H/R injury through activating the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway, suggesting that KLF11 may be provide therapeutic targets for H/R or other heart diseases.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gersh BJ, Sliwa K, Mayosi BM, Yusuf S (2010) Novel therapeutic concepts: the epidemic of cardiovascular disease in the developing world: global implications. Eur Heart J 31(6):642–648
Zweier JL, Talukder MH (2006) The role of oxidants and free radicals in reperfusion injury. Cardiovasc Res 70(2):181–190
Frank A, Bonney M, Bonney S, Weitzel L, Koeppen M, Eckle T (2012) Myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury from basic science to clinical bedside. In: Seminars in cardiothoracic and vascular anesthesia. SAGE Publications, pp 123–132
Hausenloy DJ, Yellon DM (2013) Myocardial ischemia–reperfusion injury: a neglected therapeutic target. J Clin investig 123(1):92–100
Stark GR, Darnell JE (2012) The JAK-STAT pathway at twenty. Immunity 36(4):503–514
Levy DE, Darnell J (2002) Stats: transcriptional control and biological impact. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 3(9):651–662
Barry SP, Townsend PA, Latchman DS, Stephanou A (2007) Role of the JAK–STAT pathway in myocardial injury. Trends Mol Med 13(2):82–89
Cittadini A, Monti MG, Iaccarino G, Castiello MC, Baldi A, Bossone E, Longobardi S, Marra AM, Petrillo V, Saldamarco L (2012) SOCS1 gene transfer accelerates the transition to heart failure through the inhibition of the gp130/JAK/STAT pathway. Cardiovasc Res 96(3):381–390
You L, Li L, Xu Q, Ren J, Zhang F (2011) Postconditioning reduces infarct size and cardiac myocyte apoptosis via the opioid receptor and JAK-STAT signaling pathway. Mol Biol Rep 38(1):437–443
Haghikia A, Ricke-Hoch M, Stapel B, Gorst I, Hilfiker-Kleiner D (2014) STAT3, a key regulator of cell-to-cell communication in the heart. Cardiovasc Res 102(2):281–289
McConnell BB, Yang VW (2010) Mammalian Krüppel-like factors in health and diseases. Physiol Rev 90(4):1337–1381
Pearson R, Fleetwood J, Eaton S, Crossley M, Bao S (2008) Krüppel-like transcription factors: a functional family. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 40(10):1996–2001
Yin K-J, Fan Y, Hamblin M, Zhang J, Zhu T, Li S, Hawse JR, Subramaniam M, Song C-Z, Urrutia R (2013) KLF11 mediates PPARγ cerebrovascular protection in ischaemic stroke. Brain 136(4):1274–1287
Zhang H, Chen Q, Yang M, Zhu B, Cui Y, Xue Y, Gong N, Cui A, Wang M, Shen L (2013) Mouse KLF11 regulates hepatic lipid metabolism. J Hepatol 58(4):763–770
Mathison A, Escande C, Calvo E, Seo S, White T, Salmonson A, Faubion WA Jr, Buttar N, Iovanna J, Lomberk G (2015) Phenotypic characterization of mice carrying homozygous deletion of KLF11, a gene in which mutations cause human neonatal and MODY VII diabetes. Endocrinology 156(10):3581–3595
Zheng Y, Kong Y, Li F (2014) Krüppel-like transcription factor 11 (KLF11) overexpression inhibits cardiac hypertrophy and fibrosis in mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 443(2):683–688
Yue R, Hu H, Yiu KH, Luo T, Zhou Z, Xu L, Zhang S, Li K, Yu Z (2012) Lycopene protects against hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced apoptosis by preventing mitochondrial dysfunction in primary neonatal mouse cardiomyocytes. PloS one 7(11):e50778
Haghikia A, Stapel B, Hoch M, Hilfiker-Kleiner D (2011) STAT3 and cardiac remodeling. Heart Fail Rev 16(1):35–47
Thind GS, Agrawal PR, Hirsh B, Saravolatz L, Chen-Scarabelli C, Narula J, Scarabelli TM (2015) Mechanisms of myocardial ischemia–reperfusion injury and the cytoprotective role of minocycline: scope and limitations. Future Cardiol 11(1):61–76
Fan Y, Guo Y, Zhang J, Subramaniam M, Song C-Z, Urrutia R, Chen YE (2012) Krüppel-like factor-11, a transcription factor involved in diabetes mellitus, suppresses endothelial cell activation via the nuclear factor-κB signaling pathway. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 32(12):2981–2988
Gohla G, Krieglstein K, Spittau B (2008) Tieg3/Klf11 induces apoptosis in OLI-neu cells and enhances the TGF-βeu cells and enhances the TGF-β signaling pathway by transcriptional repression of Smad7. J Cell Biochem 104(3):850–861
Wang Z, Spittau B, Behrendt M, Peters B, Krieglstein K (2007) Human TIEG2/KLF11 induces oligodendroglial cell death by downregulation of Bcl-XL expression. J Neural transm 114(7):867–875
Mathison A, Grzenda A, Lomberk G, Velez G, Buttar N, Tietz P, Hendrickson H, Liebl A, Xiong YY, Gores G (2013) Role for Kruppel-like transcription factor 11 in mesenchymal cell function and fibrosis. PloS one 8:e75311
Loft A, Forss I, Siersbæk MS, Schmidt SF, Larsen A-SB, Madsen JGS, Pisani DF, Nielsen R, Aagaard MM, Mathison A (2014) Browning of human adipocytes requires KLF11 and reprogramming of PPARγ superenhancers. Genes Dev 29(1):7–22
Babbitt SE, Sutherland MC, San Francisco B, Mendez DL, Kranz RG (2015) Mitochondrial cytochrome c biogenesis: no longer an enigma. Trends Biochem Sci 40(8):446–455
Bolli R, Dawn B, Xuan Y-T (2003) Role of the JAK–STAT pathway in protection against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. Trends Cardiovasc Med 13(2):72–79
Freitas MCS, Uchida Y, Zhao D, Ke B, Busuttil RW, Kupiec-Weglinski JW (2010) Blockade of Janus kinase-2 signaling ameliorates mouse liver damage due to ischemia and reperfusion. Liver. Transplantation 16(5):600–610
Wang Y, Wang D, Zhang L, Ye F, Li M, Wen K (2016) Role of JAK-STAT pathway in reducing cardiomyocytes hypoxia/reoxygenation injury induced by S1P postconditioning. Eur J Pharmacol 784:129–136
Li L, Li M, Li Y, Sun W, Wang Y, Bai S et al (2016) Exogenous H2S contributes to recovery of ischemic post-conditioning-induced cardioprotection by decrease of ROS level via down-regulation of NF-κB and JAK2-STAT3 pathways in the aging cardiomyocytes. Cell Biosci 6(1):1
Puigdecanet E, Espinet B, Lozano J, Sumoy L, Bellosillo B, Arenillas L, Alvarez-Larran A, Sole F, Serrano S, Besses C (2008) Gene expression profiling distinguishes JAK2V617F-negative from JAK2V617F-positive patients in essential thrombocythemia. Leukemia 22(7):1368–1376
Tetreault M-P, Alrabaa R, McGeehan M, Katz JP (2012) Krüppel-like factor 5 protects against murine colitis and activates JAK-STAT signaling in vivo. PloS one 7(5):e38338
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Shi, X., Li, J. et al. Knockdown of KLF11 attenuates hypoxia/reoxygenation injury via JAK2/STAT3 signaling in H9c2. Apoptosis 22, 510–518 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-016-1327-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-016-1327-1