Abstract
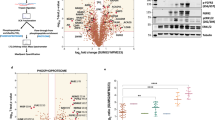
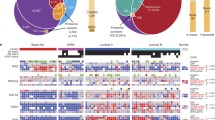
A431 cells, derived from epidermoid carcinoma, overexpress the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and when treated with a high dose of EGF will undergo apoptosis. We exploited microarray and proteomics techniques and network prediction to study the regulatory mechanisms of EGF-induced apoptosis in A431 cells. We observed significant changes in gene expression in 162 genes, approximately evenly split between pro-apoptotic and anti-apoptotic genes and identified 30 proteins from the proteomic data that had either pro or anti-apoptotic annotation. Our correlation analysis of gene expression and proteome modeled a number of distinct sub-networks that are associated with the onset of apoptosis, allowing us to identify specific pathways and components. These include components of the interferon signalling pathway, and down stream components, including cytokines and suppressors of cytokine signalling. A central component of almost all gene expression sub-networks identified was TP53, which is mutated in A431 cells, and was down regulated. This down regulation of TP53 appeared to be correlated with proteomic sub-networks of cytoskeletal or cell adhesion components that might induce apoptosis by triggering cytochrome C release. Of the only three genes also differentially expressed as proteins, only serpinb1 had a known association with apoptosis. We confirmed that up regulation and cleavage of serpinb1 into L-DNAaseII was correlated with the induction of apoptosis. It is unlikely that a single pathway, but more likely a combination of pathways is needed to trigger EGF induced apoptosis in A431cells.






Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
12 December 2017
The original version of this article unfortunately contained a mistake. The affiliation of first author Dr. Ibrahim Alanazi was incorrect.
References
Olayioye MA, Neve RM, Lane HA, Hynes NE (2000) The ErbB signaling network: receptor heterodimerization in development and cancer. EMBO J 19:3159–3167
Normanno N, Bianco C, Strizzi L et al (2005) The ErbB receptors and their ligands in cancer: an overview. Curr Drug Targets 6:243–257
Verbeek BS, Adriaansen-Slot SS, Vroom TM, Beckers T, Rijksen G (1998) Overexpression of EGFR and c-erbB2 causes enhanced cell migration in human breast cancer cells and NIH3T3 fibroblasts. FEBS Lett 425:145–150
Slamon DJ, Godolphin W, Jones LA et al (1989) Studies of the HER-2/neu proto-oncogene in human breast and ovarian cancer. Science 244:707–712
Rodeck U, Jost M, Kari C et al (1997) EGF-R dependent regulation of keratinocyte survival. J Cell Sci 110(Pt 2):113–121
Kari C, Chan TO, Rocha De Quadros M, Rodeck U (2003) Targeting the epidermal growth factor receptor in cancer: apoptosis takes center stage. Cancer Res 63:1–5
Schneeweiss A, Kolay S, Aulmann S et al (2004) Induction of remission in a patient with metastatic breast cancer refractory to trastuzumab and chemotherapy following treatment with gefitinib (‘Iressa’, ZD1839). Anticancer Drugs 15:235–238
Ciardiello F, Tortora G (2001) A novel approach in the treatment of cancer: targeting the epidermal growth factor receptor. Clin Cancer Res 7:2958–2970
Janmaat ML, Giaccone G (2003) The epidermal growth factor receptor pathway and its inhibition as anticancer therapy. Drugs Today (Barc) 39(Suppl C):61–80
Solomon B, Hagekyriakou J, Trivett MK, Stacker SA, McArthur GA, Cullinane C (2003) EGFR blockade with ZD1839 (“Iressa”) potentiates the antitumor effects of single and multiple fractions of ionizing radiation in human A431 squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Radiat Oncol 55:713–723
Schmidt M, Lichtner RB (2002) EGF receptor targeting in therapy-resistant human tumors. Drug Resist Updat 5:11–18
Woodburn JR (1999) The epidermal growth factor receptor and its inhibition in cancer therapy. Pharmacol Ther 82:241–250
Gill GN, Lazar CS (1981) Increased phosphotyrosine content and inhibition of proliferation in EGF-treated A431 cells. Nature 293:305–307
Barnes DW (1982) Epidermal growth-factor inhibits growth of A431 human epidermoid carcinoma in serum-free cell-culture. J Cell Biol 93:1–4
Gill GN, Buss JE, Lazar CS, Lifshitz A, Cooper JA (1982) Role of epidermal growth factor-stimulated protein kinase in control of proliferation of A431 cells. J Cell Biochem 19:249–257
Gulli LF, Palmer KC, Chen YQ, Reddy KB (1996) Epidermal growth factor-induced apoptosis in A431 cells can be reversed by reducing the tyrosine kinase activity. Cell Growth Differ 7:173–178
Weinstein EJ, Grimm S, Leder P (1998) The oncogene heregulin induces apoptosis in breast epithelial cells and tumors. Oncogene 17:2107–2113
Armstrong DK, Kaufmann SH, Ottaviano YL et al (1994) Epidermal growth factor-mediated apoptosis of MDA-MB-468 human breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 54:5280–5283
Pinkas-Kramarski R, Alroy I, Yarden Y (1997) ErbB receptors and EGF-like ligands: cell lineage determination and oncogenesis through combinatorial signaling. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia 2:97–107
Bromberg JF, Fan Z, Brown C, Mendelsohn J, Darnell JE Jr (1998) Epidermal growth factor-induced growth inhibition requires Stat1 activation. Cell Growth Differ 9:505–512
Chin YE, Kitagawa M, Kuida K, Flavell RA, Fu XY (1997) Activation of the STAT signaling pathway can cause expression of caspase 1 and apoptosis. Mol Cell Biol 17:5328–5337
Watanabe G, Kaganoi J, Imamura M et al (2001) Progression of esophageal carcinoma by loss of EGF-STAT1 pathway. Cancer J 7:132–139
Ichiba M, Miyazaki Y, Kitamura S (2002) Epidermal growth factor inhibits the growth of TE8 esophageal cancer cells through the activation of STAT1. J Gastroenterol 37:497–503
Kirchhoff S, Hauser H (1999) Cooperative activity between HER oncogenes and the tumor suppressor IRF-1 results in apoptosis. Oncogene 18:3725–3736
Romeo G, Fiorucci G, Chiantore MV, Percario ZA, Vannucchi S, Affabris E (2002) IRF-1 as a negative regulator of cell proliferation. J Interferon Cytokine Res 22:39–47
Kroger A, Dallugge A, Kirchhoff S, Hauser H (2003) IRF-1 reverts the transformed phenotype of oncogenically transformed cells in vitro and in vivo. Oncogene 22:1045–1056
Cuadrado A, Garcia-Fernandez LF, Gonzalez L et al (2003) Aplidin induces apoptosis in human cancer cells via glutathione depletion and sustained activation of the epidermal growth factor receptor, Src, JNK, and p38 MAPK. J Biol Chem 278:241–250
Mitsiades CS, Ocio EM, Pandiella A et al (2008) Aplidin, a marine organism-derived compound with potent antimyeloma activity in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Res 68:5216–5225
Conesa A, Nueda MJ, Ferrer A, Talon M (2006) maSigPro: a method to identify significantly differential expression profiles in time-course microarray experiments. Bioinformatics 22:1096–1102
Kopetz VA, Penno MA, Hoffmann P, Wilson DP, Beltrame JF (2012) Potential mechanisms of the acute coronary syndrome presentation in patients with the coronary slow flow phenomenon—insight from a plasma proteomic approach. Int J Cardiol 156:84–91
Wu G, Stein L (2012) A network module-based method for identifying cancer prognostic signatures. Genome Biol 13:R112
Yuryev A, Mulyukov Z, Kotelnikova E et al (2006) Automatic pathway building in biological association networks. BMC Bioinformatics 7:171
Follis AV, Chipuk JE, Fisher JC et al (2013) PUMA binding induces partial unfolding within BCL-xL to disrupt p53 binding and promote apoptosis. Nat Chem Biol 9:163–168
Oh J, Kim SH, Ahn S, Lee CE (2012) Suppressors of cytokine signaling promote Fas-induced apoptosis through downregulation of NF-kappa B and mitochondrial Bfl-1 in leukemic T cells. J Immunol 189:5561–5571
Contri A, Brunati AM, Trentin L et al (2005) Chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells contain anomalous Lyn tyrosine kinase, a putative contribution to defective apoptosis. J Clin Invest 115:369–378
Keane MM, Rivero-Lezcano OM, Mitchell JA, Robbins KC, Lipkowitz S (1995) Cloning and characterization of cbl-b: a SH3 binding protein with homology to the c-cbl proto-oncogene. Oncogene 10:2367–2377
Darnell JE Jr, Kerr IM, Stark GR (1994) Jak-STAT pathways and transcriptional activation in response to IFNs and other extracellular signaling proteins. Science 264:1415–1421
Levy DE (1995) Interferon induction of gene-expression through the Jak-Stat Pathway. Semin Virol 6:181–189
Fu XY, Zhang JJ (1993) Transcription factor p91 interacts with the epidermal growth factor receptor and mediates activation of the c-fos gene promoter. Cell 74:1135–1145
Stein S, Thomas EK, Herzog B et al (2004) NDRG1 is necessary for p53-dependent apoptosis. J Biol Chem 279:48930–48940
Torriglia A, Lepretre C, Padron-Barthe L, Chahory S, Martin E (2008) Molecular mechanism of L-DNase II activation and function as a molecular switch in apoptosis. Biochem Pharmacol 76:1490–1502
Padron-Barthe L, Courta J, Lepretre C, Nagbou A, Torriglia A (2008) Leukocyte elastase inhibitor, the precursor of L-DNase II, inhibits apoptosis by interfering with caspase-8 activation. Biochim Biophys Acta 1783:1755–1766
Kamath S, Buolamwini JK (2006) Targeting EGFR and HER-2 receptor tyrosine kinases for cancer drug discovery and development. Med Res Rev 26:569–594
Chin YE, Kitagawa M, Su WC, You ZH, Iwamoto Y, Fu XY (1996) Cell growth arrest and induction of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21 WAF1/CIP1 mediated by STAT1. Science 272:719–722
Gilmour KC, Pine R, Reich NC (1995) Interleukin 2 activates STAT5 transcription factor (mammary gland factor) and specific gene expression in T lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:10772–10776
Schere-Levy C, Buggiano V, Quaglino A et al (2003) Leukemia inhibitory factor induces apoptosis of the mammary epithelial cells and participates in mouse mammary gland involution. Exp Cell Res 282:35–47
Chustz RT, Nagarkar DR, Poposki JA et al (2011) Regulation and function of the IL-1 family cytokine IL-1F9 in human bronchial epithelial cells. Am J Resp Cell Mol 45:145–153
Minamoto S, Ikegame K, Ueno K et al (1997) Cloning and functional analysis of new members of STAT induced STAT inhibitor (SSI) family: SSI-2 and SSI-3. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 237:79–83
Wong RPC, Tsang WP, Chau PY, Co NN, Tsang TY, Kwok TT (2007) p53-R273H gains new function in induction of drug resistance through down-regulation of procaspase-3. Mol Cancer Ther 6:1054–1061
Yuan W, Collado-Hidalgo A, Yufit T, Taylor M, Varga J (1998) Modulation of cellular tryptophan metabolism in human fibroblasts by transforming growth factor-beta: selective inhibition of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase and tryptophanyl-tRNA synthetase gene expression. J Cell Physiol 177:174–186
Tseng MY, Liu SY, Chen HR et al (2009) Serine protease inhibitor (SERPIN) B1 promotes oral cancer cell motility and is over-expressed in invasive oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Oncol 45:771–776
Fombonne J, Padron L, Enjalbert A, Krantic S, Torriglia A (2006) A novel paraptosis pathway involving LEI/L-DNaseII for EGF-induced cell death in somato-lactotrope pituitary cells. Apoptosis 11:367–375
Papadopoulou N, Charalampopoulos I, Alevizopoulos K, Gravanis A, Stournaras C (2008) Rho/ROCK/actin signaling regulates membrane androgen receptor induced apoptosis in prostate cancer cells. Exp Cell Res 314:3162–3174
Gourlay CW, Ayscough KR (2006) Actin-induced hyperactivation of the Ras signaling pathway leads to apoptosis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol 26:6487–6501
Wang C, Zhou GL, Vedantam S, Li P, Field J (2008) Mitochondrial shuttling of CAP1 promotes actin- and cofilin-dependent apoptosis. J Cell Sci 121:2913–2920
Giacca M (2005) HIV-1 Tat, apoptosis and the mitochondria: a tubulin link? Retrovirology 2:7
Utsumi T, Sakura N, Nakano K, Ishisaka R (2003) C-terminal 15 kDa fragment of cytoskeletal actin is posttranslationally N-myristoylated upon caspase-mediated cleavage and targeted to mitochondria. FEBS Lett 539:37–44
Parlato S, Giammarioli AM, Logozzi M et al (2000) CD95 (APO-1/Fas) linkage to the actin cytoskeleton through ezrin in human T lymphocytes: a novel regulatory mechanism of the CD95 apoptotic pathway. EMBO J 19:5123–5134
Chan HL, Chou HC, Duran M et al (2010) Major role of epidermal growth factor receptor and Src kinases in promoting oxidative stress-dependent loss of adhesion and apoptosis in epithelial cells. J Biol Chem 285:4307–4318
Yao WJ, Gu L, Sun DG, Ka WB, Wen ZY, Chien S (2003) Wild type p53 gene causes reorganization of cytoskeleton and, therefore, the impaired deformability and difficult migration of murine erythroleukemia cells. Cell Motil Cytoskelet 56:1–12
Guo F, Gao Y, Wang L, Zheng Y (2003) p19Arf-p53 tumor suppressor pathway regulates cell motility by suppression of phosphoinositide 3-kinase and Rac1 GTPase activities. J Biol Chem 278:14414–14419
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
A correction to this article is available online at https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-017-1431-x.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alanazi, I., Ebrahimie, E., Hoffmann, P. et al. Combined gene expression and proteomic analysis of EGF induced apoptosis in A431 cells suggests multiple pathways trigger apoptosis. Apoptosis 18, 1291–1305 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-013-0887-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-013-0887-6