Abstract
“Psychrodesulfovibrio”, a proposed genus within the family Desulfovibrionaceae, is a group of sulfate-reducing bacteria with biogeochemical significance but restricted child taxa availability. In this study, a strictly anaerobic bacterium, designed strain FT415T, was isolated from mangrove sediments in Futian Mangrove Nature Reserve in Shenzhen, China. The strain was Gram-stain-negative, motile, and vibrio-shaped with a single polar flagellum, which grew at the temperature range of 15–42 °C (optimum 37 °C), pH range of 6.0–7.5 (optimum 6.8), and in the presence of 0–36 g l−1 NaCl (optimum 6 g l−1 NaCl). In the presence of sulfate, electron donors including lactate, ethanol, pyruvate, malate, fumarate, succinate, cysteine, and glycerol were incompletely oxidized to acetate, and H2 and formate were used as electron donors with acetate as the carbon source by strain FT415T. Sulfate, thiosulfate, sulfide, and anthraquinone-2,6-disulfonate were reduced in the presence of lactate. Fe(III) oxide was reduced without cell growth. Fermentative growth was observed with pyruvate and cysteine. Vitamins were not required for growth. The major cellular fatty acids (> 10%) were C16:0, summed feature 10 (C18:1 c11/t9/t6 and/or unknown ECL 17.834), C16:1 cis 9, and C18:0. The major polar lipids were phosphatidylethanolamine, phospholipids, and aminolipids. The predominant menaquinone was MK-6(H2). The genomic DNA G+C content was 56.7%. Phylogenetic analysis showed that strain FT415T shared a 98.1% similarity in 16S rRNA gene sequence, an average nucleotide identity value of 84.0%, an average amino-acid identity value of 85.4%, and a digital DNA-DNA hybridization value of 25.7% with its closest relative Desulfovibrio subterraneus HN2T, which has been proposed to be transferred to the genus “Psychrodesulfovibrio”. Based on phenotypic, phylogenetic, and genotypic evidence, a new species of the family Desulfovibrionaceae, Desulfovibrio mangrovi sp. nov. was proposed with the type strain FT415T (=GDMCC 1.3410T=KCTC 25525T).


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The 16S rRNA gene and genome sequences from the strain FT415T are available in NCBI under the accession numbers: ON970160 and CP104208, respectively. The genome sequence is additionally available in IMG with genome ID 2952831780.
Abbreviations
- SRB:
-
Sulfate-reducing bacteria
- ANI:
-
Average nucleotide identity
- AAI:
-
Average amino acid identity
- dDDH:
-
Digital DNA-DNA hybridization
- UBCG:
-
Up-to-date bacterial core gene
- TEM:
-
Transmission electron microscopy
- AQDS:
-
Anthraquinone-2,6-disulfonate
- DMSO:
-
Dimethyl sulfoxide
- OD:
-
Optical density
- MES:
-
2-(N-Morpholine) ethanesulfonic acid
- HEPES:
-
N-2-Hydroxyethylpiperazine-N’-2-ethanesulfonic acid
References
Afkar E, Reguera G, Schiffer M, Lovley DR (2005) A novel Geobacteraceae-specific outer membrane protein J (OmpJ) is essential for electron transport to Fe(III) and Mn(IV) oxides in Geobacter sulfurreducens. BMC Microbiol 5:41. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2180-5-41
Alongi DM (2014) Carbon cycling and storage in mangrove forests. Ann Rev Mar Sci 6:195–219. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-marine-010213-135020
Arndt D, Grant JR, Marcu A, Sajed T, Pon A, Liang Y, Wishart DS (2016) PHASTER: a better, faster version of the PHAST phage search tool. Nucleic Acids Res 44:W16-21. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw387
Castro HF, Williams NH, Ogram A (2000) Phylogeny of sulfate-reducing bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 31:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6941.2000.tb00665.x
Chang Y-J, Chang Y-T, Hung C-H, Lee J-W, Liao H-M, Chou H-L (2014) Microbial community analysis of anaerobic bio-corrosion in different ORP profiles. Int Biodeterior Biodegradation 95:93–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2014.04.008
Chaumeil P-A, Mussig AJ, Hugenholtz P, Parks, DH (2019) GTDB-Tk: a toolkit to classify genomes with the Genome Taxonomy Database. Bioinformatics 36:1925–1927. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btz848
Chun J, Oren A, Ventosa A, Christensen H, Arahal DR, da Costa MS, Rooney AP, Yi H, Xu XW, De Meyer S, Trujillo ME (2018) Proposed minimal standards for the use of genome data for the taxonomy of prokaryotes. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 68:461–466. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.002516
Combet-Blanc Y, Ollivier B, Streicher C, Patel BKC, Dwiviedi PP, Pot B, Prensier G, Garcia J-L (1995) Bacillus thermoamylovorans sp. nov., a moderately thermophilic and amylolytic bacterium. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 45:9–16. https://doi.org/10.1099/00207713-45-1-9
Edgar RC (2004) MUSCLE: multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res 32:1792–1797. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkh340
Felsenstein J (1981) Evolutionary trees from DNA sequences: a maximum likelihood approach. J Mol Evol 17:368–376. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01734359
Fitch WM (1971) Toward defining the course of evolution: minimum change for a specific tree topology. Syst Biol 20:406–416. https://doi.org/10.1093/sysbio/20.4.406
Galushko A, Kuever J (2020a) Desulfovibrionaceae. In: Trujillo ME et al (eds) Bergey's manual of systematics of archaea and bacteria, pp 1–13
Galushko A, Kuever J (2020b) “Psychrodesulfovibrio” gen. nov. In: Trujillo ME et al (eds) Bergey's manual of systematics of archaea and bacteria, pp 1–5
Geets J, Borremans B, Diels L, Springael D, Vangronsveld J, van der Lelie D, Vanbroekhoven K (2006) DsrB gene-based DGGE for community and diversity surveys of sulfate-reducing bacteria. J Microbiol Methods 66:194–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mimet.2005.11.002
Gerhardt P, Murray R, Wood W, Krieg N (1994) Methods for general and molecular bacteriology. American Society for Microbiology, Washintong, DC
Grant JR, Stothard P (2008) The CGView Server: a comparative genomics tool for circular genomes. Nucleic Acids Res 36:W181-184. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkn179
Holmes DE, Ueki T, Tang H-Y, Zhou J, Smith JA, Chaput G, Lovley DR (2019) A membrane-bound cytochrome enables Methanosarcina acetivorans to conserve energy from extracellular electron transfer. mBio 10:e00789–00719. https://doi.org/10.1128/mBio.00789-19
Jain C, Rodriguez RL, Phillippy AM, Konstantinidis KT, Aluru S (2018) High throughput ANI analysis of 90K prokaryotic genomes reveals clear species boundaries. Nat Commun 9:5114. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-07641-9
Kokoschka S, Dreier A, Romoth K, Taviani M, Schäfer N, Reitner J, Hoppert M (2015) Isolation of anaerobic bacteria from terrestrial mud volcanoes (Salse di Nirano, Northern Apennines, Italy). Geomicrobiol J 32:355–364. https://doi.org/10.1080/01490451.2014.940632
Konstantinidis KT, Tiedje JM (2005) Towards a genome-based taxonomy for prokaryotes. J Bacteriol 187:6258–6264. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.187.18.6258-6264.2005
Kovacs N (1956) Identification of Pseudomonas pyocyanea by the oxidase reaction. Nature 178:703–703. https://doi.org/10.1038/178703a0
Kudo K, Yamaguchi N, Makino T, Ohtsuka T, Kimura K, Dong DT, Amachi S (2013) Release of arsenic from soil by a novel dissimilatory arsenate-reducing bacterium, Anaeromyxobacter sp. strain PSR-1. Appl Environ Microbiol 79:4635–4642. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00693-13
Kumar S, Stecher G, Li M, Knyaz C, Tamura K (2018) MEGA X: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol Biol Evol 35:1547–1549. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msy096
Kushkevych I, Kovářová A, Dordevic D, Gaine J, Kollar P, Vítězová M, Rittmann SKMR (2021) Distribution of sulfate-reducing bacteria in the environment: cryopreservation techniques and their potential storage application. Processes. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9101843
Lane D (1991) 16S/23S rRNA sequencing. In: Stackebrandt EGM (ed) Nucleic acid techniques in bacterial systematics. Wiley, Chichester, pp 115–175
Letunic I, Bork P (2006) Interactive Tree Of Life (iTOL): an online tool for phylogenetic tree display and annotation. Bioinformatics 23:127–128. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btl529
Li M, Fang A, Yu X, Zhang K, He Z, Wang C, Peng Y, Xiao F, Yang T, Zhang W, Zheng X, Zhong Q, Liu X, Yan Q (2021) Microbially-driven sulfur cycling microbial communities in different mangrove sediments. Chemosphere 273:128597. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128597
Li X, Lan SM, Zhu ZP, Zhang C, Zeng GM, Liu YG, Cao WC, Song B, Yang H, Wang SF, Wu SH (2018) The bioenergetics mechanisms and applications of sulfate-reducing bacteria in remediation of pollutants in drainage: a review. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 158:162–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.04.025
Liu Y, Pei T, Du J, Chao M, Deng MR, Zhu H (2021) Roseibium litorale sp. nov., isolated from a tidal flat sediment and proposal for the reclassification of Labrenzia polysiphoniae as Roseibium polysiphoniae comb. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.004634
Lovley DR, Phillips EJ (1986) Organic matter mineralization with reduction of ferric iron in anaerobic sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol 51:683–689. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.51.4.683-689.1986
Lovley DR, Phillips EJP (1987) Rapid assay for microbially reducible ferric iron in aquatic sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol 53:1536–1540. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.53.7.1536-1540.1987
Maity JP, Liu CC, Nath B, Bundschuh J, Kar S, Jean JS, Bhattacharya P, Liu JH, Atla SB, Chen CY (2011) Biogeochemical characteristics of Kuan-Tzu-Ling, Chung-Lun and Bao-Lai hot springs in southern Taiwan. J Environ Sci Health A Tox Hazard Subst Environ Eng 46:1207–1217. https://doi.org/10.1080/10934529.2011.598788
Marquis TJ, Williams VJ, Banach DB (2021) Septic arthritis caused by Desulfovibrio desulfuricans: a case report and review of the literature. Anaerobe 70:102407. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anaerobe.2021.102407
Meier-Kolthoff JP, Auch AF, Klenk H-P, Göker M (2013) Genome sequence-based species delimitation with confidence intervals and improved distance functions. BMC Bioinform 14:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-14-60
Meier-Kolthoff JP, Carbasse JS, Peinado-Olarte RL, Göker M (2021) TYGS and LPSN: a database tandem for fast and reliable genome-based classification and nomenclature of prokaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res 50:D801–D807. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkab902
Minnikin DE, O’Donnell AG, Goodfellow M, Alderson G, Athalye M, Schaal A, Parlett JH (1984) An integrated procedure for the extraction of bacterial isoprenoid quinones and polar lipids. J Microbiol Meth 2:233–241. https://doi.org/10.1016/0167-7012(84)90018-6
Miró L, Moretó M, Amat C, Polo J, Pérez-Bosque A (2020) Aging effects on gut microbiota in SAMP8 mice. Proceedings 61:25. https://doi.org/10.3390/IECN2020-06995
Murros KE, Huynh VA, Takala TM, Saris PEJ (2021) Desulfovibrio bacteria are associated with Parkinson’s disease. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 11:652617. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2021.652617
Na SI, Kim YO, Yoon SH, Ha SM, Baek I, Chun J (2018) UBCG: Up-to-date bacterial core gene set and pipeline for phylogenomic tree reconstruction. J Microbiol 56:280–285. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-018-8014-6
Nguyen L-T, Schmidt HA, von Haeseler A, Minh BQ (2014) IQ-TREE: A fast and effective stochastic algorithm for estimating maximum-likelihood phylogenies. Mol Biol Evol 32:268–274. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msu300
Park M-J, Kim YJ, Park M, Yu J, Namirimu T, Roh Y-R, Kwon KK (2022) Establishment of genome based criteria for classification of the family Desulfovibrionaceae and proposal of two novel genera, Alkalidesulfovibrio gen. nov. and Salidesulfovibrio gen. nov. Front Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2022.738205
Postgate J (1959) A diagnostic reaction of Desulphovibrio desulphuricans. Nature 183:481–482. https://doi.org/10.1038/183481b0
Reynolds ES (1963) The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol 17:208–212. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.17.1.208
Richter M, Rossello-Mora R (2009) Shifting the genomic gold standard for the prokaryotic species definition. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:19126–19131. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0906412106
Rodriguez-R LM, Konstantinidis KT (2016) The enveomics collection: a toolbox for specialized analyses of microbial genomes and metagenomes. PeerJ Preprints 4:e1900v1. https://doi.org/10.7287/peerj.preprints.1900v1
Ryzhmanova Y, Abashina T, Petrova D, Shcherbakova V (2019) Desulfovibrio gilichinskyi sp. nov., a cold-adapted sulfate-reducing bacterium from a Yamal Peninsula cryopeg. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 69:1081–1086. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.003272
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040454
Sakaguchi T, Arakaki A, Matsunaga T (2002) Desulfovibrio magneticus sp. nov., a novel sulfate-reducing bacterium that produces intracellular single-domain-sized magnetite particles. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 52:215–221. https://doi.org/10.1099/00207713-52-1-215
Sasi Jyothsna TS, Sasikala C, Ramana ChV (2008) Desulfovibrio psychrotolerans sp. nov., a psychrotolerant and moderately alkaliphilic sulfate-reducing deltaproteobacterium from the Himalayas. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 58:821–825. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.65402-0
Sayavedra L, Li T, Bueno Batista M, Seah BKB, Booth C, Zhai Q, Chen W, Narbad A (2021) Desulfovibrio diazotrophicus sp. nov., a sulfate-reducing bacterium from the human gut capable of nitrogen fixation. Environ Microbiol 23:3164–3181. https://doi.org/10.1111/1462-2920.15538
Tang Y-Q, Ji P, Lai G-L, Chi C-Q, Liu Z-S, Wu X-L (2012) Diverse microbial community from the coalbeds of the Ordos Basin, China. Int J Coal Geol 90:21–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coal.2011.09.009
Ueki T, Lovley DR (2022) Desulfovibrio vulgaris as a model microbe for the study of corrosion under sulfate‐reducing conditions. mLife 1:13–20. https://doi.org/10.1002/mlf2.12018
Ueno A, Tamazawa S, Tamamura S, Murakami T, Kiyama T, Inomata H, Amano Y, Miyakawa K, Tamaki H, Naganuma T, Kaneko K (2021) Desulfovibrio subterraneus sp. nov., a mesophilic sulfate-reducing deltaproteobacterium isolated from a deep siliceous mudstone formation. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.004683
Vandieken V, Knoblauch C, Jorgensen BB (2006) Desulfovibrio frigidus sp. nov. and Desulfovibrio ferrireducens sp. nov., psychrotolerant bacteria isolated from Arctic fjord sediments (Svalbard) with the ability to reduce Fe(III). Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 56:681–685. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.64057-0
Wick RR, Judd LM, Gorrie CL, Holt KE (2017) Unicycler: resolving bacterial genome assemblies from short and long sequencing reads. PLoS Comput Biol 13:e1005595. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1005595
Wu S, Li R, Xie S, Shi C (2019) Depth-related change of sulfate-reducing bacteria community in mangrove sediments: the influence of heavy metal contamination. Mar Pollut Bull 140:443–450. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2019.01.042
Xu L, Dong Z, Fang L, Luo Y, Wei Z, Guo H, Zhang G, Gu YQ, Coleman-Derr D, Xia Q, Wang Y (2019) OrthoVenn2: a web server for whole-genome comparison and annotation of orthologous clusters across multiple species. Nucleic Acids Res 47:W52–W58. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkz333
Yarza P, Richter M, Peplies J, Euzeby J, Amann R, Schleifer KH, Ludwig W, Glockner FO, Rossello-Mora R (2008) The All-Species Living Tree project: a 16S rRNA-based phylogenetic tree of all sequenced type strains. Syst Appl Microbiol 31:241–250. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.syapm.2008.07.001
Yoon SH, Ha SM, Kwon S, Lim J, Kim Y, Seo H, Chun J (2017) Introducing EzBioCloud: a taxonomically united database of 16S rRNA gene sequences and whole-genome assemblies. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 67:1613–1617. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.001755
Zhang C-J, Pan J, Duan C-H, Wang Y-M, Liu Y, Sun J, Zhou H-C, Song X, Li M (2019) Prokaryotic diversity in mangrove sediments across Southeastern China fundamentally differs from that in other biomes. mSystems 4:e00442–00419. https://doi.org/10.1128/mSystems.00442-19
Zhou J, Holmes DE, Tang H-Y, Lovley DR (2021) Correlation of key physiological properties of Methanosarcina isolates with environment of origin. Appl Environ Microbiol 87:e00731-e1721. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00731-21
Acknowledgements
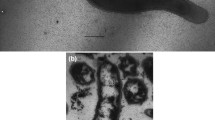
We thank the Instrument Analysis Center of Shenzhen University for the assistance with collection of transmission electron microscopy images.
Funding
This research was supported by the National Science and Technology Fundamental Resources Investigation Program of China (2019FY100700), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (42207144, 32225003, 31970105, 92251306, 32070108), the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2021TQ0212), the Innovation Team Project of Universities in Guangdong Province (2020KCXTD023), and the Shenzhen Science and Technology Program (JCYJ20200109105010363, KCXFZ20201221173404012).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JZ and ML designed the research. JZ isolated the strain, performed the research, analyzed the data, and wrote the manuscript. CJZ and ML offered critical revisions of the manuscript. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, J., Zhang, CJ. & Li, M. Desulfovibrio mangrovi sp. nov., a sulfate-reducing bacterium isolated from mangrove sediments: a member of the proposed genus “Psychrodesulfovibrio”. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 116, 499–510 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-023-01820-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-023-01820-5