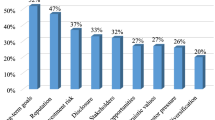
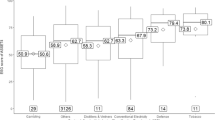
Abstract
Supplier selection is an important decision-making problem in supply chain management. Selecting appropriate suppliers based on sustainability criteria including economic, environmental, and social criteria can help companies move toward sustainable development. Data envelopment analysis (DEA) is applied to recognize the most sustainable supplier. However, conventional DEA models can be applied only to performance measurement systems characterized by positive input–output data. However, in real world, data can be negative. We propose a new DEA model for evaluating sustainability of suppliers in presence of negative data and volume discounts. Also, we present a super-efficiency model for ranking suppliers. In addition, we prove some main properties of our proposed method. Finally, we present a case study to demonstrate applicability of proposed model.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdollahi, M., Arvan, M., & Razmi, J. (2015). An integrated approach for supplier portfolio selection: Lean or agile? Expert Systems with Applications, 42(1), 679–690. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2014.08.019.
Ahmady, N., Azadi, M., Sadeghi, S. A. H., & Saen, R. F. (2013). A novel fuzzy data envelopment analysis model with double frontiers for supplier selection. International Journal of Logistics Research and Applications, 16(2), 87–98. https://doi.org/10.1080/13675567.2013.772957.
Aissaoui, N., Haouari, M., & Hassini, E. (2007). Supplier selection and order lot sizing modeling: A review. Computers & Operations Research, 34(12), 3516–3540. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cor.2006.01.016.
Allahyar, M., & Rostamy-Malkhalifeh, M. (2015). Negative data in data envelopment analysis: Efficiency analysis and estimating returns to scale. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 82, 78–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cie.2015.01.022.
Amindoust, A., Ahmed, S., Saghafinia, A., & Bahreininejad, A. (2012). Sustainable supplier selection: A ranking model based on fuzzy inference system. Applied Soft Computing, 12(6), 1668–1677. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2012.01.023.
Amirteimoori, A., Jahanshahloo, G., & Kordrostami, S. (2005). Ranking of decision making units in data envelopment analysis: A distance-based approach. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 171(1), 122–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amc.2005.01.065.
Andersen, P., & Petersen, N. C. (1993). A procedure for ranking efficient units in data envelopment analysis. Management Science, 39(10), 1261–1264. https://doi.org/10.1287/mnsc.39.10.1261.
Awasthi, A., Chauhan, S. S., & Goyal, S. K. (2010). A fuzzy multicriteria approach for evaluating environmental performance of suppliers. International Journal of Production Economics, 126(2), 370–378. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2010.04.029.
Azadeh, A., & Alem, S. M. (2010). A flexible deterministic, stochastic and fuzzy data envelopment analysis approach for supply chain risk and vendor selection problem: Simulation analysis. Expert Systems with Applications, 37(12), 7438–7448. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2010.04.022.
Azadi, M., & Farzipoor Saen, R. (2012). Developing a chance-constrained free replicability hull model for supplier selection. International Journal of Logistics Systems and Management, 12(4), 375–394.
Azadi, M., Farzipoor Saen, R., & Tavana, M. (2012). Supplier selection using chance-constrained data envelopment analysis with non-discretionary factors and stochastic data. International Journal of Industrial and Systems Engineering, 10(2), 167–196.
Azadi, M., Jafarian, M., Saen, R. F., & Mirhedayatian, S. M. (2015). A new fuzzy DEA model for evaluation of efficiency and effectiveness of suppliers in sustainable supply chain management context. Computers & Operations Research, 54, 274–285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cor.2014.03.002.
Bai, C., & Sarkis, J. (2010). Integrating sustainability into supplier selection with grey system and rough set methodologies. International Journal of Production Economics, 124(1), 252–264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2009.11.023.
Balf, F. R., Rezai, H. Z., Jahanshahloo, G. R., & Lotfi, F. H. (2012). Ranking efficient DMUs using the Tchebycheff norm. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 36(1), 46–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apm.2010.11.077.
Ballew, P. D., & Schnorbus, R. H. (1994). The impact of the auto industry on the economy. Chicago Fed Letter, 79–82.
Banker, R. D., Charnes, A., & Cooper, W. W. (1984). Some models for estimating technical and scale inefficiencies in data envelopment analysis. Management Science, 30(9), 1078–1092.
Baskaran, V., Nachiappan, S., & Rahman, S. (2012). Indian textile suppliers’ sustainability evaluation using the grey approach. International Journal of Production Economics, 135(2), 647–658.
Bender, P., Brown, R., Isaac, H., & Shapiro, J. (1985). Improving purchasing productivity at IBM with a normative decision support system. Interfaces, 15(3), 106–115.
Benton, W. (1991). Quantity discount decision under conditions of multiple items, multiple suppliers and resource limitation. International Journal of Production Research, 29(10), 1953–1961.
Beske, P., Land, A., & Seuring, S. (2014). Sustainable supply chain management practices and dynamic capabilities in the food industry: A critical analysis of the literature. International Journal of Production Economics, 152, 131–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2013.12.026.
Bowersox, D. J. C. (1996). Logistical management: The integrated supply chain process. New York: McGraw-Hill.
Büyüközkan, G., & Çifçi, G. (2011). A novel fuzzy multi-criteria decision framework for sustainable supplier selection with incomplete information. Computers in Industry, 62(2), 164–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compind.2010.10.009.
Çelebi, D., & Bayraktar, D. (2008). An integrated neural network and data envelopment analysis for supplier evaluation under incomplete information. Expert Systems with Applications, 35(4), 1698–1710. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2007.08.107.
Charnes, A., Cooper, W. W., & Rhodes, E. (1978). Measuring the efficiency of decision making units. European Journal of Operational Research, 2(6), 429–444. https://doi.org/10.1016/0377-2217(78)90138-8.
Chen, Y. (2004). Ranking efficient units in DEA. Omega, 32(3), 213–219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omega.2003.11.001.
Chen, Y.-J. (2011). Structured methodology for supplier selection and evaluation in a supply chain. Information Sciences, 181(9), 1651–1670. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2010.07.026.
Cheng, G., Zervopoulos, P., & Qian, Z. (2013). A variant of radial measure capable of dealing with negative inputs and outputs in data envelopment analysis. European Journal of Operational Research, 225(1), 100–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejor.2012.09.031.
Clift, R. (2003). Metrics for supply chain sustainability. Clean Technologies and Environmental Policy, 5(3–4), 240–247. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-003-0220-0.
Cooper, W. W., Seiford, L. M., & Tone, K. (2002). Data envelopment analysis: A comprehensive text with models, applications, references and DEA-solver software. Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Publishers.
Dao, V., Langella, I., & Carbo, J. (2011). From green to sustainability: Information Technology and an integrated sustainability framework. The Journal of Strategic Information Systems, 20(1), 63–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsis.2011.01.002.
de Boer, L., Labro, E., & Morlacchi, P. (2001). A review of methods supporting supplier selection. European Journal of Purchasing & Supply Management, 7(2), 75–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0969-7012(00)00028-9.
Dibachi, H., Behzadi, M. H., & Izadikhah, M. (2014). Stochastic multiplicative DEA model for measuring the efficiency and ranking of DMUs under VRS technology. Indian Journal of Science and Technology, 7(11), 1765–1773.
Dibachi, H., Behzadi, M. H., & Izadikhah, M. (2015). Stochastic modified MAJ model for measuring the efficiency and ranking of DMUs. Indian Journal of Science and Technology, 8(8), 549–555.
Dobos, I., & Vörösmarty, G. (2014). Green supplier selection and evaluation using DEA-type composite indicators. International Journal of Production Economics, 157, 273–278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2014.09.026.
Ehsanbakhsh, H., & Izadikhah, M. (2015). Applying BSC-DEA model to performance evaluation of industrial cooperatives: An application of fuzzy inference system. Applied Research Journal, 1(1), 9–26.
Emrouznejad, A., Anouze, A. L., & Thanassoulis, E. (2010). A semi-oriented radial measure for measuring the efficiency of decision making units with negative data, using DEA. European Journal of Operational Research, 200(1), 297–304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejor.2009.01.001.
Erol, I., Sencer, S., & Sari, R. (2011). A new fuzzy multi-criteria framework for measuring sustainability performance of a supply chain. Ecological Economics, 70(6), 1088–1100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolecon.2011.01.001.
Falagario, M., Sciancalepore, F., Costantino, N., & Pietroforte, R. (2012). Using a DEA-cross efficiency approach in public procurement tenders. European Journal of Operational Research, 218(2), 523–529. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejor.2011.10.031.
Floridi, M., Pagni, S., Falorni, S., & Luzzati, T. (2011). An exercise in composite indicators construction: Assessing the sustainability of Italian regions. Ecological Economics, 70(8), 1440–1447. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolecon.2011.03.003.
Gauthier, C. (2005). Measuring corporate social and environmental performance: The extended life-cycle assessment. Journal of Business Ethics, 59(1–2), 199–206. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10551-005-3416-x.
Giannakis, M., & Papadopoulos, T. (2016). Supply chain sustainability: A risk management approach. International Journal of Production Economics, 171(Part 4), 455–470. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2015.06.032.
Gimenez, C., & Tachizawa, E. M. (2012). Extending sustainability to suppliers: a systematic literature review. Supply Chain Management: An International Journal, 17(5), 531–543.
Gold, S., & Awasthi, A. (2015). Sustainable global supplier selection extended towards sustainability risks from (1 + n)th tier suppliers using fuzzy AHP based approach. IFAC-PapersOnLine, 48(3), 966–971. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ifacol.2015.06.208.
Govindan, K., Khodaverdi, R., & Jafarian, A. (2013). A fuzzy multi criteria approach for measuring sustainability performance of a supplier based on triple bottom line approach. Journal of Cleaner Production, 47, 345–354. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2012.04.014.
Handfield, R. B., & Nichols, E. L. (1999). Introduction to supply chain management. Upper Saddle River: Prentice Hall.
Hassini, E., Surti, C., & Searcy, C. (2012). A literature review and a case study of sustainable supply chains with a focus on metrics. International Journal of Production Economics, 140(1), 69–82.
Hervani, A. A., Helms, M. M., & Sarkis, J. (2005). Performance measurement for green supply chain management. Benchmarking: An International Journal, 12(4), 330–353.
Hsu, C.-W., & Hu, A. H. (2009). Applying hazardous substance management to supplier selection using analytic network process. Journal of Cleaner Production, 17(2), 255–264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2008.05.004.
Humphreys, P. K., Wong, Y. K., & Chan, F. T. S. (2003). Integrating environmental criteria into the supplier selection process. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 138(1–3), 349–356. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0924-0136(03)00097-9.
Hutchins, M. J., & Sutherland, J. W. (2008). An exploration of measures of social sustainability and their application to supply chain decisions. Journal of Cleaner Production, 16(15), 1688–1698. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2008.06.001.
Izadikhah, M., & Saen, R. F. (2015). A new data envelopment analysis method for ranking decision making units: An application in industrial parks. Expert Systems. https://doi.org/10.1111/exsy.12112.
Izadikhah, M., & Saen, R. F. (2016a). Evaluating sustainability of supply chains by two-stage range directional measure in the presence of negative data. Transportation Research Part D: Transport and Environment, 49, 110–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trd.2016.09.003.
Izadikhah, M., & Saen, R. F. (2016b). A new preference voting method for sustainable location planning using geographic information system and data envelopment analysis. Journal of Cleaner Production, 137, 1347–1367. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.08.021.
Izadikhah, M., Saen, R. F., & Ahmadi, K. (2017a). How to assess sustainability of suppliers in the presence of dual-role factor and volume discounts? A data envelopment analysis approach. Asia-Pacific Journal of Operational Research, 34(3), 1–25.
Izadikhah, M., Saen, R. F., & Ahmadi, K. (2017b). How to assess sustainability of suppliers in volume discount context? A new data envelopment analysis approach. Transportation Research Part D: Transport and Environment, 51, 102–121.
Jahanshahloo, G. R., & Afzalinejad, M. (2006). A ranking method based on a full-inefficient frontier. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 30(3), 248–260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apm.2005.03.023.
Jahanshahloo, G. R., Junior, H. V., Lotfi, F. H., & Akbarian, D. (2007). A new DEA ranking system based on changing the reference set. European Journal of Operational Research, 181(1), 331–337. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejor.2006.06.012.
Jahanshahloo, G. R., Lotfi, F. H., Khanmohammadi, M., Kazemimanesh, M., & Rezaie, V. (2010). Ranking of units by positive ideal DMU with common weights. Expert Systems with Applications, 37(12), 7483–7488. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2010.04.011.
Jahanshahloo, G. R., Memariani, A., Lotfi, F. H., & Rezai, H. Z. (2005). A note on some of DEA models and finding efficiency and complete ranking using common set of weights. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 166(2), 265–281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amc.2004.04.088.
Jahanshahloo, G. R., & Piri, M. (2013). Data envelopment analysis (DEA) with integer and negative inputs and outputs. Journal of Data Envelopment Analysis and Decision Science, 2013, 1–15.
Jahanshahloo, G. R., Pourkarimi, L., & Zarepisheh, M. (2006). Modified MAJ model for ranking decision making units in data envelopment analysis. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 174(2), 1054–1059. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amc.2005.06.001.
Jahanshahloo, G. R., Sanei, M., Lotfi, F. H., & Shoja, N. (2004). Using the gradient line for ranking DMUs in DEA. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 151(1), 209–219. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0096-3003(03)00333-3.
Jain, V., Kumar, A., Kumar, S., & Chandra, C. (2015). Weight restrictions in data envelopment analysis: A comprehensive genetic algorithm based approach for incorporating value judgments. Expert Systems with Applications, 42(3), 1503–1512. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2014.09.034.
Jakhar, S. K. (2015). Performance evaluation and a flow allocation decision model for a sustainable supply chain of an apparel industry. Journal of Cleaner Production, 87, 391–413. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2014.09.089.
Karsak, E. E., & Dursun, M. (2014). An integrated supplier selection methodology incorporating QFD and DEA with imprecise data. Expert Systems with Applications, 41(16), 6995–7004. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2014.06.020.
Katsikeas, C. S., Paparoidamis, N. G., & Katsikea, E. (2004). Supply source selection criteria: the impact of supplier performance ondistributor performance. Industrial Marketing Management, 33(8), 755–764.
Keskin, G. A., İlhan, S., & Özkan, C. (2010). The fuzzy ART algorithm: A categorization method for supplier evaluation and selection. Expert Systems with Applications, 37(2), 1235–1240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2009.06.004.
Khodakarami, M., Shabani, A., Saen, R. F., & Azadi, M. (2015). Developing distinctive two-stage data envelopment analysis models: An application in evaluating the sustainability of supply chain management. Measurement, 70, 62–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2015.03.024.
Kiron, D., Kruschwitz, N., Haanaes, K., & Velken, I. V. S. (2012). Sustainability nears a tipping point. MIT Sloan Management Review, 53(2), 69–74.
Kleinsorge, I. K., Schary, P. B., & Tanner, R. D. (1992). Data envelopment analysis for monitoring customer supplier relationships. Journal of Accounting and Public Policy, 11(4), 357–372.
Kordrostami, S., & Noveiri, M. J. S. (2012). Evaluating the efficiency of decision making units in the presence of flexible and negative data. Indian Journal of Science and Technology, 5(12), 78–84.
Kumar, A., Jain, V., & Kumar, S. (2014). A comprehensive environment friendly approach for supplier selection. Omega, 42(1), 109–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omega.2013.04.003.
Kuo, R. J., Wang, Y. C., & Tien, F. C. (2010). Integration of artificial neural network and MADA methods for green supplier selection. Journal of Cleaner Production, 18(12), 1161–1170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2010.03.020.
Lee, A. H. I., Kang, H.-Y., Hsu, C.-F., & Hung, H.-C. (2009). A green supplier selection model for high-tech industry. Expert Systems with Applications, 36(4), 7917–7927. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2008.11.052.
Lin, C., Madu, C. N., Kuei, C.-H., Tsai, H.-L., & Wang, K.-N. (2015). Developing an assessment framework for managing sustainability programs: A analytic network process approach. Expert Systems with Applications, 42(5), 2488–2501. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2014.09.025.
Liu, F.-H. F., & Peng, H. H. (2008). Ranking of units on the DEA frontier with common weights. Computers & Operations Research, 35(5), 1624–1637. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cor.2006.09.006.
Lotfi, F. H., Noora, A. A., Jahanshahloo, G. R., Gerami, J., & Mozaffari, M. R. (2010). A slacks-base measure of super-efficiency for DEA with negative data. Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 4(12), 6197–6210.
Lu, Y. H., Chen, P. C., & Hsiao, T. Y. (2014). Operational efficiency in credit departments of farmers’ associations with consideration of non-performing loans and negative values: Application of dynamic network DEA. The Macrotheme Review, 3(1), 150–164.
Mafakheri, F., Breton, M., & Ghoniem, A. (2011). Supplier selection-order allocation: A two-stage multiple criteria dynamic programming approach. International Journal of Production Economics, 132(1), 52–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2011.03.005.
Mahdiloo, M., Saen, R. F., & Lee, K.-H. (2015). Technical, environmental and eco-efficiency measurement for supplier selection: An extension and application of data envelopment analysis. International Journal of Production Economics, 168, 279–289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2015.07.010.
Martins, A. A., Mata, T. M., Costa, C. A. V., & Sikdar, S. K. (2007). Framework for sustainability metrics. Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Research, 46(10), 2962–2973. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie060692l.
Matin, R. K., Amin, G. R., & Emrouznejad, A. (2014). A modified semi-oriented radial measure for target setting with negative data. Measurement, 54, 152–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2014.04.018.
Matin, R. K., & Azizi, R. (2011). A two-phase approach for setting targets in DEA with negative data. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 35(12), 5794–5803. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apm.2011.05.002.
Mehrabian, S., Alirezaee, M. R., & Jahanshahloo, G. R. (1999). A complete efficiency ranking of decision making units in data envelopment analysis. Computational Optimization and Applications, 14, 261–266.
Mirhedayatian, S. M., Azadi, M., & Saen, R. F. (2014). A novel network data envelopment analysis model for evaluating green supply chain management. International Journal of Production Economics, 147, 544–554. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2013.02.009.
Mirhedayatian, S. M., Vahdat, S. E., Jelodar, M. J., & Saen, R. F. (2013). Welding process selection for repairing nodular cast iron engine block by integrated fuzzy data envelopment analysis and TOPSIS approaches. Materials and Design, 43, 272–282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2012.07.010.
Oliveira, R. C., & Lourenço, J. C. (2002). A multicriteria model for assigning new orders to service suppliers. European Journal of Operational Research, 139(2), 390–399. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0377-2217(01)00367-8.
Orji, I. J., & Wei, S. (2015). An innovative integration of fuzzy-logic and systems dynamics in sustainable supplier selection: A case on manufacturing industry. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 88, 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cie.2015.06.019.
Pal, O., Gupta, A. K., & Garg, R. K. (2013). Supplier selection criteria and methods in supply chains: A review. International Journal of Social, Behavioral, Educational, Economic, Business and Industrial Engineering, 7(10), 2667–2773.
Portela, M. C. A. S., & Thanassoulis, E. (2010). Malmquist-type indices in the presence of negative data: An application to bank branches. Journal of Banking & Finance, 34(7), 1472–1483. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbankfin.2010.01.004.
Portela, M. C. A. S., Thanassoulis, E., & Simpson, G. (2004). Negative data in DEA: A directional distance approach applied to bank branches. The Journal of the Operational Research Society, 55(10), 1111–1121. https://doi.org/10.2307/4101957.
Punniyamoorthy, M., Mathiyalagan, P., & Parthiban, P. (2011). A strategic model using structural equation modeling and fuzzy logic in supplier selection. Expert Systems with Applications, 38(1), 458–474. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2010.06.086.
Saen, R. F. (2008). Using super-efficiency analysis for ranking suppliers in the presence of volume discount offers. International Journal of Physical Distribution & Logistics Management, 38(8), 637–651.
Saen, R. F. (2009a). Suppliers selection in volume discount environments in the presence of both cardinal and ordinal data. International Journal of Information Systems and Supply Chain Management, 2(1), 69–80.
Saen, R. F. (2009b). A decision model for ranking suppliers in the presence of cardinal and ordinal data, weight restrictions, and nondiscretionary factors. Annals of Operations Research, 172(1), 177–192. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-009-0556-x.
Saen, R. F. (2010). A new algorithm for ranking suppliers in volume discount environments. Asia Pacific Management Review, 15(3), 341–358.
Saen, R. F., & Zohrehbandian, M. (2008). A data envelopment analysis approach to supplier selection in volume discount environments. International Journal of Procurement Management, 1(4), 472–488.
Sarkis, J., & Dhavale, D. G. (2015). Supplier selection for sustainable operations: A triple-bottom-line approach using a Bayesian framework. International Journal of Production Economics, 166, 177–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2014.11.007.
Scheel, H. (2001). Undesirable outputs in efficiency valuations. European Journal of Operational Research, 132(2), 400–410. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0377-2217(00)00160-0.
Seuring, S., & Müller, M. (2008). From a literature review to a conceptual framework for sustainable supply chain management. Journal of Cleaner Production, 16(15), 1699–1710. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2008.04.020.
Sharp, J. A., Meng, W., & Liu, W. (2007). A modified slacks-based measure model for data envelopment analysis with ‘natural’ negative outputs and inputs. The Journal of the Operational Research Society, 58(12), 1672–1677. https://doi.org/10.2307/4622864.
Shaverdi, M., Heshmati, M. R., Eskandaripour, E., & Tabar, A. A. A. (2013). Developing sustainable SCM evaluation model using fuzzy AHP in publishing industry. Procedia Computer Science, 17, 340–349. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2013.05.044.
Sridhar, K., & Jones, G. (2013). The three fundamental criticisms of the triple bottom line approach: An empirical study to link sustainability reports in companies based in the Asia-Pacific region and TBL shortcomings. Asian Journal of Business Ethics, 2(1), 91–111. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13520-012-0019-3.
Tahriri, F., Osman, R., Ali, A., Yusuff, R. M., & Esfandiary, A. (2008). AHP approach for supplier evaluation and selection in a steel manufacturing company. Journal of Industrial Engineering and Management, 1(2), 54–76.
Talluri, S., Narasimhan, R., & Nair, A. (2006). Vendor performance with supply risk: A chance-constrained DEA approach. International Journal of Production Economics, 100(2), 212–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2004.11.012.
Tao, L., Chen, Y., Liu, X., & Wang, X. (2012). An integrated multiple criteria decision making model applying axiomatic fuzzy set theory. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 36(10), 5046–5058. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apm.2011.12.042.
Tohidi, G., & Khodadadi, M. (2013). Allocation models for DMUs with negative data. Journal of Industrial Engineering International, 9(16), 1–6.
Toloo, M., & Nalchigar, S. (2011). A new DEA method for supplier selection in presence of both cardinal and ordinal data. Expert Systems with Applications, 38(12), 14726–14731. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2011.05.008.
Torgersen, A. M., Forsund, F. R., & Kittelsen, S. A. C. (1996). Slack-adjusted efficiency measures and ranking of efficient units. Journal of Productivity Analysis, 7(4), 379–398.
Trapp, A. C., & Sarkis, J. (2016). Identifying robust portfolios of suppliers: A sustainability selection and development perspective. Journal of Cleaner Production, 112(Part 3), 2088–2100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2014.09.062.
Tseng, M. L., & Chiu, A. S. F. (2013). Evaluating firm’s green supply chain management in linguistic preferences. Journal of Cleaner Production, 40, 22–31.
Tsoulfas, G. T., & Pappis, C. P. (2006). Environmental principles applicable to supply chains design and operation. Journal of Cleaner Production, 14(18), 1593–1602. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2005.05.021.
Turner, I. (1988). An independent system for the evaluation of contract tenders. Operational Research Society, 39(6), 551–561.
Wang, M., & Li, Y. (2014). Supplier evaluation based on Nash bargaining game model. Expert Systems with Applications, 41(9), 4181–4185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2013.12.044.
Wang, Y.-M., Luo, Y., & Liang, L. (2009). Ranking decision making units by imposing a minimum weight restriction in the data envelopment analysis. Journal of Computational and Applied Mathematics, 223(1), 469–484. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cam.2008.01.022.
Weber, C. A. (1996). A data envelopment analysis approach to measuring vendor performance. Supply Chain Management: An International Journal, 1(1), 28–39.
Wu, D. (2009). Supplier selection: A hybrid model using DEA, decision tree and neural network. Expert Systems with Applications, 36(5), 9105–9112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2008.12.039.
Wu, D. D. (2010). A systematic stochastic efficiency analysis model and application to international supplier performance evaluation. Expert Systems with Applications, 37(9), 6257–6264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2010.02.097.
Wu, D., & Olson, D. L. (2008). Supply chain risk, simulation, and vendor selection. International Journal of Production Economics, 114(2), 646–655. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2008.02.013.
Wu, J., Yang, F., & Liang, L. (2010). A modified complete ranking of DMUs using restrictions in DEA models. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 217(2), 745–751. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amc.2010.06.012.
Xia, W., & Wu, Z. (2007). Supplier selection with multiple criteria in volume discount environments. Omega, 35, 494–504.
Yeh, W.-C., & Chuang, M.-C. (2011). Using multi-objective genetic algorithm for partner selection in green supply chain problems. Expert Systems with Applications, 38(4), 4244–4253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2010.09.091.
Yu, J.-R., & Tsai, C.-C. (2008). A decision framework for supplier rating and purchase allocation: A case in the semiconductor industry. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 55(3), 634–646.
Zeydan, M., Çolpan, C., & Çobanoğlu, C. (2011). A combined methodology for supplier selection and performance evaluation. Expert Systems with Applications, 38(3), 2741–2751. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2010.08.064.
Zhou, X., Pedrycz, W., Kuang, Y., & Zhang, Z. (2016). Type-2 fuzzy multi-objective DEA model: An application to sustainable supplier evaluation. Applied Soft Computing, 46, 424–440. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2016.04.038.
Zhu, Q., Dou, Y., & Sarkis, J. (2010). A portfolio-based analysis for green supplier management using the analytical network process. Supply Chain Management: An International Journal, 15, 306–319.
Acknowledgements
We appreciate constructive comments of two anonymous Reviewers.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Izadikhah, M., Saen, R.F. & Roostaee, R. How to assess sustainability of suppliers in the presence of volume discount and negative data in data envelopment analysis?. Ann Oper Res 269, 241–267 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-018-2790-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-018-2790-6