Abstract
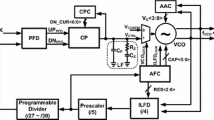
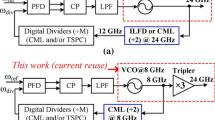
This study focused on the design principle and implementation of a high-frequency, wide-range frequency synthesizer by using a dual control path phase-lock loop (PLL) and a varactorless oscillator controlled by inductive–capacitive (LC-type) voltage (i.e., a voltage-controlled oscillator, VCO). Without a varactor in the LC tank, the tuned-transducer oscillator with Q-enhanced functionality can easily arrive at the requirements of high-frequency wide-range low-noise operations. We utilized a difference tuned varactorless VCO to create two different KVCOs and applied it to a dual control path PLL architecture to obtain wide tuning range and more favorable phase noise. In addition, a high-speed current-mode logic divider was employed given its high speed (because of the use of a transformer inductor), extremely high operation frequency, and wide-range. The proposed PLL was assembled using the standard 0.13-μm CMOS technology on a 0.95 × 1.05 mm2 chip. The PLL dissipated 40 mW at a 1.2 V supply. The measurement of phase noise at 17.64 GHz was − 98.12 dBc/Hz at a 1 MHz offset.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bae, J., Yan, L., & Yoo, H. J. (2011). A low energy injection-locked FSK transceiver with frequency-to-amplitude conversion for body sensor applications. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 46(4), 928–937.
Razavi, B. (2008). A millimeter-wave CMOS heterodyne receiver with on-chip LO and divider. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 43(2), 477–485.
Yang, C. Y., & Tsai, M. T. (2006). High-frequency low-noise voltage-controlled LC-tank oscillators using a tunable inductor technique. IEICE Transactions on Electronics, E89-C(11), 1567–1574.
Kwok, K., & Long, J. R. (2007). A 23-to-29 GHz transconductor-tuned VCO MMIC in 0.13 μm CMOS. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 42(12), 2878–2886.
Yang, C.-Y., Chang, C.-H., & Weng, J.H. (2013). A 35-GHz frequency synthesizer using frequency doubling and phase rotating technology. In International symposium on communications and information technologies (ISCIT), Samui Island, Thailand (pp. 266–270).
Lin, L., & Gray, P. R. (2000). A 1.4 GHz differential low-noise CMOS frequency synthesizer using a wideband PLL architecture. In IEEE international solid-state circuits conference digest of technical paper, San Francisco, CA (pp. 204–205, 458).
Koo, Y., Huh, H., Cho, Y., Lee, J., Park, J., Lee, K., et al. (2002). A fully integrated CMOS frequency synthesizer with charge-averaging charge pump and dual-path loop filter for PCS- and cellular-CDMA wireless systems. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 37, 536–542.
Sarang, K., Khayrollah, H., & Abdollah, K. (2015). A wide-range low-jitter PLL based on fast-response VCO and simplifed straightforward methodology of loop stabilization in integer-N PLLs. Journal of Circuits, Systems, and Computers, 24(7), 1550104-1–1550104-24.
Fong, N. H. W., Plouchart, J. O., Zamdmer, N., Liu, D., Wagner, L. F., Plett, C., et al. (2003). A 1-V 3.8-5.7-GHz wide-band VCO with differential tuned accumulation MOS varactors for common-mode noise rejection in CMOS SOI technology. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 51(8), 1952–1959.
Tang, Z., He, J., & Min, H. (2005). A low-phase-noise 1-GHz LC VCO differentially tuned by switched step capacitors. IEEE Asian Solide-State Circuits Conference (pp. 409–412). Taiwan: Hsinchu.
Mizuno, M., Yamashina, M., Furuta, K., Igura, H., Abiko, H., Okabe, K., et al. (1996). A GHz MOS adaptive pipeline technique using MOS current-mode logic. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 31(6), 784–791.
Piazza, F., & Huang, Q. (1997). A low power CMOS dual modulus prescaler for high-speed frequency synthesizer. IEICE Transactions on Electronics, E80-C(2), 314–319.
Yuan, J., & Svensson, C. (1989). High-speed CMOS circuit technique. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 24(1), 62–70.
Worapishet, A. (2006). Extended phase noise performance in mutual negative resistance CMOS LC oscillator for low supply voltages. IEICE Transactions on Electronics, E89-C(6), 732–738.
Herzel, F., Fischer, G., Gustat, H., & Weger, P. (2002). An integrated CMOS PLL for low-jitter applications. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems, 49, 427–429.
Craninckx, J., & Steyaert, M. (1998). A fully integrated CMOS DCS-1800 frequency synthesizer. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 33, 2054–2065.
Ding, Y., & Kenneth, K. O. (2007). A 21-GHz 8-modulus prescaler and a 20-GHz phase-locked loop fabricated in 130-nm CMOS. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 42(6), 1240–1249.
Kang, K., & Lin, F. (2010). A 20-GHz integer-N frequency synthesizer for 60-GHz transceivers in 90 nm CMOS. In Proceedings of the IEEE-ICUWB, Nanjing, China (pp. 1–4).
Cao, C., & Kenneth, K. O. (2005). A power efficient 26-GHz 32: 1 static frequency divider in 130-nm bulk CMOS. IEEE Microwave and Wireless Components Letters, 15(11), 721–723.
Adem, A., & Mohammed, I. (2004). CMOS PLLs and VCOs for 4G wireless. Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Publishers.
Leeson, D. B. (1966). A simple model of feedback oscillator noise spectrum. Proceedings of IEEE, 54(2), 329–330.
Razavi, B. (1996). Monolithic phase-locked loops and clock recovery. Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press.
Rylyakov, A., Tierno, J., Ainspan, H., Plouchart, J.O., Bulzacchelli, J., & Deniz, Z.T., et al. (2009). Bang-bang digital PLLs at 11 and 20 GHz with sub-200 fs integrated jitter for high-speed serial communication applications. In IEEE ISSCC digest of technical papers, San Francisco, CA (pp. 94–95).
Kim, J., Kim, J. K., Lee, B. J., Kim, N., Jeong, D. K., & Kim, W. (2006). A 20-GHz phase-locked loop for 40-Gb/s Serializing Transmitter in 0.13-μn CMOS. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 41, 899–908.
Floyd, B. (2008). A 16–18 GHz sub-integer-N frequency synthesizer for 60-GHz transceivers. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 43(5), 1076–1086.
Weng, J. H., Cheng, S., Chiu, C. K., & Chang, C. H. (2016). Ka-band frequency synthesizer involving a varactorless LC-type voltage-controlled oscillator and phase rotation. Microelectronics Journal, 49, 19–28.
Chen, Y., & Mouthaan, K. (2010). Wideband varactorless LC VCO using a tunable negative-inductance cell. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Paper, 57(10), 2609–2617.
Yang, C. Y., & Tsai, M. T. (2007). A voltage-controlled varactorless LC-tank oscillator with a transformer-feedback technique. Microwave and Optical Technology Letters, 49(11), 2808–2810.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by Tunghai University, Taiwan, R.O.C. The author would like to thank the National Chip Implementation Center (CIC), Taiwan, R.O.C., for fabricating the chip. This study was also supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology (MOST 106-2221-E-029-028), Taiwan, R.O.C.
Funding
The study was funded by the Ministry of Science and Technology (Grant Number MOST 106-2221-E-029-028), Taiwan, R.O.C.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declares there are no conflicts of interest.
Research involving human participants and/or animals
There were not any human participants and/or animals in the study.
Informed consent
There were not any informed consent in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Weng, JH., Teng, KW. A Ku-band dual control path frequency synthesizer using varactorless Q-enhanced LC-type VCO. Analog Integr Circ Sig Process 100, 47–59 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-019-01454-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-019-01454-6