Abstract
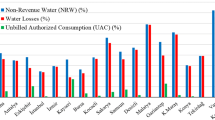
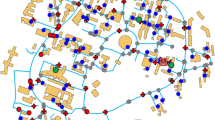
Recent advances in intelligent water meter technology have improved the quantitative monitoring in water supply and distribution systems. Smart meters using automated meter reading (AMR) technology allow water utilities to: (a) provide clear consumption patterns which can help customers to track and control their water usage and (b) improve active leakage targeting and leak detection capability. This paper presents a feedback about the use of AMR system to detect leakage in a large-scale experimentation, which is conducted at the Scientific Campus of the University of Lille, which stands for a small town of 25,000 users. This paper presents the demonstration site as well as its monitoring using AMR technology and how this technology allowed a rapid detection of water leakage.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
van de Meene, S. J., Brown, R. R., & Farrelly, M. A. (2011). Towards understanding governance for sustainable urban water management. Global Environmental Change, 21(3), 1117–1127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2011.04.003.
GrowingBlue. (2011). Water economics life.
Sharma, S. K., & Vairavamoorthy, K. (2009). Urban water demand management: Prospects and challenges for the developing countries. Water and Environment Journal, 23(3), 210–218. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1747-6593.2008.00134.x.
Fanner, P. V., Sturm, R., Thornton, J., Liemberger, R., Davis, S. E., & Hoogerwerf, T. (2007). Leakage management technologies. Denver CO: American Water Works Association (AWWA) Research Foundation.
Depuru, S. S. S. R., Wang, L., & Devabhaktuni, V. (2011). Smart meters for power grid: Challenges, issues, advantages and status. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 15(6), 2736–2742. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2011.02.039.
Soh, S. C., & Kerk, S. G. (2005). The electricity and metering trends in Singapore. In 2005 international power engineering conference, November 29 2005–December 2 (pp. 1–152). https://doi.org/10.1109/ipec.2005.206896.
Sehgal, A. (2005). AMR offers multiple benefits. In Pipeline and gas technology. Itron Inc., Spokane, Washington.
Christodoulou, S., Agathokleous, A., Kranioti, S., Xanthos, S., & Gagatsis, A. (2012). Wireless sensors for leak detection and automatic meter reading (AMR). In NIREAS-IWRC/D5.15.1. Nicosia, Cyprus.
Britton, T. C., Stewart, R. A., & Wiskar, D. (2009). Smart metering as a tool for revealing the characteristics of household leakage during a typical readings cycle. In Ozwater conference, Melbourne, VIC, Australia, 15–18 March 2009.
Willis, R., Stewart, R. A., Giurco, D., Panuwatwanich, K., & Capati, B. (2009). Gold Coast domestic water end use study. Water: Journal of the Australian Water Association, 36(6), 84.
Li, L., Xiaoguang, H., & Weicun, Z. (2009). Design of an ARM-based power meter having WIFI wireless communication module. In Proceedings of the 4th IEEE conference on industrial electronics and applications, Xi’an, China, 25–27 May 2009 (pp. 403–407). https://doi.org/10.1109/iciea.2009.5138237.
Han, D. M., & Lim, J. H. (2010). Smart home energy management system using IEEE 802.15.4 and zigbee. IEEE Transactions on Consumer Electronics, 56(3), 1403–1410. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCE.2010.5606276.
Yaacoub, E. (2014). On real-time smart meter reading using OFDMA-based random access. In Proceedings of the 17th IEEE Mediterranean electrotechnical conference MELECON, 13–16 April 2014 (pp. 156–162). https://doi.org/10.1109/melcon.2014.6820524.
Thornton, J., Sturm, R., & Kunkel, G. (2008). Water loss control (2nd ed.). London: McGraw Hill.
Lambert, A. (2002). International report: Water losses management and techniques. Water Science and Technology: Water Supply, 2(4), 1–20.
Kvanli, A., Pavur, R., & Keeling, K. (2006). Concise managerial statistics. Mason, OH: South-Western Thomson Learning.
Shahrour, I., Abbas, O., Abdallah, A., Abou Rjeily, Y., Afaneh, A., Aljer, A., et al. (2017). Lessons from a large scale demonstrator of the smart and sustainable city. In A. Brdulak & H. Brdulak (Eds.), Happy city—How to plan and create the best livable area for the people (pp. 193–206). Cham: Springer.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Farah, E., Shahrour, I. Smart water technology for leakage detection: feedback of large-scale experimentation. Analog Integr Circ Sig Process 96, 235–242 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-018-1137-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-018-1137-1