Abstract
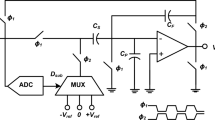
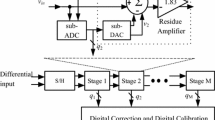
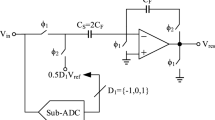
A new non-binary multiplying digital-to-analog converter (MDAC) structure with signal-dependent dithering scaling technique is proposed in this paper. A full digital background calibration algorithm based on pseudo-random dithers injection is used to calibrate the nonlinear errors of MDAC. By measuring sampling capacitor mismatch and op-amp gain errors of the pipelined analog-to-digital converter (ADC) in background, the errors will be greatly reduced by the proposed calibration algorithm. At the same time, the signal-dependent dithering scaling technique provides a swing margin to the injected pseudo-random signal. By using this technique, the errors caused by the capacitor mismatch and op-amp gain errors can be calibrated at the same time. What’s more, this method greatly accelerates the convergence speed. A two-stage 14-bit pipelined ADC is used to simulate and verify the proposed algorithm. The simulation results indicate the effectiveness of the technique, in which the signal-to-noise plus distortion (SNDR) and the spurious-free dynamic range (SFDR) performance of a 14-bit two-step ADC are improved from 49.12 and 56.25 to 85.68 and 102.23 dB with the input frequency being 0.06 * f s , respectively. The SFDR is more than 98 dB. The SNDR reaches 84 dB in the whole Nyquist bandwidth after calibration. Integral nonlinearity is improved from 80 to 1.5 least significant bits after calibration.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali, A. M. A., et al. (2010). A 16-bit 250-MS/s IF sampling pipelined ADC with background calibration. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 45(12), 2602–2612.
Wang, G., Kacani, F., & Chiu, Y. (2014). IRD digital background calibration of SAR ADC with coarse reference ADC acceleration. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 61(1), 11–15.
Sun, N. (2012). Exploiting process variation and noise in comparators to calibrate inter stage gain nonlinearity in pipelined ADCs. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 59(4), 685–695.
Peng, B., et al. (2010). An offset double conversion technique for digital calibration of pipelined ADCs. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 57, 961–965.
Liu, W., et al. (2011). A 12-bit, 45-MS/s, 3-mW redundant successive-approximation-register analog-to-digital converter with digital calibration. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 46, 2661–2672.
McNeill, J., et al. (2005). Split ADC architecture for deterministic digital background calibration of a 16-bit 1-MS/s ADC. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 40, 2437–2445.
Sehgal, R., van der Goes, F., & Bult, K. (2015). A 12 b 53 mW 195 MS/s pipeline ADC with 82 dB SFDR using split-ADC calibration. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 50(7), 1592–1603.
Hung, L.-H., & Lee, T.-C. (2009). A split-based digital background calibration technique in pipelined ADCs. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 56, 855–859.
Adel, H., Louerat, M.-M., & Sabut, M. (2012). Fast split background calibration for pipelined ADCs enabled by slope mismatch averaging technique. Electronics Letters, 48(6), 318–320.
Ahmed, I., & Johns, D. A. (2008). An 11-bit 45-MS/s pipelined ADC with rapid calibration of DAC errors in a multibit pipeline stage. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 43, 2437–2445.
Sarkar, S., Zhou, Y., Elies, B., & Chiu, Y. (2015). PN-assisted deterministic digital background calibration of multistage split-pipelined ADC. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 62(3), 654–661.
Ding, L., et al. (2013). A 13-bit 60 MS/s split pipelined ADC with background gain and mismatch error calibration. In IEEE Asian Solid-State Circuits Conference, pp. 77–80.
Shu, Y.-S., & Song, B.-S. (2008). A 15-bit linear 20-MS/s pipelined ADC digitally calibrated with signal dependent dithering. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 43(2), 342–350.
Li, J., & Moon, U.-K. (2003). Background calibration techniques for multistage pipelined ADCs with digital redundancy. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II Analog Digit. Signal Process, 50(9), 531–538.
Keane, J. P., Hurst, P. J., & Lewis, S. H. (2005). Background inter stage gain calibration technique for pipelined ADCs. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 52(1), 32–43.
He, L., Jin, L., Yang, J., Lin, F., Yao, L., & Jiang, X. (2015). Self-dithering technique for high-resolution SAR ADC design. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 62(12), 1124–1128.
Zhou, Y., Xu, B., & Chiu, Y. (2015). A 12 bit 160 MS/s two-step SAR ADC with background bit-weight calibration using a time-domain proximity detector. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 50(4), 920–931.
Peng, B., Li, H., Lin, P., & Chiu, Y. (2010). An offset double conversion technique for digital calibration of pipelined ADCs. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 57(12), 961–965.
Ali, A. M. A., et al. (2014). A 14 bit 1 GS/s RF sampling pipelined ADC with background calibration. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 49(12), 2857–2867.
Shin, S. K., et al. (2014). A 12 bit 200 MS/s zero-crossing-based pipelined ADC with early sub-ADC decision and output residue background calibration. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 49(6), 1366–1382.
Chang, D. Y., Li, J., & Moon, U. (2004). Radix-based digital calibration techniques for multi-stage recycling pipelined ADCs. IEEE Transactions on Circuits Systems I, Regular Papers, 51(11), 2133–2140.
Grace, C. R., Hurst, P. J., & Lewis, S. H. (2004) A 12b 80 MS/s pipelinedADC with bootstrapped digital calibration. In IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference (ISSCC) Digest Technical Papers, pp. 460–539.
Gholami, P., & Yavari, M. Digital background calibration with histogram of decision points in pipelined ADCs. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 99, 1–1.
Ragab, K., Chen, L., Sanyal, A., & Sun, N. (2015). Digital background calibration for pipelined ADCs based on comparator decision time quantization. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 62(5), 456–460.
Acknowledgements
Funding was provided by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 61504103, 61574103, 61674118, 61574105).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, M., Hu, J., Zhang, S. et al. PN-assisted digital background calibration of two-step ADC to over 14-bit accuracy. Analog Integr Circ Sig Process 94, 75–82 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-017-1088-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-017-1088-y