Abstract
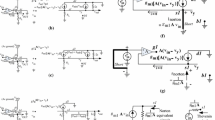
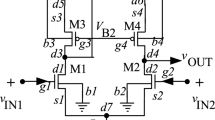
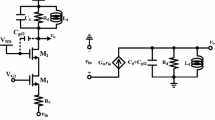
This article demonstrates simplified mid-band derivations for CMOS cascode and g m-boosted cascode. While the cascode mid-band analysis is addressed in some textbooks through varying brief treatments, it is provided in this paper in a more in-depth and consolidated form using an easy approach. The detailed analysis of g m-boosted cascode stage is mostly not available in textbooks (or any Web source) despite being an important analog building block in achieving gain enhancements. The mid-band analysis of this stage is made easy in this paper using a simple short circuit and inspection technique. There is no need to write or solve lengthy equations. Transformation of dependent current sources through “opportunistic short circuits” is utilized often in achieving this ease in derivation. An interesting new concept of “Algebraic ground” or “Meta-ground” is introduced in relation to the g m-boosted cascode. Some novel compound cascode stages with simplified approach to their mid-band derivations is also provided. Additional insight is also provided through a comparison of the cascode with the g m-boosted cascode using the simplified models and derivations which is rarely available elsewhere.




















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Razavi, B. (2008). Fundamentals of microelectronics. Hoboken, NJ: Wiley.
Razavi, B. (2001). Design of analog CMOS integrated circuits. Boston, MA: McGraw Hill.
Allen, P. E., & Holberg, D. A. (2002). CMOS analog circuit design (2nd ed.). Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Johns, D., & Martin, K. W. (1997). Analog integrated circuit design. Hoboken, NJ: Wiley.
Jack, J., & Hasan, S. R. (2013). Design and performance analysis of a 866 MHz low-power optimized CMOS LNA for UHF RFID”. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 60(5), 1840–1849.
Sedra, A. S., & Smith, K. C. (2010). Microelectronic circuits (6th ed.). New York, NJ: Oxford University Press.
Rezaul Hasan, S. M. (2015). Simplified analog CMOS mid-band small-signal analysis utilizing short-circuits and incremental perturbations. International Journal of Electrical Engineering Education (IJEEE), 52(4), 356–369.
Sadiku, A. (2007). Fundamentals of electric circuits. Boston, MA: McGraw Hill.
Sundararajan, A., & Rezaul Hasan, S. M. (2015). Elliptic diaphragm capacitive pressure sensor and signal conditioning circuit fabricated in SiGe CMOS integrated MEMS. IEEE Sensors Journal, 15(3), 1825–1837.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rezaul Hasan, S.M. Novel inspection-based mid-band derivations for CMOS cascodes and g m-boosted topologies along-with simplified compound structure gain-analysis. Analog Integr Circ Sig Process 91, 21–41 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-016-0881-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-016-0881-3