Abstract
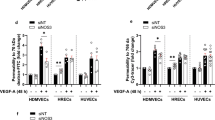
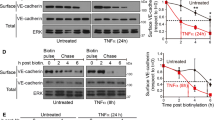
Vascular integrity is a critical parameter in normal growth and development. Loss of appropriate vascular barrier function is present in various immune- and injury-mediated pathological conditions. CD44 is an adhesion molecule expressed by multiple cell types, including endothelial cells (EC). The goal of the present study was to examine how loss of CD44 affected vascular permeability. Using C57BL/6 WT and CD44-KO mice, we found no significant permeability to Evan’s Blue in either strain at baseline. However, there was significantly increased histamine-induced permeability in CD44-deficient mice compared to WT counterparts. Similar results were observed in vitro, where CD44-deficient endothelial monolayers were also impermeable to 40kD-FITC dextran in the absence of vasoactive challenge, but exhibited enhanced and prolonged permeability following histamine. However, CD44-KO monolayers have reduced baseline barrier strength by electrical resistance, which correlated with increased permeability, at baseline, to smaller molecular weight 4-kD FITC-dextran, suggesting weakly formed endothelial junctions. The CD44-KO EC displayed several characteristics consistent with impaired barrier function/dysfunctional EC junctions, including differential expression, phosphorylation, and localization of endothelial junction proteins, increased matrix metalloprotease expression, and altered cellular morphology. Reduced platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1 (PECAM-1) expression by CD44-KO EC in vivo and in vitro was also observed. Reconstitution of murine CD44 or PECAM-1 restored these defects to near WT status, suggesting CD44 regulates vascular permeability and integrity through a PECAM-1 dependent mechanism.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Isacke CM, Yarwood H (2002) The hyaluronan receptor, CD44. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 34(7):718–721
Ponta H, Sherman L, Herrlich PA (2003) CD44: from adhesion molecules to signalling regulators. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 4(1):33–45. doi:10.1038/nrm1004
Thorne RF, Legg JW, Isacke CM (2004) The role of the CD44 transmembrane and cytoplasmic domains in co-ordinating adhesive and signalling events. J Cell Sci 117(Pt 3):373–380. doi:10.1242/jcs.00954
Borland G, Ross JA, Guy K (1998) Forms and functions of CD44. Immunology 93(2):139–148
Kalomiris EL, Bourguignon LY (1988) Mouse T lymphoma cells contain a transmembrane glycoprotein (GP85) that binds ankyrin. J Cell Biol 106(2):319–327
Tsukita S, Oishi K, Sato N, Sagara J, Kawai A (1994) ERM family members as molecular linkers between the cell surface glycoprotein CD44 and actin-based cytoskeletons. J Cell Biol 126(2):391–401
Bourguignon LY, Singleton PA, Zhu H, Zhou B (2002) Hyaluronan promotes signaling interaction between CD44 and the transforming growth factor beta receptor I in metastatic breast tumor cells. J Biol Chem 277(42):39703–39712. doi:10.1074/jbc.M204320200
Orian-Rousseau V, Chen L, Sleeman JP, Herrlich P, Ponta H (2002) CD44 is required for two consecutive steps in HGF/c-Met signaling. Genes Dev 16(23):3074–3086. doi:10.1101/gad.242602
Shi X, Leng L, Wang T, Wang W, Du X, Li J, McDonald C, Chen Z, Murphy JW, Lolis E, Noble P, Knudson W, Bucala R (2006) CD44 is the signaling component of the macrophage migration inhibitory factor-CD74 receptor complex. Immunity 25(4):595–606. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2006.08.020
Singleton PA, Salgia R, Moreno-Vinasco L, Moitra J, Sammani S, Mirzapoiazova T, Garcia JG (2007) CD44 regulates hepatocyte growth factor-mediated vascular integrity. Role of c-Met, Tiam1/Rac1, dynamin 2, and cortactin. J Biol Chem 282(42):30643–30657. doi:10.1074/jbc.M702573200
Tremmel M, Matzke A, Albrecht I, Laib AM, Olaku V, Ballmer-Hofer K, Christofori G, Heroult M, Augustin HG, Ponta H, Orian-Rousseau V (2009) A CD44v6 peptide reveals a role of CD44 in VEGFR-2 signaling and angiogenesis. Blood 114(25):5236–5244. doi:10.1182/blood-2009-04-219204
Okamoto I, Kawano Y, Murakami D, Sasayama T, Araki N, Miki T, Wong AJ, Saya H (2001) Proteolytic release of CD44 intracellular domain and its role in the CD44 signaling pathway. J Cell Biol 155(5):755–762. doi:10.1083/jcb.200108159
Lee JL, Wang MJ, Chen JY (2009) Acetylation and activation of STAT3 mediated by nuclear translocation of CD44. J Cell Biol 185(6):949–957. doi:10.1083/jcb.200812060
Janiszewska M, De Vito C, Le Bitoux MA, Fusco C, Stamenkovic I (2010) Transportin regulates nuclear import of CD44. J Biol Chem 285(40):30548–30557. doi:10.1074/jbc.M109.075838
Dejana E, Orsenigo F, Lampugnani MG (2008) The role of adherens junctions and VE-cadherin in the control of vascular permeability. J Cell Sci 121(Pt 13):2115–2122. doi:10.1242/jcs.017897
Dejana E, Tournier-Lasserve E, Weinstein BM (2009) The control of vascular integrity by endothelial cell junctions: molecular basis and pathological implications. Dev Cell 16(2):209–221. doi:10.1016/j.devcel.2009.01.004
Dudek SM, Garcia JG (2001) Cytoskeletal regulation of pulmonary vascular permeability. J Appl Physiol 91(4):1487–1500
Kim MP, Park SI, Kopetz S, Gallick GE (2009) Src family kinases as mediators of endothelial permeability: effects on inflammation and metastasis. Cell Tissue Res 335(1):249–259. doi:10.1007/s00441-008-0682-9
Bennett J, Basivireddy J, Kollar A, Biron KE, Reickmann P, Jefferies WA, McQuaid S (2010) Blood-brain barrier disruption and enhanced vascular permeability in the multiple sclerosis model EAE. J Neuroimmunol 229(1–2):180–191. doi:10.1016/j.jneuroim.2010.08.011
Yuan SY, Breslin JW, Perrin R, Gaudreault N, Guo M, Kargozaran H, Wu MH (2007) Microvascular permeability in diabetes and insulin resistance. Microcirculation 14(4–5):363–373. doi:10.1080/10739680701283091
Lee JM, Zhai G, Liu Q, Gonzales ER, Yin K, Yan P, Hsu CY, Vo KD, Lin W (2007) Vascular permeability precedes spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage in stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rats. Stroke 38(12):3289–3291. doi:10.1161/STROKEAHA.107.491621
Druey KM, Greipp PR (2010) Narrative review: the systemic capillary leak syndrome. Ann Intern Med 153(2):90–98. doi:10.1059/0003-4819-153-2-201007200-00005
Wallez Y, Huber P (2008) Endothelial adherens and tight junctions in vascular homeostasis, inflammation and angiogenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta 1778(3):794–809. doi:10.1016/j.bbamem.2007.09.003
Dejana E, Orsenigo F, Molendini C, Baluk P, McDonald DM (2009) Organization and signaling of endothelial cell-to-cell junctions in various regions of the blood and lymphatic vascular trees. Cell Tissue Res 335(1):17–25. doi:10.1007/s00441-008-0694-5
Komarova Y, Malik AB (2010) Regulation of endothelial permeability via paracellular and transcellular transport pathways. Annu Rev Physiol 72:463–493. doi:10.1146/annurev-physiol-021909-135833
Vestweber D, Winderlich M, Cagna G, Nottebaum AF (2009) Cell adhesion dynamics at endothelial junctions: VE-cadherin as a major player. Trends Cell Biol 19(1):8–15. doi:10.1016/j.tcb.2008.10.001
Mehta D, Malik AB (2006) Signaling mechanisms regulating endothelial permeability. Physiol Rev 86(1):279–367. doi:10.1152/physrev.00012.2005
Corada M, Mariotti M, Thurston G, Smith K, Kunkel R, Brockhaus M, Lampugnani MG, Martin-Padura I, Stoppacciaro A, Ruco L, McDonald DM, Ward PA, Dejana E (1999) Vascular endothelial-cadherin is an important determinant of microvascular integrity in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96(17):9815–9820
Hordijk PL, Anthony E, Mul FP, Rientsma R, Oomen LC, Roos D (1999) Vascular-endothelial-cadherin modulates endothelial monolayer permeability. J Cell Sci 112(Pt 12):1915–1923
Nwariaku FE, Liu Z, Zhu X, Turnage RH, Sarosi GA, Terada LS (2002) Tyrosine phosphorylation of vascular endothelial cadherin and the regulation of microvascular permeability. Surgery 132(2):180–185
Roura S, Miravet S, Piedra J, Garcia de Herreros A, Dunach M (1999) Regulation of E-cadherin/catenin association by tyrosine phosphorylation. J Biol Chem 274(51):36734–36740
Shasby DM, Ries DR, Shasby SS, Winter MC (2002) Histamine stimulates phosphorylation of adherens junction proteins and alters their link to vimentin. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 282(6):L1330–L1338. doi:10.1152/ajplung.00329.2001
Angelini DJ, Hyun SW, Grigoryev DN, Garg P, Gong P, Singh IS, Passaniti A, Hasday JD, Goldblum SE (2006) TNF-alpha increases tyrosine phosphorylation of vascular endothelial cadherin and opens the paracellular pathway through fyn activation in human lung endothelia. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 291(6):L1232–L1245. doi:10.1152/ajplung.00109.2006
Huber AH, Stewart DB, Laurents DV, Nelson WJ, Weis WI (2001) The cadherin cytoplasmic domain is unstructured in the absence of beta-catenin. A possible mechanism for regulating cadherin turnover. J Biol Chem 276(15):12301–12309. doi:10.1074/jbc.M010377200
Lampugnani MG, Resnati M, Dejana E, Marchisio PC (1991) The role of integrins in the maintenance of endothelial monolayer integrity. J Cell Biol 112(3):479–490
Form DM, Pratt BM, Madri JA (1986) Endothelial cell proliferation during angiogenesis. In vitro modulation by basement membrane components. Lab Invest 55(5):521–530
Partridge CA, Horvath CJ, Del Vecchio PJ, Phillips PG, Malik AB (1992) Influence of extracellular matrix in tumor necrosis factor-induced increase in endothelial permeability. Am J Physiol 263(6 Pt 1):L627–L633
Partridge CA, Jeffrey JJ, Malik AB (1993) A 96-kDa gelatinase induced by TNF-alpha contributes to increased microvascular endothelial permeability. Am J Physiol 265(5 Pt 1):L438–L447
Herren B, Levkau B, Raines EW, Ross R (1998) Cleavage of beta-catenin and plakoglobin and shedding of VE-cadherin during endothelial apoptosis: evidence for a role for caspases and metalloproteinases. Mol Biol Cell 9(6):1589–1601
Rosenberg GA, Yang Y (2007) Vasogenic edema due to tight junction disruption by matrix metalloproteinases in cerebral ischemia. Neurosurg Focus 22(5):E4
Feng S, Cen J, Huang Y, Shen H, Yao L, Wang Y, Chen Z (2011) Matrix metalloproteinase-2 and -9 secreted by leukemic cells increase the permeability of blood-brain barrier by disrupting tight junction proteins. PLoS ONE 6(8):e20599. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0020599
Flynn KM, Michaud M, Madri JA (2013) CD44 Deficiency contributes to enhanced experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis: a role in immune cells and vascular cells of the blood-brain barrier. Am J Pathol. doi:10.1016/j.ajpath.2013.01.003
Lampugnani MG, Zanetti A, Breviario F, Balconi G, Orsenigo F, Corada M, Spagnuolo R, Betson M, Braga V, Dejana E (2002) VE-cadherin regulates endothelial actin activating Rac and increasing membrane association of Tiam. Mol Biol Cell 13(4):1175–1189. doi:10.1091/mbc.01-07-0368
Muller WA, Ratti CM, McDonnell SL, Cohn ZA (1989) A human endothelial cell-restricted, externally disposed plasmalemmal protein enriched in intercellular junctions. J Exp Med 170(2):399–414
Ilan N, Madri JA (2003) PECAM-1: old friend, new partners. Curr Opin Cell Biol 15(5):515–524
Albelda SM, Oliver PD, Romer LH, Buck CA (1990) EndoCAM: a novel endothelial cell–cell adhesion molecule. J Cell Biol 110(4):1227–1237
Matsumura T, Wolff K, Petzelbauer P (1997) Endothelial cell tube formation depends on cadherin 5 and CD31 interactions with filamentous actin. J Immunol 158(7):3408–3416
Ilan N, Cheung L, Pinter E, Madri JA (2000) Platelet-endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1 (CD31), a scaffolding molecule for selected catenin family members whose binding is mediated by different tyrosine and serine/threonine phosphorylation. J Biol Chem 275(28):21435–21443. doi:10.1074/jbc.M001857200
Ilan N, Mahooti S, Rimm DL, Madri JA (1999) PECAM-1 (CD31) functions as a reservoir for and a modulator of tyrosine-phosphorylated beta-catenin. J Cell Sci 112(Pt 18):3005–3014
Enciso JM, Gratzinger D, Camenisch TD, Canosa S, Pinter E, Madri JA (2003) Elevated glucose inhibits VEGF-A-mediated endocardial cushion formation: modulation by PECAM-1 and MMP-2. J Cell Biol 160(4):605–615. doi:10.1083/jcb.200209014
Graesser D, Solowiej A, Bruckner M, Osterweil E, Juedes A, Davis S, Ruddle NH, Engelhardt B, Madri JA (2002) Altered vascular permeability and early onset of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in PECAM-1-deficient mice. J Clin Invest 109(3):383–392. doi:10.1172/JCI13595
Carrithers M, Tandon S, Canosa S, Michaud M, Graesser D, Madri JA (2005) Enhanced susceptibility to endotoxic shock and impaired STAT3 signaling in CD31-deficient mice. Am J Pathol 166(1):185–196. doi:10.1016/S0002-9440(10)62243-2
Privratsky JR, Paddock CM, Florey O, Newman DK, Muller WA, Newman PJ (2011) Relative contribution of PECAM-1 adhesion and signaling to the maintenance of vascular integrity. J Cell Sci 124(Pt 9):1477–1485. doi:10.1242/jcs.082271
Biswas P, Canosa S, Schoenfeld D, Schoenfeld J, Li P, Cheas LC, Zhang J, Cordova A, Sumpio B, Madri JA (2006) PECAM-1 affects GSK-3beta-mediated beta-catenin phosphorylation and degradation. Am J Pathol 169(1):314–324
Gunthert U (1993) CD44: a multitude of isoforms with diverse functions. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 184:47–63
Okamoto I, Kawano Y, Tsuiki H, Sasaki J, Nakao M, Matsumoto M, Suga M, Ando M, Nakajima M, Saya H (1999) CD44 cleavage induced by a membrane-associated metalloprotease plays a critical role in tumor cell migration. Oncogene 18(7):1435–1446. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1202447
Gal I, Lesley J, Ko W, Gonda A, Stoop R, Hyman R, Mikecz K (2003) Role of the extracellular and cytoplasmic domains of CD44 in the rolling interaction of lymphoid cells with hyaluronan under physiologic flow. J Biol Chem 278(13):11150–11158. doi:10.1074/jbc.M210661200
Almendro N, Bellon T, Rius C, Lastres P, Langa C, Corbi A, Bernabeu C (1996) Cloning of the human platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1 promoter and its tissue-specific expression. Structural and functional characterization. J Immunol 157(12):5411–5421
Braganca J, Eloranta JJ, Bamforth SD, Ibbitt JC, Hurst HC, Bhattacharya S (2003) Physical and functional interactions among AP-2 transcription factors, p300/CREB-binding protein, and CITED2. J Biol Chem 278(18):16021–16029. doi:10.1074/jbc.M208144200
Schwartz C, Beck K, Mink S, Schmolke M, Budde B, Wenning D, Klempnauer KH (2003) Recruitment of p300 by C/EBPbeta triggers phosphorylation of p300 and modulates coactivator activity. EMBO J 22(4):882–892. doi:10.1093/emboj/cdg076
Bannister AJ, Kouzarides T (1995) CBP-induced stimulation of c-Fos activity is abrogated by E1A. EMBO J 14(19):4758–4762
Huang WH, Mai RT, Lee YH (2008) Transcription factor YY1 and its associated acetyltransferases CBP and p300 interact with hepatitis delta antigens and modulate hepatitis delta virus RNA replication. J Virol 82(15):7313–7324. doi:10.1128/JVI.02581-07
Tarbell JM, Pahakis MY (2006) Mechanotransduction and the glycocalyx. J Intern Med 259(4):339–350. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2796.2006.01620.x
Pinter E, Barreuther M, Lu T, Imhof BA, Madri JA (1997) Platelet-endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1 (PECAM-1/CD31) tyrosine phosphorylation state changes during vasculogenesis in the murine conceptus. Am J Pathol 150(5):1523–1530
Eliceiri BP, Paul R, Schwartzberg PL, Hood JD, Leng J, Cheresh DA (1999) Selective requirement for Src kinases during VEGF-induced angiogenesis and vascular permeability. Mol Cell 4(6):915–924
Giaever I, Keese CR (1991) Micromotion of mammalian cells measured electrically. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88(17):7896–7900
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by United States Public Health Service grants R37-HL28373, RO1-HL51018, and the Reed Foundation to Joseph A. Madri, and T32 GM007223 and T32 DK07556 to Kelly M. Romano (Flynn).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Flynn, K.M., Michaud, M., Canosa, S. et al. CD44 regulates vascular endothelial barrier integrity via a PECAM-1 dependent mechanism. Angiogenesis 16, 689–705 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-013-9346-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-013-9346-9