Abstract
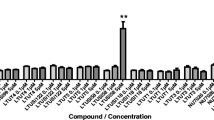
Small molecular kinase inhibitors are promising novel drugs. Initially, they were designed for the highest possible specificity. Recently, this concept has been challenged by multikinase inhibitors, which are clinically more potent. This change of paradigm calls for re-examination of already known compounds in different functional contexts. We have compared 6 reported structurally different inhibitors of cyclin-dependent kinases (Cdks) regarding their functional effects on endothelial cells (proliferation, cell cycle, apoptosis, migration, tube formation), as well as their actions on some kinases (AKT, p38, ERK1/2, c-src, GSK3β). Only some of these compounds had anti-angiogenic effects in concentrations up to 10 μM (aminopurvalanol, indirubin-3′-monoxime, and alsterpaullone), depending on their kinase profile. Interestingly, the impact of the compounds on Cdks seemed to be of minor importance, as compared to other mechanisms. Aminopurvalanol, indirubin-3′-monoxime, and alsterpaullone might turn out as interesting scaffolds for the development of novel anti-angiogenic drugs.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carmeliet P (2005) Angiogenesis in life, disease and medicine. Nature 438:932–936
Ferrara N, Kerbel RS (2005) Angiogenesis as a therapeutic target. Nature 438:967–974
Quesada AR, Medina MA, Alba E (2007) Playing only one instrument may be not enough: limitations and future of the antiangiogenic treatment of cancer. Bioessays 29:1159–1168
Zimmermann GR, Lehar J, Keith CT (2007) Multi-target therapeutics: when the whole is greater than the sum of the parts. Drug Discov Today 12:34–42
Bostrom J, Yu SF, Kan D et al (2009) Variants of the antibody herceptin that interact with HER2 and VEGF at the antigen binding site. Science 323:1610–1614
Vesely J, Havlicek L, Strnad M et al (1994) Inhibition of cyclin-dependent kinases by purine analogues. Eur J Biochem 224:771–786
Knockaert M, Greengard P, Meijer L (2002) Pharmacological inhibitors of cyclin-dependent kinases. Trends Pharmacol Sci 23:417–425
Bain J, McLauchlan H, Elliott M et al (2003) The specificities of protein kinase inhibitors: an update. Biochem J 371:199–204
Bain J, Plater L, Elliott M et al (2007) The selectivity of protein kinase inhibitors: a further update. Biochem J 408:297–315
Knight ZA, Shokat KM (2005) Features of selective kinase inhibitors. Chem Biol 12:621–637
Meijer L, Raymond E (2003) Roscovitine and other purines as kinase inhibitors. From starfish oocytes to clinical trials. Acc Chem Res 36:417–425
Marko D, Schatzle S, Friedel A et al (2001) Inhibition of cyclin-dependent kinase 1 (CDK1) by indirubin derivatives in human tumour cells. Br J Cancer 84:283–289
Leost M, Schultz C, Link A et al (2000) Paullones are potent inhibitors of glycogen synthase kinase-3beta and cyclin-dependent kinase 5/p25. Eur J Biochem 267:5983–5994
Mettey Y, Gompel M, Thomas V et al (2003) Aloisines, a new family of CDK/GSK-3 inhibitors. SAR study, crystal structure in complex with CDK2, enzyme selectivity, and cellular effects. J Med Chem 46:222–236
Bach S, Knockaert M, Reinhardt J et al (2005) Roscovitine targets, protein kinases and pyridoxal kinase. J Biol Chem 280:31208–31219
Knockaert M, Gray N, Damiens E et al (2000) Intracellular targets of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors: identification by affinity chromatography using immobilised inhibitors. Chem Biol 7:411–422
Hoessel R, Leclerc S, Endicott JA et al (1999) Indirubin, the active constituent of a Chinese antileukaemia medicine, inhibits cyclin-dependent kinases. Nat Cell Biol 1:60–67
Ades EW, Candal FJ, Swerlick RA et al (1992) HMEC-1: establishment of an immortalized human microvascular endothelial cell line. J Invest Dermatol 99:683–690
Rothmeier AS, Ischenko I, Joore J et al (2008) Investigation of the marine compound spongistatin 1 links the inhibition of PKC{alpha} translocation to nonmitotic effects of tubulin antagonism in angiogenesis. FASEB J 23:1127–1137
Blumenthal SB, Kiemer AK, Tiegs G et al (2005) Metalloporphyrins inactivate caspase-3 and -8. FASEB J 19:1272–1279
Meijer L, Skaltsounis AL, Magiatis P et al (2003) GSK-3-selective inhibitors derived from Tyrian purple indirubins. Chem Biol 10:1255–1266
Knockaert M, Lenormand P, Gray N et al (2002) p42/p44 MAPKs are intracellular targets of the CDK inhibitor purvalanol. Oncogene 21:6413–6424
Blagden S, de BJ (2005) Drugging cell cycle kinases in cancer therapy. Curr Drug Targets 6:325–335
Tran TC, Sneed B, Haider J et al (2007) Automated, quantitative screening assay for antiangiogenic compounds using transgenic zebrafish. Cancer Res 67:11386–11392
Meijer L, Borgne A, Mulner O et al (1997) Biochemical and cellular effects of roscovitine, a potent and selective inhibitor of the cyclin-dependent kinases cdc2, cdk2 and cdk5. Eur J Biochem 243:527–536
Nam S, Buettner R, Turkson J et al (2005) Indirubin derivatives inhibit Stat3 signaling and induce apoptosis in human cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:5998–6003
Kim HS, Skurk C, Thomas SR et al (2002) Regulation of angiogenesis by glycogen synthase kinase-3beta. J Biol Chem 277:41888–41896
Zachary I (2003) VEGF signalling: integration and multi-tasking in endothelial cell biology. Biochem Soc Trans 31:1171–1177
Orr AW, Murphy-Ullrich JE (2004) Regulation of endothelial cell function BY FAK and PYK2. Front Biosci 9:1254–1266
Knockaert M, Wieking K, Schmitt S et al (2002) Intracellular targets of Paullones. Identification following affinity purification on immobilized inhibitor. J Biol Chem 277:25493–25501
Newcomb EW (2004) Flavopiridol: pleiotropic biological effects enhance its anti-cancer activity. Anticancer Drugs 15:411–419
Jain RK, Duda DG, Clark JW et al (2006) Lessons from phase III clinical trials on anti-VEGF therapy for cancer. Nat Clin Pract Oncol 3:24–40
Acknowledgments
We thank Prof. L. Meijer (Roscoff, France) for supplying us with the Cdk compounds.
The authors gratefully acknowledge the expert technical assistance by C. Niemann, and J. Peliskova. This work was supported by a grant of the EC (FP6-2002-Life Sciences & Health, PRO-KINASE Research Project, Project no. LSHB-CT-2004-503467).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zahler, S., Liebl, J., Fürst, R. et al. Anti-angiogenic potential of small molecular inhibitors of cyclin dependent kinases in vitro. Angiogenesis 13, 239–249 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-010-9181-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-010-9181-1