Abstract
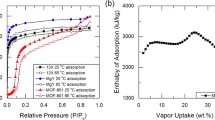
Zeolites are widely employed in the industrial drying of gases by Temperature Swing Adsorption (TSA). In a typical TSA process, the adsorbent is packed in a fixed bed, which is sequentially subjected to a “cold” feed (adsorption) and a hot flush (desorption). Due to the hydrothermal stress, adsorbents may suffer from reduced drying capacity in long-term service. The aim of this work is to assess the impact of thermal aging of two zeolite materials (LTA and CHA) having similar pore openings but different Si/Al ratios. We examined how simulated thermal aging affected porous texture, coke deposition and water vapor adsorption equilibrium and kinetics. Both zeolites showed reduced uptake of probe molecules (N2 at 77 K and CO2 at 273 K) and water vapor (303 K) when subjected to simulated thermal aging. In Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) analyses, only the aged LTA zeolite showed bands related to the presence of aromatic compounds. Water vapor adsorption uptake decreased 28.6% and 18.4% for LTA and CHA at 30 mbar, respectively. Kinetic studies indicate a reduction in water diffusion coefficient after the aging cycles. Although LTA has a significantly higher affinity for water as compared to CHA, the latter is much more resistant to hydrothermal aging with comparatively faster water diffusion.










Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- a :
-
Conglomerate external surface area per unit volume (m−1)
- \(C_{ps}\) :
-
Solid specific heat capacity (J kg−1 K−1)
- \(C_{pw}\) :
-
Water specific heat capacity (J kg−1 K−1)
- \(\overline{{C_{p} }}\) :
-
Specific heat capacity average (J kg−1 K−1)
- \(D_{\mu }\) :
-
Diffusion coefficient (m2 s−1)
- \(D_{\mu }^{0}\) :
-
Corrected diffusion coefficient (m2 s−1)
- \(D_{\mu , b}^{0}\) :
-
Diffusion coefficient in a reference temperature (m2 s−1)
- \(\Delta H_{ads}\) :
-
Adsorption enthalpy (J mol−1)
- \(\Delta t\) :
-
Time interval to achieve the final pressure (s)
- \(E_{a}\) :
-
Adsorption activation energy (J mol−1 K−1)
- \(h_{f}\) :
-
Heat transfer coefficient (W m−2 K−1)
- P:
-
Pressure (Pa)
- \(P_{b}\) :
-
Phase bulk pressure (Pa)
- \(P_{bi}\) :
-
Phase bulk initial pressure (Pa)
- \(P_{f}\) :
-
Final pressure (Pa)
- \(P_{i}\) :
-
Initial pressure (Pa)
- q:
-
Adsorbed amount (mol kg−1)
- \(q_{s}\) :
-
Maximum adsorbed amount (mol kg−1)
- \(\overline{q}\) :
-
Volumetric average adsorbed amount (mol kg−1)
- r:
-
Radial coordinate (m)
- R:
-
Particle radius (m)
- \(R_{IG}\) :
-
Universal gas constant (J mol−1 K−1)
- \(\rho_{s}\) :
-
Solid specific volume (kg m−3)
- t:
-
Time (s)
- T:
-
Temperature (K)
- \(T_{b}\) :
-
Phase bulk temperature (K)
References
Mokhatab, S., Poe, W.A., Mak, J.Y.: Natural gas dehydration and mercaptans removal. In: Mokhatab, S., Poe, W.A., Mak, J.Y. (eds.) Handbook of Natural Gas Transmission and Processing: Principles and Practices, pp. 307–348. Gulf Professional Publishing, Cambridge (2019)
Nastaj, J., Ambrozek, B.: Analysis of gas dehydration in TSA system with multi-layered bed of solid adsorbents. Chem. Eng. Process. 96, 44–53 (2015)
Haque, M.E., Xu, Q., Palanki, S.: Glycol loss minimization for a natural gas dehydration plant under upset conditions. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 58, 1994–2008 (2019)
Rouquerol, F., Rouquerol, J., Sing, K.S.W., Llewellyn, P.L., Maurin, G.: Adsorption by Powders and Porous Solids: Principles, Methodology and Applications, 2nd edn. Elsevier/Academic Press, Amsterdam (2014)
Berg, F., Pasel, F., Eckardt, T., Bathen, D.: Temperature swing adsorption in natural gas processing: a concise overview. Chem. Biol. Eng. Rev. 3, 59–71 (2019)
Pham, T.D., Liu, Q., Lobo, R.F.: Carbon dioxide and nitrogen adsorption on cation-exchanged SSZ-13 zeolites. Langmuir 29, 832–839 (2013)
Ruthven, D.M.: Principles of Adsorption and Adsorption Processes. Wiley, New York (1984)
Thomas, W.J., Crittenden, B.: Adsorption Technology & Design. Butterworth Heinemann, Lymington (1998)
Santiago, R.G., Santos, B.F., Lima, I.G., Moura, K.O., Melo, D.C., Grava, W.M., Bastos-Neto, M., de Lucena, S.M.P., de Azevedo, D.C.S.: Investigation of premature aging of zeolites used in the drying of gas streams. Chem. Eng. Commun. 206, 1378–1385 (2019)
Do, D.D.: Adsorption Analysis: Equilibria and Kinetics. Imperial College Press, London (1998)
Siqueira, R.M., Vilarrasa-García, E., Torres, A.E.B., de Azevedo, D.C.S., Bastos-Neto, M.: Simple procedure to estimate mass transfer coefficients from uptake curves on activated carbons. Chem. Eng. Technol. 41, 1622–1630 (2018)
Kärger, J., Ruthven, D.M.: Diffusion in nanoporous materials: Fundamental principles, insights and challenges. New. J. Chem. 40, 4027–4048 (2016)
Wang, J.-Y., Mangano, E., Brandani, S., Ruthven, D.M.: A review of common practices in gravimetric and volumetric adsorption kinetic experiments. Adsorption 27, 295–318 (2021)
Database of zeolite structure. Structure Commission of the International Zeolite Association (IZA-SC). http://www.iza-structure.org/databases/ (2017). Accessed 30 March 2021
Zamechek, W.: Determination of the Elemental Compositor of Zeolitic Materials: Verified Syntheses of Zeolitic Materials, pp. 51–53. Elsevier, Amsterdam (2001)
Thommes, M., Kaneko, K., Neimark, A.V., Olivier, J.P., Rodriguez-Reinoso, F., Rouquerol, J., Sing, K.S.W.: Physisorption of gases, with special reference to the evaluation of surface area and pore size distribution (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 87, 1051–1069 (2015)
Jensen, N.K., Rufford, T.E., Watson, G., Zhang, D.K., Chan, K.I., May, E.F.: Screening zeolites for gas separation applications involving methane, nitrogen, and carbon dioxide. J. Chem. Eng. Data 57, 106–113 (2012)
Seabra, R., Ribeiro, A.M., Gleichmann, K., Ferreira, A.F.P., Rodrigues, A.E.: Adsorption equilibrium and kinetics of carbon dioxide, methane and nitrogen on binderless zeolite 4A adsorbents. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 277, 105–114 (2019)
Tounsi, H., Mseddi, S., Djemel, S.: Preparation and characterization of Na-LTA zeolite from Tunisian sand and aluminum scrap. Phys. Procedia 2, 1065–1074 (2009)
Valiullin, R., Kärger, J., Cho, K., Choi, M., Ryoo, R., et al.: Dynamics of water diffusion in mesoporous zeolites. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 142, 236–244 (2011)
Zavareh, S., Farrokhzad, Z., Darvishi, F.: Modification of zeolite 4A for use as an adsorbent for glyphosate and as an antibacterial agent for water. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 155, 1–8 (2018)
Moreira, J.C., Santa, R.A.A.B., Miraglia, G.L., Soares, C., Riella, H.G.: Evaluation of different reaction systems to obtain zeolite 4A via reverse microemulsion. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 279, 262–270 (2019)
Kim, W., Choi, D., Kim, S.: Sonochemical synthesis of zeolite A from metakaolinite in NaOH solution. Mater. Trans. 51(9), 1694-–1698 (2010)
Markovic, S., Dondur, V., Dimitrijevic, R.: FTIR spectroscopy of framework aluminosilicate structures: carnegieite and pure sodium nepheline. J. Mol. Struct. 654(1–3), 223–234 (2003)
Aysan, H., Edebali, S., Ozdemir, C., Karakaya, M.C., Karakaya, N.: Use of chabazite, a naturally abundant zeolite, for the investigation of the adsorption kinetics and mechanism of methylene blue dye. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 235, 78–86 (2016)
Geng, H., Li, G., Liu, D., Liu, C.: Rapid and efficient synthesis of CHA-type zeolite by interzeolite conversion of LTA-type zeolite in the presence of N, N, N-trimethyladamantammonium hydroxide. J. Solid State Chem. 265, 193–199 (2018)
Guisnet, M., Ribeiro, F.R.: Deactivation and Regeneration of Zeolite Catalysts. Imperial College Press, London (2011)
Colthup, N.B., Daly, L.H., Wiberley, S.E.: Introduction to Infrared and Raman Spectroscopy, 3rd edn. Academic Press, San Diego (1990)
Park, J.W., Seo, G.: IR study on methanol-to-olefin reaction over zeolites with different pore structures and acidities. Appl. Catal. A 356, 180–188 (2009)
Montanari, T., Busca, G.: On the mechanism of adsorption and separation of CO2 on LTA zeolites: an IR investigation. Vib. Spectrosc. 46, 45–51 (2008)
Xiong, Z., Syed-Hassan, S.S.A., Xu, J., Wang, Y., Hu, S., Su, S., Zhang, S., Xiang, J.: Evolution of coke structures during the pyrolysis of bio-oil at various temperatures and heating rates. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 134, 336–342 (2018)
Iqbal, A., Sattar, H., Haider, R., Munir, S.: Synthesis and characterization of pure phase zeolite 4A from coal fly ash. J. Clean. Prod 219, 258–267 (2019)
Ng, E.-P., Mintova, S.: Nanoporous materials with enhanced hydrophilicity and high water sorption capacity. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 114, 1–26 (2008)
Tatlier, M., Munz, G., Henninger, S.K.: Relation of water adsorption capacities of zeolites with their structural properties. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 264, 70–75 (2018)
Wang, Y.: Measurements and modeling of water adsorption isotherms of zeolite linde-type A crystals. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 59, 8304–8314 (2020)
Yamamoto, T., Kim, Y.H., Kim, B.C., Endo, A., Thongprachan, N., Ohmori, T.: Adsorption characteristics of zeolites for dehydration of ethanol: evaluation of diffusivity of water in porous structure. Chem. Eng. J. 181–182, 443–448 (2012)
Jänchen, J., Bish, D.L., Möhlman, D.T.F., Stach, H.: Investigation of the water sorption properties of Mars-relevant micro- and mesoporous minerals. Icarus 180, 353–358 (2006)
Fals, J., García, J.R., Falco, M., Sedran, U.: Coke from SARA fractions in VGO. Impact on Y zeolite acidity and physical properties. Fuel 225, 26–34 (2018)
Ruthven, D.M.: Diffusion in type A zeolites: New insights from old data. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 162, 69–79 (2012)
Dawoud, B., Vedder, U., Amer, E.-H., Dunne, S.: Non-isothermal adsorption kinetics of water vapour into a consolidated zeolite layer. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 50, 2190–2199 (2007)
Qiu, L., Murashov, V., White, M.A.: Zeolite 4A: heat capacity and thermodynamic properties. Solid State Sci. 2, 841–846 (2000)
Chipera, S.J., Bish, D.L., Carlos, B.A.: Equilibrium modeling of the formation of zeolites in fractures at Yucca Mountain, Nevada. Natural Zeolites ‘93: Occurrence, Properties, Use, pp. 565–577 (1995)
Jänchen, J., Stach, H., Hellwig, U.: Water sorption in faujasite- and chabazite type zeolites of varying lattice composition for heat storage applications. Stud. Surf. Sci. Catal. 174, 599–602 (2008)
Barrer, R.M., Fender, B.E.F.: The diffusion and sorption of water in zeolites-II. Intrinsic and self-diffusion. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 21, 12–24 (1961)
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledged the financial support from PETROBRAS and the ANP (Agência Nacional de Petróleo, Gás Natural e Biocombustíveis – ANP, Brasil) through the Clause of Investments in Research, Development and Innovation in contracts for Exploration, Development and Production of Petroleum and Natural Gas. They also thank CNPq (Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico) process 402561/2007-4, Notice MCY/CNPq nº10/2007 for XRD analyses and LEVM (Laboratório de Microscopia Vibracional) for the FTIR analyses.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nascimento, B.O., dos Santos, B.F., Maia, D.A.S. et al. Water adsorption in fresh and thermally aged zeolites: equilibrium and kinetics. Adsorption 27, 1043–1053 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10450-021-00331-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10450-021-00331-x