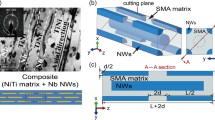
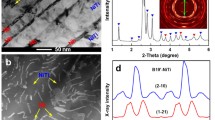
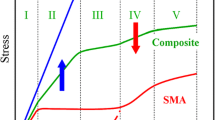
Abstract
A continuous martensite transformation is indispensable for achieving large linear superelasticity and low modulus in phase transforming metal-based composites. However, determining how to accurately condition the residual martensite in a shape memory alloy matrix though the reinforcement shape to achieve continuous martensite transformation has been a challenge. Here, we take the finite element method to perform a comparative study of the effects of nanoinclusion shape on the interaction and martensite phase transformation in this new composite. Two typical samples are compared: one reinforced by metallic nanowires and the other by nanoparticles. We find that the residual martensite within the shape memory alloy matrix after a pretreatment can be tailored by the reinforcement shape. In particular, our results show that the shape memory alloy matrix can retain enough residual martensite phases to achieve continuous martensite transformation in the subsequent loading when the aspect ratio of nanoreinforcement is larger than 20. In contrast, the composites reinforced with spherical or low aspect ratio reinforcement show a typical nonlinear superelasticity as a result of a low stress transfer-induced discontinuous martensite transformation within the shape memory alloy matrix.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hao, S., Cui, L., Jiang, D., Han, X., Ren, Y., Jiang, J., Liu, Y., Liu, Z., Mao, S., Wang, Y., Li, Y., Ren, X., Ding, X., Wang, S., Yu, C., Shi, X., Du, M., Yang, F., Zheng, Y., Zhang, Z., Li, X., Brown, D.E., Li, J.: A transforming metal nanocomposite with large elastic strain, low modulus, and high strength. Science. 339(6124), 1191–1194 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1228602
Zhou, M.: Exceptional properties by design. Science. 339(6124), 1161–1162 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1236378
Li, J., Shan, Z., Ma, E.: Elastic strain engineering for unprecedented materials properties. MRS Bull. 39(02), 108–117 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1557/mrs.2014.3
Chen, Y., Liu, Y., Sun, C., Yu, K.Y., Song, M., Wang, H., Zhang, X.: Microstructure and strengthening mechanisms in Cu/Fe multilayers. Acta Mater. 60(18), 6312–6321 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2012.08.005
Thilly, L., Petegem, S.V., Renault, P.O., Lecouturier, F., Vidal, V., Schmitt, B., Swygenhoven, H.V.: A new criterion for elasto-plastic transition in nanomaterials: application to size and composite effects on Cu–Nb nanocomposite wires. Acta Mater. 57(11), 3157–3169 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2009.03.021
Sun, Y., Sun, J., Liu, M., Chen, Q.: Mechanical strength of carbon nanotube–nickel nanocomposites. Nanotechnology. 18(50), 505704 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/18/50/505704
Thilly, L., Renault, P.O., Vidal, V., Lecouturier, F., Van Petegem, S., Stuhr, U., van Swygenhoven, H.: Plasticity of multiscale nanofilamentary Cu/Nb composite wires during in situ neutron diffraction: Codeformation and size effect. Appl. Phys. Lett. 88(19), 191906 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2202720
Dzenis, Y.: Structural nanocomposites. Science. 319(5862), 419–420 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1151434
Podsiadlo, P., Kaushik, A.K., Arruda, E.M., Waas, A.M., Shim, B.S., Xu, J., Nandivada, H., Pumplin, B.G., Lahann, J., Ramamoorthy, A., Kotov, N.A.: Ultrastrong and stiff layered polymer nanocomposites. Science. 318(5847), 80–83 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1143176
Coleman, J.N., Khan, U., Gun’ko, Y.K.: Mechanical reinforcement of polymers using carbon nanotubes. Adv. Mater. 18(6), 689–706 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.200501851
Otsuka, K., Ren, X.: Physical metallurgy of Ti–Ni-based shape memory alloys. Prog. Mater. Sci. 50(5), 511–678 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmatsci.2004.10.001
Otsuka, K., Wayman, C.M.: Shape Memory Materials. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1998)
Hao, S., Cui, L., Guo, F., Liu, Y., Shi, X., Jiang, D., Brown, D.E., Ren, Y.: Achieving large linear elasticity and high strength in bulk nanocompsite via synergistic effect. Sci. Rep. 5(1), 8892 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep08892
Yang, F., Ni, D., Hao, S., Li, S., Ma, Z., Liu, Y., Feng, C., Cui, L.: Microstructure and phase stress partition of Mo fiber reinforced CuZnAl composite. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 628, 419–422 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2015.01.068
Liu, Z., Cui, L., Liu, Y., Jiang, D., Jiang, J., Shi, X., Shao, Y., Zheng, Y.: Influence of internal stress coupling on the deformation behavior of NiTi-Nb nanowire composites. Scripta Mater. 77, 75–78 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2014.01.027
Dong, Y., Cong, D., Nie, Z., He, Z., Li, L., Wang, Z., et al.: Stress transfer during different deformation stages in a nano-precipitate-strengthened Ni-Ti shape memory alloy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 107(20), 201901 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4935691
Hao, S.J., Jiang, D.Q., Cui, L.S., Wang, Y.D., Shi, X.B., Nie, Z.H., Brown, D.E., Ren, Y.: Phase-stress partition and stress-induced martensitic transformation in NbTi/NiTi nanocomposite. Appl. Phys. Lett. 99(8), 084103 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3629768
Yu, C., Liu, Z., Liu, Y., Shao, Y., Ren, Y., Cui, L.: Load transfer in phase transforming matrix–nanowire composite revealing the significant load carrying capacity of the nanowires. Mater. Des. 89, 721–726 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2015.10.029
Li, Y., RAMESH, K.T.: Influence of particle volume fraction, shape, and aspect ratio on the behavior of particle-reinforced metal–matrix composites at high rates of strain. Acta Mater. 46, 5633-5646 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1359-6454(98)00250-X
Xin, L., Yang, W., Zhao, Q., Dong, R., Liang, X., Xiu, Z., Hussain, M., Wu, G.: Effect of extrusion treatment on the microstructure and mechanical behavior of SiC nanowires reinforced al matrix composites. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 682, 38–44 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2016.11.042
Hao, S., Cui, L., Wang, H., Jiang, D., Liu, Y., Yan, J., Ren, Y., Han, X., Brown, D.E., Li, J.: Retaining large and adjustable elastic strains of kilogram-scale Nb nanowires. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 8(5), 2917–2922 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.5b10840
Segurado, J., Llorca, J.: A numerical approximation to the elastic properties of sphere-reinforced composites. J. Mech. Phys. Solids. 50(10), 2107–2121 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-5096(02)00021-2
Tian, W., Qi, L., Zhou, J., Guan, J.: Effects of the fiber orientation and fiber aspect ratio on the tensile strength of Csf /Mg composites. Comput. Mater. Sci. 89, 6–11 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.commatsci.2014.03.004
Mirkhalaf, S.M., Andrade Pires, F.M., Simoes, R.: Determination of the size of the representative volume element (RVE) for the simulation of heterogeneous polymers at finite strains. Finite Elem. Anal. Des. 119, 30–44 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.finel.2016.05.004
Zare, Y., YopRhee, K., Hui, D.: Influences of nanoparticles aggregation/agglomeration on the interfacial/interphase and tensile properties of nanocomposites. Compos. Pt. B-Eng. 122, 41–46 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2017.04.008
Xia, Z., Zhang, Y., Ellyin, F.: A unified periodical boundary conditions for representative volume elements of composites and applications. Int. J. Solids Struct. 40(8), 1907–1921 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0020-7683(03)00024-6
Xia, Z., Zhou, C., Yong, Q., Wang, X.: On selection of repeated unit cell model and application of unified periodic boundary conditions in micro-mechanical analysis of composites. Int. J. Solids Struct. 43(2), 266–278 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2005.03.055
Auricchio, F., Taylor, R.L.: Shape-memory alloys: modelling and numerical simulations of the finite-strain superelastic behavior. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 143(1-2), 175–194 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0045-7825(96)01147-4
Auricchio, F., Taylor, R.L., Lubliner, J.: Shape-memory alloys: macromodelling and numerical simulations of the superelastic behavior. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 146(3-4), 281–312 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0045-7825(96)01232-7
Gong, X., Pelton, A.: ABAQUS Analysis on Nitinol Medical Applications. SMST Society, California (2002)
Lei, H., Wang, Z., Zhou, B., Tong, L., Wang, X.: Simulation and analysis of shape memory alloy fiber reinforced composite based on cohesive zone model. Mater. Des. 40, 138–147 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2012.03.037
Lei, H., Wang, Z., Tong, L., Zhou, B., Fu, J.: Experimental and numerical investigation on the macroscopic mechanical behavior of shape memory alloy hybrid composite with weak interface. Compos. Struct. 101, 301–312 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2013.02.006
Cohen, D.E., Bevk, J.: Enhancement of the Young’s modulus in the ultrafine Cu-Nb filamentary composites. Appl. Phys. Lett. 39(8), 595–597 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.92842
Nemat-Nasser, S., Guo, W.: Superelastic and cyclic response of NiTi SMA at various strain rates and temperatures. Mech. Mater. 38(5-6), 463–474 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mechmat.2005.07.004
Machado, G., Louche, H., Alonso, T., Favier, D.: Superelastic cellular NiTi tube-based materials: fabrication, experiments and modeling. Mater. Des. 65, 212–220 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2014.09.007
Jiang, J., Jiang, D., Hao, S., Yu, C., Zhang, J., Ren, Y., Lu, D., Xie, S., Cui, L.: A nano lamella NbTi–NiTi composite with high strength. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 633, 121–124 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2015.03.010
Jia, Z., Ma, H., Cheng, L., Lau, K., Hui, D., Yuan, G.: Stress transfer properties of carbon nanotube reinforced polymer composites at low temperature environment. Compos. Pt. B-Eng. 106, 356–365 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2016.09.006
Mohonee, V.K., Goh, K.L.: Effects of fibre-fibre interaction on stress uptake in discontinuous fibre reinforced composites. Compos. Pt. B-Eng. 86, 221–228 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2015.10.015
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to appreciate the support of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51231008, 51320105014, 51501141) and 111 project (B06025). X. Z acknowledges the computational resources provided by the HPC platform of Xi’an Jiaotong University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Ren, J., Wang, X. et al. Insight into the Effects of Reinforcement Shape on Achieving Continuous Martensite Transformation in Phase Transforming Matrix Composites. Appl Compos Mater 25, 1369–1384 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10443-017-9671-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10443-017-9671-z