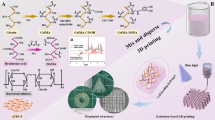
Abstract
Due to the limited self-repair capacity of the hyaline cartilage, the repair of cartilage remains an unsolved clinical problem. Tissue engineering strategy with 3D bioprinting technique has emerged a new insight by providing patient’s personalized cartilage grafts using autologous cells for hyaline cartilage repair and regeneration. In this review, we first summarized the intrinsic property of hyaline cartilage in both maxillofacial and orthopedic regions to establish the requirement for 3D bioprinting cartilage tissue. We then reviewed the literature and provided opinion pieces on the selection of bioprinters, bioink materials, and cell sources. This review aims to identify the current challenges for hyaline cartilage bioprinting and the directions for future clinical development in bioprinted hyaline cartilage.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adamiak, K., and A. J. Sionkowska. Current methods of collagen cross-linking. Int. J. Biol Macromol. 161:550–560, 2020.
Aksoy, F., Y. Yildirim, H. Demirhan, O. Özturan, and S. Solakoglu. Structural characteristics of septal cartilage and mucoperichondrium. J. Laryngol. Otol. 126(1):38–42, 2012.
Anderson, K., M. Henneberg, and R. Norris. Anatomy of the nasal profile. J. Anatomy. 213(2):210–216, 2008.
Andrews, S. H., M. Kunze, A. Mulet-Sierra, L. Williams, K. Ansari, M. Osswald, and A. B. Adesida. Strategies to mitigate variability in engineering human nasal cartilage. Sci. Rep. 7(1):6490, 2017.
Apelgren, P., M. Amoroso, A. Lindahl, C. Brantsing, N. Rotter, P. Gatenholm, and L. J. P. O. Kölby. Chondrocytes and stem cells in 3D-bioprinted structures create human cartilage in vivo. PLoS ONE. 12(12):e0189428, 2017.
Apelgren, P., M. Amoroso, K. Säljö, A. Lindahl, C. Brantsing, L. S. Orrhult, K. Markstedt, P. Gatenholm, and L. Kölby. Long-term in vivo integrity and safety of 3D-bioprinted cartilaginous constructs. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B. 109(1):126–136, 2021.
Apelgren, P., M. Amoroso, K. Säljö, M. Montelius, A. Lindahl, L. S. Orrhult, P. Gatenholm, and L. J. B. Kölby. Vascularization of tissue engineered cartilage-Sequential in vivo MRI display functional blood circulation. Biomaterials.276:121002, 2021.
Apelgren, P., E. Karabulut, M. Amoroso, A. Mantas, H. C. M. Ávila, L. Kölby, T. Kondo, G. Toriz, and P. Gatenholm. In vivo human cartilage formation in three-dimensional bioprinted constructs with a novel bacterial nanocellulose bioink. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 5(5):2482–2490, 2019.
Ashrafi, A. T. Management of upper lateral cartilages (ULCs) in rhinoplasty. World J. Plast. Surg. 3(2):129, 2014.
Aung, A., G. Gupta, G. Majid, and S. J. A. Varghese. Osteoarthritic chondrocyte–secreted morphogens induce chondrogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. Rheumatism. 63(1):148–158, 2011.
Ávila, H. M., S. Schwarz, N. Rotter, and P. Gatenholm. 3D bioprinting of human chondrocyte-laden nanocellulose hydrogels for patient-specific auricular cartilage regeneration. Bioprinting. 1:22–35, 2016.
Awwad, H. A., L. Thiagarajan, J. M. Kanczler, M. H. Amer, G. Bruce, S. Lanham, R. M. Rumney, R. O. Oreffo, and J. E. Dixon. Genetically-programmed, mesenchymal stromal cell-laden & mechanically strong 3D bioprinted scaffolds for bone repair. J. Control. Release. 325:335–346, 2020.
Bader, D., and G. J. B. Kempson. The short-term compressive properties of adult human articular cartilage. Engineering. 4(3):245–256, 1994.
De Bari, C., F. Dell’Accio, and F. P. Luyten. Failure of in vitro–differentiated mesenchymal stem cells from the synovial membrane to form ectopic stable cartilage in vivo. Arthritis Rheum. 50(1):142–150, 2004.
Bornes, T. D., A. B. Adesida, and N. M. Jomha. Mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of traumatic articular cartilage defects: a comprehensive review. Therapy. 16(5):1–19, 2014.
Bornes, T. D., A. B. Adesida, and N. M. Jomha. Mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of traumatic articular cartilage defects: a comprehensive review. Arthritis Res Therapy. 16(5):432, 2014.
Boschetti, F., G. Pennati, F. Gervaso, G. M. Peretti, and G. J. B. Dubini. Biomechanical properties of human articular cartilage under compressive loads. Biorheology. 41(3–4):159–166, 2004.
Bottini, D., P. Gentile, A. Donfrancesco, L. Fiumara, and V. J. Cervelli. Augmentation rhinoplasty with autologous grafts. Aesthet. Plast. Surg. 32(1):136–142, 2008.
Brittberg, M., A. Lindahl, A. Nilsson, C. Ohlsson, O. Isaksson, and L. J. Peterson. Treatment of deep cartilage defects in the knee with autologous chondrocyte transplantation. N. Engl. J. 331(14):889–895, 1994.
Caffrey, J. P., A. M. Kushnaryov, M. S. Reuther, V. W. Wong, K. K. Briggs, K. Masuda, R. L. Sah, and D. J. O. Watson. Flexural properties of native and tissue-engineered human septal cartilage. N. Surgery. 148(4):576–581, 2013.
Campos, D. F. D., M. Rohde, M. Ross, P. Anvari, A. Blaeser, M. Vogt, C. Panfil, G. H. F. Yam, J. S. Mehta, and H. J. Fischer. Corneal bioprinting utilizing collagen-based bioinks and primary human keratocytes. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A. 107(9):1945–1953, 2019.
Candrian, C., D. Vonwil, A. Barbero, E. Bonacina, S. Miot, J. Farhadi, D. Wirz, S. Dickinson, A. Hollander, and M. J. A. Jakob. Engineered cartilage generated by nasal chondrocytes is responsive to physical forces resembling joint loading. Arthritis Rheum. 58(1):197–208, 2008.
Cervelli, V., D. J. Bottini, P. Gentile, L. Fantozzi, A. Arpino, C. Cannatà, L. Fiumara, and C. U. Casciani. Reconstruction of the nasal dorsum with autologous rib cartilage. Ann. Plast. Surg. 56(3):256–262, 2006.
Chen, P., L. Zheng, Y. Wang, M. Tao, Z. Xie, C. Xia, C. Gu, J. Chen, P. Qiu, and S. J. T. Mei. Desktop-stereolithography 3D printing of a radially oriented extracellular matrix/mesenchymal stem cell exosome bioink for osteochondral defect regeneration. Theranostics. 9(9):2439, 2019.
Choe, R., E. Devoy, B. Kuzemchak, M. Sherry, E. Jabari, J. D. Packer, and J. P. J. B. Fisher. Computational investigation of interface printing patterns within 3D printed multilayered scaffolds for osteochondral tissue engineering. Biofabrication. 14(2):025015, 2022.
Chua, K., B. Aminuddin, N. Fuzina, and B. Ruszymah. Insulin-transferrin-selenium prevent human chondrocyte dedifferentiation and promote the formation of high quality tissue engineered human hyaline cartilage. Eur. Cell Mater. 9(9):58–67, 2005.
Cohen, N. P., R. J. Foster, and V. C. J. Mow. Composition and dynamics of articular cartilage: structure, function, and maintaining healthy state. J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 28(4):203–215, 1998.
Compaan, A. M., K. Christensen, and Y. Huang. Inkjet bioprinting of 3D silk fibroin cellular constructs using sacrificial alginate. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 3(8):1519–1526, 2017.
Cooke, M. E., and D. H. Rosenzweig. The rheology of direct and suspended extrusion bioprinting. APL Bioeng.5(1):011502, 2021.
Critchley, S., E. J. Sheehy, G. Cunniffe, P. Diaz-Payno, S. F. Carroll, O. Jeon, E. Alsberg, P. A. Brama, and D. J. Kelly. 3D printing of fibre-reinforced cartilaginous templates for the regeneration of osteochondral defects. Acta Biomater. 113:130–143, 2020.
Cui, X., D. Dean, Z. M. Ruggeri, and T. Boland. Cell damage evaluation of thermal inkjet printed Chinese hamster ovary cells. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 106(6):963–969, 2010.
Daly, A. C., S. E. Critchley, E. M. Rencsok, and D. J. Kelly. A comparison of different bioinks for 3D bioprinting of fibrocartilage and hyaline cartilage. Biofabrication. 8(4):045002, 2016.
Daly, A. C., F. E. Freeman, T. Gonzalez-Fernandez, S. E. Critchley, J. Nulty, and D. J. Kelly. 3D bioprinting for cartilage and osteochondral tissue engineering. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 6(22):1700298, 2017.
Daly, A. C., and D. J. J. B. Kelly. Biofabrication of spatially organised tissues by directing the growth of cellular spheroids within 3D printed polymeric microchambers. Biomaterials. 197:194–206, 2019.
Dash, S., and P. A. J. B. Trainor. The development, patterning and evolution of neural crest cell differentiation into cartilage and bone. Bone. 137:115409, 2020.
Davoodi, E., E. Sarikhani, H. Montazerian, S. Ahadian, M. Costantini, W. Swieszkowski, S. M. Willerth, K. Walus, M. Mofidfar, and E. Toyserkani. Extrusion and microfluidic-based bioprinting to fabricate biomimetic tissues and organs. Adv. Mater. Technol. 5(8):1901044, 2020.
Derakhshanfar, S., R. Mbeleck, K. Xu, X. Zhang, W. Zhong, and M. J. B. Xing. 3D bioprinting for biomedical devices and tissue engineering: a review of recent trends and advances. Bioact. Mater. 3(2):144–156, 2018.
Diamantides, N., L. Wang, T. Pruiksma, J. Siemiatkoski, C. Dugopolski, S. Shortkroff, S. Kennedy, and L. J. J. B. Bonassar. Correlating rheological properties and printability of collagen bioinks: the effects of riboflavin photocrosslinking and pH. Biofabrication. 9(3):034102, 2017.
Dufour, A., X. B. Gallostra, C. O’keeffe, K. Eichholz, S. Von Euw, O. Garcia, and D. J. B. Kelly. Integrating melt electrowriting and inkjet bioprinting for engineering structurally organized articular cartilage. Biomaterials. 283:121405, 2022.
Eyre, D. J. A. R. Articular cartilage and changes in arthritis: collagen of articular cartilage. Therapy. 4(1):1–6, 2001.
Farhadi, J., I. Fulco, S. Miot, D. Wirz, M. Haug, S. C. Dickinson, A. P. Hollander, A. U. Daniels, G. Pierer, and M. J. Heberer. Precultivation of engineered human nasal cartilage enhances the mechanical properties relevant for use in facial reconstructive surgery. Ann. Surg. 244(6):978, 2006.
Fatimi, A., O. V. Okoro, D. Podstawczyk, J. Siminska-Stanny, and A. J. G. Shavandi. Natural hydrogel-based bio-inks for 3D bioprinting in tissue engineering: a review. Gels. 8(3):179, 2022.
Ferré, F. C., H. Larjava, L.-S. Loison-Robert, T. Berbar, G. R. Owen, A. Berdal, H. Chérifi, B. Gogly, L. Häkkinen, and B. P. Fournier. Formation of cartilage and synovial tissue by human gingival stem cells. Stem Cells Dev. 23(23):2895–2907, 2014.
Fox, A. J. S., A. Bedi, and S. A. Rodeo. The basic science of articular cartilage: structure, composition, and function. Sports Health. 1(6):461–468, 2009.
Frank, R. M., E. J. Cotter, I. Nassar, B. J. S. M. Cole, and A. Review. Failure of bone marrow stimulation techniques. Sports Med. Arthrosc. Rev. 25(1):2–9, 2017.
Franz, T., E. Hasler, R. Hagg, C. Weiler, R. Jakob, and P. J. O. Mainil-Varlet. In situ compressive stiffness, biochemical composition, and structural integrity of articular cartilage of the human knee joint. Cartilage. 9(6):582–592, 2001.
Fulco, I., S. Miot, M. D. Haug, A. Barbero, A. Wixmerten, S. Feliciano, F. Wolf, G. Jundt, A. Marsano, and J. Farhadi. Engineered autologous cartilage tissue for nasal reconstruction after tumour resection: an observational first-in-human trial. Lancet. 384(9940):337–346, 2014.
Gao, Y., S. Liu, J. Huang, W. Guo, J. Chen, L. Zhang, B. Zhao, J. Peng, A. Wang, and Y. Wang, The ECM-cell interaction of cartilage extracellular matrix on chondrocytes. BioMed. Res. Int. 2014 (2014).
Gebeyehu, A., S. K. Surapaneni, J. Huang, A. Mondal, V. Z. Wang, N. F. Haruna, A. Bagde, P. Arthur, S. Kutlehria, and N. Patel. Polysaccharide hydrogel based 3D printed tumor models for chemotherapeutic drug screening. Sci. Rep. 11(1):1–15, 2021.
Ghadially, F. N. Structure and function of articular cartilage. Clin. Rheum. Dis. 7(1):3–28, 1981.
Glasgold, M. J., Y. P. Kato, D. Christiansen, J. A. Hauge, A. I. Glasgold, and F. H. Silver. Mechanical properties of Septai cartilage homografts. Otolaryngology. 99(4):374–379, 1988.
Gotterbarm, T., W. Richter, M. Jung, S. B. Vilei, P. Mainil-Varlet, T. Yamashita, and S. J. J. B. Breusch. An in vivo study of a growth-factor enhanced, cell free, two-layered collagen–tricalcium phosphate in deep osteochondral defects. Biomaterials. 27(18):3387–3395, 2006.
Grad, S., D. Eglin, M. Alini, and M. J. Stoddart. Physical stimulation of chondrogenic cells in vitro: a review. Relat. Res. 469(10):2764–2772, 2011.
Grässel, S., and A. Aszódi. Cartilage. Berlin: Springer, 2016.
Griffin, M., Y. Premakumar, A. Seifalian, M. Szarko, and P. Butler. Biomechanical characterisation of the human nasal cartilages; implications for tissue engineering. J. Mater. Sci. 27(1):11, 2016.
Gu, Z., J. Fu, H. Lin, and Y. He. Development of 3D bioprinting: From printing methods to biomedical applications. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 15(5):529–557, 2020.
Guo, J., A. E. N. Asli, K. R. Williams, P. L. Lai, X. Wang, R. Montazami, and N. N. Hashemi. Viability of neural cells on 3D printed graphene bioelectronics. Biosensors. 9(4):112, 2019.
Gupta, S., and A. Bit. 3D bioprinting in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. Cell Tissue Bank. 23:1–14, 2021.
Hakobyan, D., O. Kerouredan, M. Remy, N. Dusserre, C. Medina, R. Devillard, J.-C. Fricain, and H. Oliveira. Laser-Assisted Bioprinting for Bone Repair, 3D Bioprinting. Berlin: Springer, pp. 135–144, 2020.
Hall, B. K., and J. A. Gillis. Incremental evolution of the neural crest, neural crest cells and neural crest-derived skeletal tissues. J. Anatomy. 222(1):19–31, 2013.
Hauptstein, J., T. Böck, M. Bartolf-Kopp, L. Forster, P. Stahlhut, A. Nadernezhad, G. Blahetek, A. Zernecke-Madsen, R. Detsch, and T. J. Jüngst. Hyaluronic acid-based bioink composition enabling 3d bioprinting and improving quality of deposited cartilaginous extracellular matrix. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 9(15):2000737, 2020.
Hiller, T., J. Berg, L. Elomaa, V. Röhrs, I. Ullah, K. Schaar, A.-C. Dietrich, M. A. Al-Zeer, A. Kurtz, and A. C. Hocke. Generation of a 3D liver model comprising human extracellular matrix in an alginate/gelatin-based bioink by extrusion bioprinting for infection and transduction studies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 19(10):3129, 2018.
Homicz, M. R., K. B. McGowan, L. M. Lottman, G. Beh, R. L. Sah, and D. Watson. A compositional analysis of human nasal septal cartilage. Archiv. Fac. Plast. Surg. 5(1):53–58, 2003.
Hong, H., Y. B. Seo, J. S. Lee, Y. J. Lee, H. Lee, O. Ajiteru, M. T. Sultan, O. J. Lee, S. H. Kim, and C. H. J. B. Park. Digital light processing 3D printed silk fibroin hydrogel for cartilage tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 232:119679, 2020.
Huang, Y., X. Li, A. J. Poudel, W. Zhang, and L. J. Xiao. Hydrogel-based bioinks for 3D bioprinting articular cartilage: a comprehensive review with focus on mechanical reinforcement. Appl. Mater. Today. 29:101668, 2022.
Jia, L., Y. Hua, J. Zeng, W. Liu, D. Wang, G. Zhou, X. Liu, and H. J. Jiang. Bioprinting and regeneration of auricular cartilage using a bioactive bioink based on microporous photocrosslinkable acellular cartilage matrix. Bioact. Mater. 16:66–81, 2022.
Jiao, A., N. E. Trosper, H. S. Yang, J. Kim, J. H. Tsui, S. D. Frankel, C. E. Murry, and D.-H. Kim. Thermoresponsive nanofabricated substratum for the engineering of three-dimensional tissues with layer-by-layer architectural control. ACS nano. 8(5):4430–4439, 2014.
Jodat, Y. A., K. Kiaee, D. V. Jarquin, R. L. Hernández, et al. A 3D-printed hybrid nasal cartilage with functional electronic olfaction. Adv. Sci. 7(5):1901878, 2020.
Jurvelin, J., M. Buschmann, and E. J. Hunziker. Mechanical anisotropy of the human knee articular cartilage in compression. J. Eng. Med. H. 217(3):215–219, 2003.
Kafienah, W. E., M. Jakob, O. Démarteau, A. Frazer, M. D. Barker, I. Martin, and A. P. Hollander. Three-dimensional tissue engineering of hyaline cartilage: comparison of adult nasal and articular chondrocytes. Tissue Eng. 8(5):817–826, 2002.
Kawecki, F., W. P. Clafshenkel, F. A. Auger, J.-M. Bourget, J. Fradette, and R. Devillard. Self-assembled human osseous cell sheets as living biopapers for the laser-assisted bioprinting of human endothelial cells. Biofabrication.10(3):035006, 2018.
Keriquel, V., H. Oliveira, M. Rémy, S. Ziane, S. Delmond, B. Rousseau, S. Rey, S. Catros, J. Amédée, and F. Guillemot. In situ printing of mesenchymal stromal cells, by laser-assisted bioprinting, for in vivo bone regeneration applications. Sci. Rep. 7(1):1–10, 2017.
Kérourédan, O., J.-M. Bourget, M. Rémy, S. Crauste-Manciet, J. Kalisky, S. Catros, N. B. Thébaud, and R. Devillard. Micropatterning of endothelial cells to create a capillary-like network with defined architecture by laser-assisted bioprinting. J. Mater. Sci. 30(2):28, 2019.
Kesti, M., C. Eberhardt, G. Pagliccia, D. Kenkel, D. Grande, A. Boss, and M. J. Zenobi-Wong. Bioprinting complex cartilaginous structures with clinically compliant biomaterials. Adv. Funct. Mater. 25(48):7406–7417, 2015.
Kheir, E., and D. J. O. Shaw. Hyaline articular cartilage. Trauma. 23(6):450–455, 2009.
Kim, S.H., D.Y. Kim, T.H. Lim, and C.H. Park, Silk fibroin bioinks for digital light processing (DLP) 3D bioprinting. Adv. Tissue Eng. Regener. Med. 53–66 (2020).
Kim, W., and G. J. B. Kim. Collagen/bioceramic-based composite bioink to fabricate a porous 3D hASCs-laden structure for bone tissue regeneration. Biofabrication. 12(1):015007, 2019.
Koch, L., O. Brandt, A. Deiwick, and B. Chichkov, Laser-assisted bioprinting at different wavelengths and pulse durations with a metal dynamic release layer: a parametric study. Int. J. Bioprint. 3(1) (2017).
Koch, L., A. Deiwick, S. Schlie, S. Michael, M. Gruene, V. Coger, D. Zychlinski, A. Schambach, K. Reimers, and P. M. Vogt. Skin tissue generation by laser cell printing. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 109(7):1855–1863, 2012.
Kundu, J., J. H. Shim, J. Jang, S. W. Kim, and D. W. Cho. An additive manufacturing-based PCL–alginate–chondrocyte bioprinted scaffold for cartilage tissue engineering. J. Tissue Eng. Regener. Med. 9(11):1286–1297, 2015.
Lam, T., T. Dehne, J. P. Krüger, S. Hondke, M. Endres, A. Thomas, R. Lauster, M. Sittinger, and L. J. Kloke. Photopolymerizable gelatin and hyaluronic acid for stereolithographic 3D bioprinting of tissue-engineered cartilage. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B. 107(8):2649–2657, 2019.
Lan, X., Y. Liang, E. J. Erkut, M. Kunze, A. Mulet-Sierra, T. Gong, M. Osswald, K. Ansari, H. Seikaly, and Y. J. Boluk. Bioprinting of human nasoseptal chondrocytes-laden collagen hydrogel for cartilage tissue engineering. FASEB J. 35(3):e21191, 2021.
Lan, X., Y. Liang, M. Vyhlidal, E. J. Erkut, M. Kunze, A. Mulet-Sierra, M. Osswald, K. Ansari, H. Seikaly, and Y. J. Boluk. In vitro maturation and in vivo stability of bioprinted human nasal cartilage. J. Tissue Eng. 13:20417314221086370, 2022.
Lavernia, L., W. E. Brown, B. J. Wong, J. C. Hu, and K. A. Athanasiou. Toward tissue-engineering of Nasal Cartilages. Acta Biomater. 88:42–56, 2019.
Lawlor, K. T., J. M. Vanslambrouck, J. W. Higgins, A. Chambon, K. Bishard, D. Arndt, P. X. Er, S. B. Wilson, S. E. Howden, and K. S. Tan. Cellular extrusion bioprinting improves kidney organoid reproducibility and conformation. Nat. Mater. 20(2):260–271, 2021.
Lee, A., A. Hudson, D. Shiwarski, J. Tashman, T. Hinton, S. Yerneni, J. Bliley, P. Campbell, and A. Feinberg. 3D bioprinting of collagen to rebuild components of the human heart. Science. 365(6452):482–487, 2019.
Lee, W., J. Pinckney, V. Lee, J.-H. Lee, K. Fischer, S. Polio, J.-K. Park, and S.-S.J.N. Yoo. Three-dimensional bioprinting of rat embryonic neural cells. Neuroreport. 20(8):798–803, 2009.
Lee, Y.-B., S. Polio, W. Lee, G. Dai, L. Menon, R. S. Carroll, and S.-S. Yoo. Bio-printing of collagen and VEGF-releasing fibrin gel scaffolds for neural stem cell culture. Exp. Neurol. 223(2):645–652, 2010.
Levingstone, T. J., A. Ramesh, R. T. Brady, P. A. Brama, C. Kearney, J. P. Gleeson, and F. J. J. B. O’Brien. Cell-free multi-layered collagen-based scaffolds demonstrate layer specific regeneration of functional osteochondral tissue in caprine joints. Biomaterials. 87:69–81, 2016.
Li, T., S. Chen, and M. Pei. Contribution of neural crest-derived stem cells and nasal chondrocytes to articular cartilage regeneration. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 77(23):4847–4859, 2020.
Li, W., M. Wang, H. Ma, F.A. Chapa-Villarreal, A.O. Lobo, and Y.S.J. Zhang, Stereolithography apparatus and digital light processing-based 3D bioprinting for tissue fabrication. Iscience (2023).
Lim, M. H., J. H. Jeun, S. H. Park, W. Lee, S. H. Park, M. Y. Kwon, S. H. Hwang, and S. W. Kim. Evaluation of polycaprolactone-associated human nasal chondrocytes as a therapeutic agent for cartilage repair. Tissue Eng. Regener. Med. 16(6):605–614, 2019.
Liu, J. A., and M. J. Cheung. Neural crest stem cells and their potential therapeutic applications. Dev. Biol. 419(2):199–216, 2016.
Liu, Y., G. Zhou, and Y. J. E. Cao. Recent progress in cartilage tissue engineering—our experience and future directions. Engineering. 3(1):28–35, 2017.
Mandelli, J. S., J. Koepp, A. Hama, S. Sanaur, G. A. Rae, and C. R. Rambo. Cell viability and cytotoxicity of inkjet-printed flexible organic electrodes on parylene C. Biomed. Microdev. 23(1):1–12, 2021.
Mandrycky, C., Z. Wang, K. Kim, and D.-H. Kim. 3D bioprinting for engineering complex tissues. Biotechnol. Adv. 34(4):422–434, 2016.
Markstedt, K., A. Mantas, I. Tournier, H. C. M. Ávila, D. Hägg, and P. Gatenholm. 3D bioprinting human chondrocytes with nanocellulose–alginate bioink for cartilage tissue engineering applications. Biomacromolecules. 16(5):1489–1496, 2015.
Masaeli, E., V. Forster, S. Picaud, F. Karamali, M. H. Nasr-Esfahani, and C. Marquette. Tissue engineering of retina through high resolution 3-dimensional inkjet bioprinting. Biofabrication.12(2):025006, 2020.
Maxson, E. L., M. D. Young, C. Noble, J. L. Go, B. Heidari, R. Khorramirouz, D. W. Morse, and A. J. B. Lerman. In vivo remodeling of a 3D-Bioprinted tissue engineered heart valve scaffold. Bioprinting. 16:e00059, 2019.
Mayo, V., Y. Sawatari, C.-Y.C. Huang, and F. J. Garcia-Godoy. Neural crest-derived dental stem cells—where we are and where we are going. J. Dent. 42(9):1043–1051, 2014.
Migliorini, F., N. Maffulli, A. Baroncini, J. Eschweiler, M. Knobe, M. Tingart, and H. J. Schenker. Allograft versus autograft osteochondral transplant for chondral defects of the talus: systematic review and meta-analysis. Am. J. Sports Med. 50:3447–3455, 2021.
Moldovan, N. I. Three-dimensional bioprinting of anatomically realistic tissue constructs for disease modeling and drug testing. Tissue Eng. C. 27(3):225–231, 2021.
Moshaverinia, A., X. Xu, C. Chen, K. Akiyama, M. L. Snead, and S. J. A. B. Shi. Dental mesenchymal stem cells encapsulated in an alginate hydrogel co-delivery microencapsulation system for cartilage regeneration. Acta Biomater. 9(12):9343–9350, 2013.
Moxon, S. R., M. J. Ferreira, P. D. Santos, B. Popa, A. Gloria, R. Katsarava, D. Tugushi, A. C. Serra, N. M. Hooper, and S. J. J. P. Kimber. A Preliminary evaluation of the pro-chondrogenic potential of 3D-bioprinted poly (ester urea) scaffolds. Polymers. 12(7):1478, 2020.
Mumme, M., A. Barbero, S. Miot, A. Wixmerten, S. Feliciano, F. Wolf, A. M. Asnaghi, D. Baumhoer, O. Bieri, and M. Kretzschmar. Nasal chondrocyte-based engineered autologous cartilage tissue for repair of articular cartilage defects: an observational first-in-human trial. Lancet. 388(10055):1985–1994, 2016.
Mumme, M., A. Steinitz, K. M. Nuss, K. Klein, S. Feliciano, P. Kronen, M. Jakob, B. von Rechenberg, I. Martin, and A. J. Barbero. Regenerative potential of tissue-engineered nasal chondrocytes in goat articular cartilage defects. Tissue Eng. A. 22(21–22):1286–1295, 2016.
Murphy, S. V., and A. Atala. 3D bioprinting of tissues and organs. Nature biotechnology. 32(8):773, 2014.
Murphy, S. V., A. Skardal, and A. Atala. Evaluation of hydrogels for bio-printing applications. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A. 101(1):272–284, 2013.
Narayanan, L. K., P. Huebner, M. B. Fisher, J. T. Spang, B. Starly, and R. A. Shirwaiker. 3D-bioprinting of polylactic acid (PLA) nanofiber–alginate hydrogel bioink containing human adipose-derived stem cells. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2(10):1732–1742, 2016.
Neuman, M. K., K. K. Briggs, K. Masuda, R. L. Sah, and D. J. T. L. Watson. A compositional analysis of cadaveric human nasal septal cartilage. Laryngoscope. 123(9):2120–2124, 2013.
Nguyen, D., D. A. Hägg, A. Forsman, J. Ekholm, P. Nimkingratana, C. Brantsing, T. Kalogeropoulos, S. Zaunz, S. Concaro, and M. J. Brittberg. Cartilage tissue engineering by the 3D bioprinting of iPS cells in a nanocellulose/alginate bioink. Sci. Rep. 7(1):1–10, 2017.
Pareek, A., P. J. Reardon, T. G. Maak, B. A. Levy, M. J. Stuart, A. J. Krych, and R. Surgery. Long-term outcomes after osteochondral autograft transfer: a systematic review at mean follow-up of 10.2 years. Arthroscopy. 32(6):1174–1184, 2016.
Pelttari, K., M. Mumme, A. Barbero, and I. J. Martin. Nasal chondrocytes as a neural crest-derived cell source for regenerative medicine. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 47:1–6, 2017.
Pelttari, K., B. Pippenger, M. Mumme, S. Feliciano, C. Scotti, P. Mainil-Varlet, A. Procino, B. Von Rechenberg, T. Schwamborn, and M. J. Jakob. Adult human neural crest–derived cells for articular cartilage repair. Sci. Transist. Med. 6(251):251ra119, 2014.
Pelttari, K., A. Winter, E. Steck, K. Goetzke, T. Hennig, B. G. Ochs, T. Aigner, and W. J. A. Richter. Premature induction of hypertrophy during in vitro chondrogenesis of human mesenchymal stem cells correlates with calcification and vascular invasion after ectopic transplantation in SCID mice. Rheumatology. 54(10):3254–3266, 2006.
Perez-Valle, A., C. Del Amo, and I. J. Andia. Overview of current advances in extrusion bioprinting for skin applications. Int. J. Mol. 21(18):6679, 2020.
Popko, M., R. Bleys, J. De Groot, and E. H. J. R. Huizing. Histological structure of the nasal cartilages and their perichondrial envelope I. The septal and lobular cartilage. Rhinology. 45(2):148, 2007.
Rahman, S., A. R. A. Szojka, Y. Liang, M. Kunze, V. Goncalves, A. M. Sierra, N. M. Jomha, and A. B. Adesida. Inability of low oxygen tension to induce chondrogenesis in human infrapatellar fat pad-mesenchymal stem cells. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 9:1780, 2021.
Rastogi, P., and B. J. B. Kandasubramanian. Review of alginate-based hydrogel bioprinting for application in tissue engineering. Biofabrication.11(4):042001, 2019.
Read-Fuller, A. M., D. M. Yates, A. Radwan, A. M. Schrodt, and R. A. Finn. The use of allogeneic cartilage for grafting in functional and reconstructive rhinoplasty. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 76(7):1560, 2018.
Ren, X., F. Wang, C. Chen, X. Gong, L. Yin, and L. J. B. Yang. Engineering zonal cartilage through bioprinting collagen type II hydrogel constructs with biomimetic chondrocyte density gradient. BMC Musculoskelet. 17:1–10, 2016.
Richmon, J. D., A. B. Sage, V. W. Wong, A. C. Chen, C. Pan, R. L. Sah, and D. J. Watson. Tensile biomechanical properties of human nasal septal cartilage. Am. J. Rhinol. 19(6):617–622, 2005.
Richmon, J. D., A. Sage, V. W. Wong, A. C. Chen, R. L. Sah, and D. J. Watson. Compressive biomechanical properties of human nasal septal cartilage. Am. J. Rhinol. 20(5):496–501, 2006.
Rotter, N., L. J. Bonassar, G. Tobias, M. Lebl, A. K. Roy, and C. A. J. B. Vacanti. Age dependence of biochemical and biomechanical properties of tissue-engineered human septal cartilage. Biomaterials. 23(15):3087–3094, 2002.
Rotter, N., G. Tobias, M. Lebl, A. K. Roy, M. C. Hansen, C. A. Vacanti, and L. J. Bonassar. Age-related changes in the composition and mechanical properties of human nasal cartilage. Archiv. Biochem. Biophys. 403(1):132–140, 2002.
Ruiz-Cantu, L., A. Gleadall, C. Faris, J. Segal, K. Shakesheff, and J. J. Yang. Multi-material 3D bioprinting of porous constructs for cartilage regeneration. Mater. Sci. Eng. C. 109:110578, 2020.
Sajjadian, A., R. Rubinstein, and N. J. P. Naghshineh. Current status of grafts and implants in rhinoplasty: part I. Autologous grafts. Plast Reconstruct. Surg. 125(2):40e–49e, 2010.
Salamone, M., S. Rigogliuso, A. Nicosia, M. Tagliavia, S. Campora, P. Cinà, C. Bruno, and G. J. C. Ghersi. Neural crest-derived chondrocytes isolation for tissue engineering in regenerative medicine. Cells. 9(4):962, 2020.
Salinas, E. Y., J. C. Hu, and K. J. Athanasiou. A guide for using mechanical stimulation to enhance tissue-engineered articular cartilage properties. Tissu Eng. B. 24(5):345–358, 2018.
Sánchez, E. M., J. C. Gómez-Blanco, E. L. Nieto, J. G. Casado, A. Macías-García, M. A. D. Díez, J. P. Carrasco-Amador, D. T. Martín, F. M. Sánchez-Margallo, and J. B. Pagador. Hydrogels for bioprinting: a systematic review of hydrogels synthesis, bioprinting parameters, and bioprinted structures behavior. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 8:776, 2020.
Sayed, K. E., U. Marzahn, T. John, M. Hoyer, H. Zreiqat, A. Witthuhn, B. Kohl, A. Haisch, and G. J. Schulze-Tanzil. PGA-associated heterotopic chondrocyte cocultures: implications of nasoseptal and auricular chondrocytes in articular cartilage repair. J. Tissue Eng. Regener. Med. 7(1):61–72, 2013.
Schipani, R., S. Scheurer, R. Florentin, S. E. Critchley, and D. J. J. B. Kelly. Reinforcing interpenetrating network hydrogels with 3D printed polymer networks to engineer cartilage mimetic composites. Biofabrication. 12(3):035011, 2020.
Schwarz, S., S. Kuth, T. Distler, C. Gögele, K. Stölzel, R. Detsch, A. R. Boccaccini, and G. Schulze-Tanzil. 3D printing and characterization of human nasoseptal chondrocytes laden dual crosslinked oxidized alginate-gelatin hydrogels for cartilage repair approaches. Mater. Sci. Eng. C. 116:111189, 2020.
Scotti, C., A. Osmokrovic, F. Wolf, S. Miot, G. M. Peretti, A. Barbero, and I. Martin. Response of human engineered cartilage based on articular or nasal chondrocytes to interleukin-1β and low oxygen. Tissue Eng. Part A. 18(3–4):362–372, 2012.
Shafiee, A., M. Kabiri, N. Ahmadbeigi, S. O. Yazdani, M. Mojtahed, S. Amanpour, and M. J. S. C. Soleimani. Nasal septum-derived multipotent progenitors: a potent source for stem cell-based regenerative medicine. Stem Cells Dev. 20(12):2077–2091, 2011.
Sharpe, P. T. J. D. Dental mesenchymal stem cells. Development. 143(13):2273–2280, 2016.
Shepherd, D., and B. J. R. Seedhom. The “instantaneous” compressive modulus of human articular cartilage in joints of the lower limb. Rheumatology. 38(2):124–132, 1999.
Shi, L., Y. Hu, M. W. Ullah, H. Ou, W. Zhang, L. Xiong, and X. Zhang. Cryogenic free-form extrusion bioprinting of decellularized small intestinal submucosa for potential applications in skin tissue engineering. Biofabrication.11(3):035023, 2019.
Shim, J.-H., J. Y. Kim, M. Park, J. Park, and D.-W.J.B. Cho. Development of a hybrid scaffold with synthetic biomaterials and hydrogel using solid freeform fabrication technology. Biofabrication.3(3):034102, 2011.
Song, K., A. M. Compaan, W. Chai, and Y. J. Huang. Injectable gelatin microgel-based composite ink for 3D bioprinting in air. Interfaces. 12(20):22453–22466, 2020.
Steinwachs, M., T. Guggi, and P. J. I. Kreuz. Marrow stimulation techniques. Injury. 39(1):26–31, 2008.
Stichler, S., T. Böck, N. Paxton, S. Bertlein, R. Levato, V. Schill, W. Smolan, J. Malda, J. Teßmar, and T. J. B. Blunk. Double printing of hyaluronic acid/poly (glycidol) hybrid hydrogels with poly (ε-caprolactone) for MSC chondrogenesis. Biofabrication. 9(4):044108, 2017.
Sun, Y., Y. You, W. Jiang, Z. Zhai, and K. J. T. Dai. 3D-bioprinting a genetically inspired cartilage scaffold with GDF5-conjugated BMSC-laden hydrogel and polymer for cartilage repair. Theranostics. 9(23):6949, 2019.
Tavares, M. T., V. M. Gaspar, M. V. Monteiro, J. P. S. Farinha, C. Baleizão, and J. F. Mano. GelMA/bioactive silica nanocomposite bioinks for stem cell osteogenic differentiation. Biofabrication.13(3):035012, 2021.
Thayer, P. S., L. S. Orrhult, and H. Martínez. Bioprinting of cartilage and skin tissue analogs utilizing a novel passive mixing unit technique for bioink precellularization. J. Visual. Exp. 131:e56372, 2018.
Tijore, A., J.-M. Behr, S. A. Irvine, V. Baisane, and S. Venkatraman. Bioprinted gelatin hydrogel platform promotes smooth muscle cell contractile phenotype maintenance. Biomed. Microdev. 20(2):1–10, 2018.
Townsend, J. M., E. C. Beck, S. H. Gehrke, C. J. Berkland, and M. S. Detamore. Flow behavior prior to crosslinking: the need for precursor rheology for placement of hydrogels in medical applications and for 3D bioprinting. Progr. Polym. 91:126–140, 2019.
Wakitani, S., T. Mitsuoka, N. Nakamura, Y. Toritsuka, Y. Nakamura, and S. J. C. T. Horibe. Autologous bone marrow stromal cell transplantation for repair of full-thickness articular cartilage defects in human patellae: two case reports. Cell Transpl. 13(5):595–600, 2004.
Weadock, K., and R. M. Olson. Evaluation of collagen crosslinking techniques. Biomater. Med. Dev. Artif. Organs. 11(4):293–318, 1983.
Westreich, R. W., H.-W. Courtland, P. Nasser, K. Jepsen, and W. J. Lawson. Defining nasal cartilage elasticity: biomechanical testing of the tripod theory based on a cantilevered model. Archiv. Fac. Plast. Surg. 9(4):264–270, 2007.
Wu, J.-J., M. A. Weis, L. S. Kim, and D. R. Eyre. Type III collagen, a fibril network modifier in articular cartilage. J. Biol. Chem. 285(24):18537–18544, 2010.
Xu, C., W. Chai, Y. Huang, and R. R. Markwald. Scaffold-free inkjet printing of three-dimensional zigzag cellular tubes. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 109(12):3152–3160, 2012.
Xu, T., K. W. Binder, M. Z. Albanna, D. Dice, W. Zhao, J. J. Yoo, and A. J. B. Atala. Hybrid printing of mechanically and biologically improved constructs for cartilage tissue engineering applications. Biofabrication.5(1):015001, 2012.
Xu, Y., H.-J. Sun, Y. Lv, J.-C. Zou, B.-L. Liu, and T.-C.J.C. Hua. Effects of freezing rates and cryoprotectant on thermal expansion of articular cartilage during freezing process. Cryoletters. 34(4):313–323, 2013.
Yang, X., Z. Lu, H. Wu, W. Li, L. Zheng, and J. Zhao. Collagen-alginate as bioink for three-dimensional (3D) cell printing based cartilage tissue engineering. Mater. Sci. Eng. C. 83:195–201, 2018.
Yu, J., S. Lee, S. Choi, K. K. Kim, B. Ryu, C.-Y. Kim, C.-R. Jung, B.-H. Min, Y.-Z. Xin, and S. A. J. P. Park. Fabrication of a polycaprolactone/alginate bipartite hybrid scaffold for osteochondral tissue using a three-dimensional bioprinting system. Polymers. 12(10):2203, 2020.
Yuan, T.-Y., J. Zhang, T. Yu, J.-P. Wu, and Q.-Y. Liu, 3D bioprinting for spinal cord injury repair. Biotechnology 10 (2022).
Zhang, A. P., X. Qu, P. Soman, K. C. Hribar, J. W. Lee, S. Chen, and S. J. A. M. He. Rapid fabrication of complex 3D extracellular microenvironments by dynamic optical projection stereolithography. Adv. Mater. 24(31):4266–4270, 2012.
Zhang, J., Q. Hu, S. Wang, J. Tao, and M.J. Gou, Digital light processing based three-dimensional printing for medical applications. Int. J. Bioprint. 6(1) (2020).
Zhang, L., J. Hu, and K. A. Athanasiou. The role of tissue engineering in articular cartilage repair and regeneration. Crit. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 37(1–2):100, 2009.
Zhou, M., B. H. Lee, Y. J. Tan, and L. P. J. B. Tan. Microbial transglutaminase induced controlled crosslinking of gelatin methacryloyl to tailor rheological properties for 3D printing. Biofabrication. 11(2):025011, 2019.
Zhu, W., X. Ma, M. Gou, D. Mei, K. Zhang, and S. J. Chen. 3D printing of functional biomaterials for tissue engineering. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 40:103–112, 2016.
Funding
Funding was provided by Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC RGPIN 06431), Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR PS 159661), and Alberta Cancer Foundation (ACF-MIBRP 27128).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Associate Editor Emmanuel Opara oversaw the review of this article.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lan, X., Boluk, Y. & Adesida, A.B. 3D Bioprinting of Hyaline Cartilage Using Nasal Chondrocytes. Ann Biomed Eng (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-023-03176-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-023-03176-3