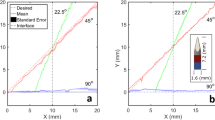
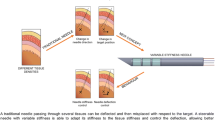
Abstract
Accurate needle targeting is critical for many clinical procedures, such as transcutaneous biopsy or radiofrequency ablation of tumors. However, targeting errors may arise, limiting the widespread adoption of these procedures. Advances in flexible needle (FN) steering are emerging to mitigate these errors. This review summarizes the state-of-the-art developments of FNs and addresses possible targeting errors that can be overcome with steering actuation techniques. FN steering techniques can be classified as passive and active. Passive steering directly results from the needle-tissue interaction forces, whereas active steering requires additional forces to be applied at the needle tip, which enhances needle steerability. Therefore, the corresponding targeting errors of most passive FNs and active FNs are between 1 and 2 mm, and less than 1 mm, respectively. However, the diameters of active FNs range from 1.42 to 12 mm, which is larger than the passive steering needle varying from 0.5 to 1.4 mm. Therefore, the development of active FNs is an area of active research. These active FNs can be steered using tethered internal direct actuation or untethered external actuation. Examples of tethered internal direct actuation include tendon-driven, longitudinal segment transmission and concentric tube transmission. Tendon-driven FNs have various structures, and longitudinal segment transmission needles could be adapted to reduce tissue damage. Additionally, concentric tube needles have immediate advantages and clinical applications in natural orifice surgery. Magnetic actuation enables active FN steering with untethered external actuation and facilitates miniaturization. The challenges faced in the fabrication, sensing, and actuation methods of FN are analyzed. Finally, bio-inspired FNs may offer solutions to address the challenges faced in FN active steering mechanisms.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abayazid, M., M. Kemp, and S. Misra. 3D flexible needle steering in soft-tissue phantoms using fiber bragg grating sensors. in Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. Robot. Autom., Karlsruhe, Germany, 2013, pp. 5843–5849.
Abayazid, M., P. Moreira, N. Shahriari, S. Patil, R. Alterovitz, and S. Misra. Ultrasound-guided three-dimensional needle steering in biological tissue with curved surfaces. Med. Eng. Phys. 37:145–150, 2015
Abayazid, M., R. J. Roesthuis, R. Reilink, and S. Misra. Integrating deflection models and image feedback for real-time flexible needle steering. IEEE Trans. Robot. 29:542–553, 2012
Adagolodjo, Y., L. Goffin, M. De Mathelin, and H. Courtecuisse. Robotic insertion of flexible needle in deformable structures using inverse finite-element simulation. IEEE Trans. Robot. 35:697–708, 2019
Adebar, T., A. Fletcher, and A. Okamura. 3D ultrasound-guided robotic needle steering in biological tissue. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 61:2899–2910, 2014
Adebar, T. K., J. D. Greer, P. F. Laeseke, G. L. Hwang, and A. M. Okamura. Methods for improving the curvature of steerable needles in biological tissue. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 63:1167–1177, 2015
Aggravi, M., D. A. Estima, A. Krupa, S. Misra, and C. Pacchierotti. Haptic teleoperation of flexible needles combining 3d ultrasound guidance and needle tip force feedback. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 6:4859–4866, 2021
Amanov, E., T.-D. Nguyen, and J. Burgner-Kahrs. Tendon-driven continuum robots with extensible sections - A model-based evaluation of path following motions. Int. J. Robot. Res. 40:7–23, 2021
Beirne, P. V., S. Hennessy, S. L. Cadogan, F. Shiely, T. Fitzgerald, and F. MacLeod. Needle size for vaccination procedures in children and adolescents. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD010720.pub3
van de Berg, N. J., J. Dankelman, and J. J. van den Dobbelsteen. Design of an actively controlled steerable needle with tendon actuation and fbg-based shape sensing. Med. Eng. Phys. 37:617–622, 2015
Bernardes, M. C., B. V. Adorno, P. Poignet, and G. A. Borges. Robotassisted automatic insertion of steerable needles with closed-loop imaging feedback and intraoperative trajectory replanning. Mechatronics. 23:630–645, 2013
Burgner, J., D. C. Rucker, H. B. Gilbert, P. J. Swaney, P. T. Russell, K. D. Weaver, and R. J. Webster III. A telerobotic system for transnasal surgery. IEEE Trans. Mechatron. 19:996–1006, 2014
Cai, C., C. Sun, Y. Han, and Q. Zhang. Clinical flexible needle puncture path planning based on particle swarm optimization. Comput. Meth. Prog. Biol.193:105511, 2020
Carpi, F., and C. Pappone. Stereotaxis niobe® magnetic navigation system for endocardial catheter ablation and gastrointestinal capsule endoscopy. Expert. Rev. Med. Devic. 6:487–498, 2014
Cerkvenik, U., B. Van de Straat, S. W. Gussekloo, and J. L. Van Leeuwen. Mechanisms of ovipositor insertion and steering of a parasitic wasp. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 114:E7822–E7831, 2017
Chautems, C., A. Tonazzini, Q. Boehler, S. H. Jeong, D. Floreano, and B. J. Nelson. Magnetic continuum device with variable stiffness for minimally invasive surgery. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2:1–9, 2020
Chautems, C., A. Tonazzini, D. Floreano, and B. J. Nelson. A variable stiffness catheter controlled with an external magnetic field. in Proc. IEEE/RSJ Int. Conf. Intell. Robots Syst., Vancouver, BC, Canada, 2017, pp. 181–186.
Chevrie, J., N. Shahriari, M. Babel, A. Krupa, and S. Misra. Flexible needle steering in moving biological tissue with motion compensation using ultrasound and force feedback. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 3:2338–2345, 2018
Chiroiu, V., N. Nedelcu, D. Pisla, L. Munteanu, and C. Rugina. On the flexible needle insertion into the human liver. Sci. Rep. 11:1–14, 2021
Conci, A., Brazil, A. L., Popovici, D., Jiga, G., and Lebon, F. Modeling the behavior of human body tissues on penetration. AIP Conf. Proc. 1932: 020006-1–020006-6, 2018.
da Veiga, T., J. H. Chandler, P. Lloyd, G. Pittiglio, N. J. Wilkinson, A. K. Hoshiar, R. A. Harris, and P. Valdastri. Challenges of continuum robots in clinical context: a review. P Biomed. Eng. 2:032003, 2020
De Falco, I., C. Culmone, A. Menciassi, J. Dankelman, and J. J. van Den Dobbelsteen. A variable stiffness mechanism for steerable percutaneous instruments: integration in a needle. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 56:2185–2199, 2018
de Kater, E. P., A. Sakes, J. Bloemberg, D. J. Jager, and P. Breedveld. Design of a flexible wasp-inspired tissue transport mechanism. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2021.782037
de Ruiter, Q. M., J. R. Fontana, W. F. Pritchard, M. Mauda-Havakuk, I. Bakhutashvili, J. A. Esparza-Trujillo, N. A. Varble, M. Verstege, S. Xu, R. Seifabadi, et al. Endovascular steerable and endobronchial precurved guiding sheaths for transbronchial needle delivery under augmented fluoroscopy and cone beam CT image guidance. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 10:3627–3644, 2021
De Vries, M., J. Sikorski, S. Misra, and J. van den Dobbelsteen. Axially rigid steerable needle with compliant active tip control. PLoS ONE. 16:1–18, 2021
DiMaio, S. P., and S. E. Salcudean. Needle insertion modeling and simulation. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 19:864–875, 2003
Dupont, P. E., J. Lock, B. Itkowitz, and E. Butler. Design and control of concentric-tube robots. IEEE Trans. Robot. 26:209–225, 2010
Edelmann, J., A. J. Petruska, and B. J. Nelson. Magnetic control of continuum devices. Int. J. Robot. Res. 36:68–85, 2017
Limpabandhu, C., Y. Hu, H. Ren, W. Song, and Z. Tse. Towards catheter steering using magnetic tractor beam coupling. Proc. IMechE Part H: J Eng. Med. 236:583–591, 2022.
Farooq, M. U., B. Xu, and S. Y. Ko. A concentric tube-based 4-DOF puncturing needle with a novel miniaturized actuation system for vitrectomy. Biomed. Eng. Online. 18:1–16, 2019
Gafford, J. B., S. Webster, N. Dillon, E. Blum, R. Hendrick, F. Maldon-ado, E. A. Gillaspie, O. B. Rickman, S. D. Herrell, and R. J. Webster. A concentric tube robot system for rigid bronchoscopy: a feasibility study on central airway obstruction removal. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 48:181–189, 2020
Gang, E. S., B. L. Nguyen, Y. Shachar, L. Farkas, L. Farkas, B. Marx, D. Johnson, M. C. Fishbein, C. Gaudio, and S. J. Kim. Dynamically shaped magnetic fields: initial animal validation of a new remote electrophysiology catheter guidance and control system. Circ- Arrhythmia Electr. 4:770–777, 2011
Gilbert, H. B., J. Neimat, and R. J. Webster. Concentric tube robots as steerable needles: achieving follow-the-leader deployment. IEEE Trans. Robot. 31:246–258, 2015
Han, D., R. S. Morde, S. Mariani, A. L. Mattina, E. Vignali, C. Yang, G. Barillaro, and H. Lee. 4D Printing of a bioinspired microneedle array with backward-facing barbs for enhanced tissue adhesion. Adv. Funct. Mater. 30:1–12, 2020
Hendrick, R. J., S. D. Herrell and R. J. Webster III. A multi-arm hand-held robotic system for transurethral laser prostate surgery. in Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. Robot. Autom., Hong Kong, China, 2014, pp. 2850–2855.
Henken, K., D. Van Gerwen, J. Dankelman, and J. Van Den Dobbelsteen. Accuracy of needle position measurements using fiber bragg gratings. Minim. Invasiv. Ther. 21:408–414, 2012
Heunis, C., J. Sikorski, and S. Misra. Flexible instruments for endovascular interventions: Improved magnetic steering, actuation, and image-guided surgical instruments. IEEE Robot. Autom. Mag. 25:71–82, 2018
Hong, A., A. J. Petruska, A. Zemmar, and B. J. Nelson. Magnetic control of a flexible needle in neurosurgery. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 68:616–627, 2020
Hu, X., A. Chen, Y. Luo, C. Zhang, and E. Zhang. Steerable catheters for minimally invasive surgery: a review and future directions. Comput. Assist. Surg. 23:21–41, 2018
Ilami, M., R. J. Ahmed, A. Petras, B. Beigzadeh, and H. Marvi. Magnetic needle steering in soft phantom tissue. Sci. Rep. 10:1–11, 2020
Issatayeva, A., A. Amantayeva, W. Blanc, D. Tosi, and C. Molardi. Design and analysis of a fiber-optic sensing system for shape reconstruction of a minimally invasive surgical needle. Sci. Rep. 11:1–12, 2021
Jiang, S., B. Jiang, P. Fang, and Z. Yang. Pre-operative motion planner for steerable needles using cost map based on repulsive field and empirical model of needle deflection. J. Med. Devices. 16:021004, 2022
Karimi, S., and B. Konh. Self-sensing feedback control of multiple interacting shape memory alloy actuators in a 3d steerable active needle. J. Intel. Mat. Syst. Str. 31:1524–1540, 2020
Khadem, M., C. Rossa, N. Usmani, R. S. Sloboda, and M. Tavakoli. A two-body rigid/flexible model of needle steering dynamics in soft tissue. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mech. 21:2352–2364, 2016
Khashei Varnamkhasti, Z., and B. Konh. Cable-driven 3d steerable surgical needle for needle-based procedures. in Proc. Conf Des Med Dev., Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2020, pp. V001T06A008-1-5.
Kimura, T., S. Takatsuki, A. Oishi, M. Negishi, S. Kashimura, Y. Katsumata, T. Nishiyama, N. Nishiyama, Y. Tanimoto, Y. Aizawa, et al. Operator-blinded contact force monitoring during pulmonary vein isolation using conventional and steerable sheaths. Int. J. Cardiol. 177:970–976, 2014
Ko, S. Y., L. Frasson, and F. R. y Baena. Closed-loop planar motion control of a steerable probe with a “programmable bevel” inspired by nature. IEEE Trans. Robot. 27:970–983, 2011
Ko, S., and Y. B. F. Rodriguez. Toward a miniaturized needle steering system with path planning for obstacle avoidance. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 60:910–917, 2013
Kratchman, L. B., M. M. Rahman, J. R. Saunders, P. J. Swaney, and R. J. Webster III. Toward robotic needle steering in lung biopsy: a tendon-actuated approach. Proc. SPIE, Med. Imag. Vis., Image-Guided Procedures, Model. 7964:79641I-1–79641I-8, 2011.
Lee, H., and J. Kim. Estimation of flexible needle deflection in layered soft tissues with different elastic moduli. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 52:729–740, 2014
Lee, W., J. Nam, J. Kim, E. Jung, N. Kim, and G. Jang. Steering, tunneling, and stent delivery of a multifunctional magnetic catheter robot to treat occlusive vascular disease. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 68:391–400, 2020
Lee, J., J. Wang, and W. Park. Efficient mechanism design and systematic operation planning for tube-wire flexible needles. J. Mech. Robot. 10:1–9, 2018
Li, M., D. Gao, Y. Lei, and T. Xu. Dynamic path planning for beveltip flexible needle insertion into soft tissue based on a real-time finite element model. Math. Probl. Eng. 1–13:2020, 2020
Li, A. D., K. B. Putra, L. Chen, J. S. Montgomery, and A. Shih. Mosquito proboscis-inspired needle insertion to reduce tissue deformation and organ displacement. Sci Rep. 10:1–14, 2020
Lu, M., Y. Zhang, and H. Du. Design and control of a novel magnetic resonance imaging-compatible breast intervention robot. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Sysm. 17:1–14, 2020
Mahoney, A. W., and J. J. Abbott. 5-DOF manipulation of an untethered magnetic device in fluid using a single permanent magnet. in Proc. Conf. Robotics: Sci. Syst. 2014.
Majewicz, A., T. R. Wedlick, K. B. Reed, and A. M. Okamura. Evaluation of robotic needle steering in ex vivo tissue. in Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. Robot. Autom., Anchorage, Alaska, USA. 2010, pp. 2068–2073.
Matheson, E., and F. Rodriguez y Baena. Biologically inspired surgical needle steering: technology and application of the programmable beveltip needle. Biomimetics. 5:1–23, 2020
Moreira, P., K. J. Boskma, and S. Misra. Towards MRI-guided flexible needle steering using fiber bragg grating-based tip tracking. in Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. Robot. Autom., Singapore, 2017, pp. 4849–4854.
Moreira, P., and S. Misra. Biomechanics-based curvature estimation for ultrasound-guided flexible needle steering in biological tissues. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 43:1716–1726, 2015
Neubach, Z., and M. Shoham. Ultrasound-guided robot for flexible needle steering. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 57:799–805, 2010
Neumann, M., and J. Burgner-Kahrs. Considerations for follow-the -leader motion of extensible tendon-driven continuum robots. in Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. Robot. Autom., 2016, pp. 917–923.
Norton, J. C., P. R. Slawinski, H. S. Lay, J. W. Martin, B. F. Cox, G. Cummins, M. P. Desmulliez, R. E. Clutton, K. L. Obstein, S. Cochran, et al. Intelligent magnetic manipulation for gastrointestinal ultrasound. Sci. Robot. 4:eaav7725, 2019
Padasdao, B., and B. Konh. Shape memory alloy actuators in an active needle—modeling, precise assembly, and performance evaluation. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. 143:1–10, 2021
Park, Y. L., S. Elayaperumal, B. Daniel, S. C. Ryu, M. Shin, J. Savall, R. J. Black, B. Moslehi, and M. R. Cutkosky. Real-time estimation of 3-D needle shape and deflection for MRI-guided interventions. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mech. 15:906–915, 2010
Patil, J., S. Ford, C. Egeler, and D. Williams. The effect of needle dimensions and infusion rates on injection pressures in regional anaesthesia needles: a bench-top study. Anaesthesia. 70:183–189, 2015
Pattanshetti, S., and S. C. Ryu. Design and fabrication of lasermachined hinge joints on miniature tubes for steerable medical devices. J. Mech. Robot. 10:011002, 2018
Pattanshetti, S., R. Sandström, A. Kottala, N. M. Amato, and S. C. Ryu. Feasibility Study of Robotic Needles with a Rotational Tip-Joint and Notch Patterns. in Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. Robot. Autom., 2019, pp. 1534–1540.
Petruska, A. J., F. Ruetz, A. Hong, L. Regli, O. Surucu, A. Zemmar, and B. J. Nelson. Magnetic needle guidance for neurosurgery: Initial design and proof of concept. in Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. Robot. Autom., Stockholm, Sweden, 2016, pp. 4392–4397.
Piskarev, Y., J. Shintake, C. Chautems, J. Lussi, Q. Boehler, B. J. Nelson, and D. Floreano. A variable stiffness magnetic catheter made of a conductive phase-change polymer for minimally invasive surgery. Adv. Funct. Mater. 32:2107662, 2022
Ponten, R., C. B. Black, A. J. Russ, and D. C. Rucker. Analysis of a concentric-tube robot design and feasibility for endoscopic deployment. in Medical Imaging 2017: Image-Guided Procedures, Robotic Interventions, and Modeling.10135. SPIE, pp. 290–300, 2017.
Pratt, R. L., and A. J. Petruska. Empirically comparing magnetic needle steering models using expectation-maximization. Robotics. 11:1–18, 2022
Qi, B., Z. Yu, Z. K. Varnamkhasti, Y. Zhou, and J. Sheng. Toward a telescopic steerable robotic needle for minimally invasive tissue biopsy. IEEE Robot. Autom. Let. 6:1989–1996, 2021
Roesthuis, R. J., N. J. van de Berg, J. J. van den Dobbelsteen, and S. Misra. Modeling and steering of a novel actuated-tip needle through a soft-tissue simulant using fiber bragg grating sensors. in Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. Robot. Autom., Washington, USA, 2015, pp. 2283–2289.
Roesthuis, R. J., M. Kemp, J. J. van den Dobbelsteen, and S. Misra. Three-dimensional needle shape reconstruction using an array of fiber bragg grating sensors. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 19:1115–1126, 2014
Ryan, P., and E. Diller. Magnetic actuation for full dexterity microrobotic control using rotating permanent magnets. IEEE Trans. Robot. 33:1398–1409, 2017
Ryu, S. C., Z. F. Quek, J.-S. Koh, P. Renaud, R. J. Black, B. Moslehi, B. L. Daniel, K.-J. Cho, and M. R. Cutkosky. Design of an optically controlled MR-compatible active needle. IEEE Trans. Robot. 31:1–11, 2014
Ryu, S. C., Z. F. Quek, P. Renaud, R. J. Black, B. L. Daniel, and M. R. Cutkosky. An optical actuation system and curvature sensor for a MRcompatible active needle. in Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. Robot. Autom., Saint Paul, MN, USA, 2012, pp. 1589–1594.
Scali, M., D. Kreeft, P. Breedveld, and D. Dodou. Design and evaluation of a wasp-inspired steerable needle. Proc. SPIE 10162, Bioinspiration, Biomimetics, and Bioreplication 2017, 10162:34–46, 2017.
Scali, M., T. Pusch, P. Breedveld, and D. Dodou. Ovipositor-inspired steerable needle: design and preliminary experimental evaluation. Bioinspir Biomim. 13:016006, 2017
Scali, M., P. A. Veldhoven, P. W. Henselmans, D. Dodou, and P. Breedveld. Design of an ultra-thin steerable probe for percutaneous interventions and preliminary evaluation in a gelatine phantom. PLoS ONE. 14:e0221165, 2019
Secoli, R., E. Matheson, M. Pinzi, S. Galvan, A. Donder, T. Watts, M. Riva, D. D. Zani, L. Bello, and F. R. Baena. Modular robotic platform for precision neurosurgery with a bio-inspired needle: system overview and first in-vivo deployment. PloS one. 17:e0275686, 2022
Seifabadi, R., E. E. Gomez, F. Aalamifar, G. Fichtinger, and I. Iordachita. Real-time tracking of a bevel-tip needle with varying insertion depth: Toward teleoperated MRI-guided needle steering. in Proc. IEEE/RSJ Int. Conf. Intell. Robots Syst., Tokyo, Japan. 2013, pp 469–476.
Shahriari, N., J. R. Georgiadis, M. Oudkerk, and S. Misra. Hybrid control algorithm for flexible needle steering: demonstration in phantom and human cadaver. PLoS ONE. 13:e0210052, 2018
Shi, C., X. Luo, P. Qi, T. Li, S. Song, Z. Najdovski, T. Fukuda, and H. Ren. Shape sensing techniques for continuum robots in minimally invasive surgery: a survey. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 64:1665–1678, 2017
Sikorski, J., I. Dawson, A. Denasi, E. E. Hekman, and S. Misra. Introducing BigMag—a novel system for 3d magnetic actuation of flexible surgical manipulators. in Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. Robot. Autom., Singapore, 2017, pp. 3594–3599.
Sikorski, J., A. Denasi, G. Bucchi, S. Scheggi, and S. Misra. Visionbased 3-D control of magnetically actuated catheter using BigMag—An array of mobile electromagnetic coils. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mech. 24:505–516, 2019
Song, S., Z. Li, H. Yu, and H. Ren. Electromagnetic positioning for tip tracking and shape sensing of flexible robots. IEEE Sens J. 15:4565–4575, 2015
Su, H., K.-W. Kwok, K. Cleary, I. Iordachita, M. C. Cavusoglu, J. P. Desai, and G. S. Fischer. State of the art and future opportunities in MRI-guided robot-assisted surgery and interventions. Proc. IEEE. 110:968–992, 2022
Swaney, P. J., J. Burgner, H. B. Gilbert, and R. J. Webster. A flexurebased steerable needle: high curvature with reduced tissue damage. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 60:906–909, 2012
Swaney, P. J., A. W. Mahoney, B. I. Hartley, A. A. Remirez, E. Lamers, R. H. Feins, R. Alterovitz, and R. J. Webster III. Toward transoral peripheral lung access: Combining continuum robots and steerable needles. J. Med. Robot. Res. 2:1–14, 2017
Swaney, P. J., A. W. Mahoney, A. A. Remirez, E. Lamers, B. I. Hartley, R. H. Feins, R. Alterovitz, and R. J. Webster. Tendons, concentric tubes, and a bevel tip: Three steerable robots in one transoral lung access system. in Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. Robot. Autom., 2015, pp. 5378–5383.
Tang, L. B., Y. H. Chen, and X. J. He. Magnetic force aided compliant needle navigation and needle performance analysis. in Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. Robot. Biomi., Sanya, China, 2007, pp. 612–616.
Thakur Singh, R. R., I. Tekko, K. McAvoy, H. McMillan, D. Jones, and R. F. Donnelly. Minimally invasive microneedles for ocular drug delivery. Expert Opin. Drug Del. 14:525–537, 2017
Tillander, H. Magnetic guidance of a catheter with articulated steel tip. Acta Radiol. 35:62–64, 1951
Van de Berg, N. J., D. J. van Gerwen, J. Dankelman, and J. J. van den Dobbelsteen. Design choices in needle steering—a review. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mech. 20:2172–2183, 2015
Van, G., J. Dennis, D. Jenny, and J. John. Needle-tissue interaction forces—a survey of experimental data. Med. Eng. Phys. 34:665–680, 2012
Varnamkhasti, Z. K., and B. Konh. Compact 3D-printed active flexible needle for percutaneous procedures. Surg. Innov. 27:402–405, 2020
Varnamkhasti, Z. K., and B. Konh. Design, fabrication, and testing of a flexible three-dimensional printed percutaneous needle with embedded actuators. J. Med. Devices. 15:021007, 2021
Vrooijink, G. J., M. Abayazid, S. Patil, R. Alterovitz, and S. Misra. Needle path planning and steering in a three-dimensional non-static environment using two-dimensional ultrasound images. Int. J. Robot. Res. 33:1361–1374, 2014
Wang, J., Q. Cong, X. Qi, and Y. Zhang. Optimum structural design and analysis of drag reduction mechanism of bionic needles inspired by cicada stylet. J. Jilin Univ. (Eng. Technol. Ed.). 44:696–700, 2014
Wang, J., X. Yang, P. Li, S. Song, L. Liu, and M.Q.-H. Meng. Design of a multi-arm concentric-tube robot system for transnasal surgery. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 58:497–508, 2020
Wang, Y. Z., Z. G. Zhou, Y. H. Chen, and H. F. Huang. Towards a magnetic articulated needle. Biotechnol. Chem. Mater. Eng. Adv. Mater. Res. 393:1060–1063, 2012
Webster, R. J., III., J. S. Kim, N. J. Cowan, G. S. Chirikjian, and A. M. Okamura. Nonholonomic modeling of needle steering. Int. J. Robot. Res. 25:509–525, 2006
Webster, R. J., A. M. Okamura, and N. J. Cowan. Toward active cannulas: Miniature snake-like surgical robots. in Proc. IEEE Conf. RSJ Intell. Robot. Syst., pp. 2857–2863, 2006.
Wu, L., S. Song, K. Wu, C. M. Lim, and H. Ren. Development of a compact continuum tubular robotic system for nasopharyngeal biopsy. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 55:403–417, 2017
Xiao, X., H. Poon, C. M. Lim, M.Q.-H. Meng, and H. Ren. Pilot study of trans-oral robotic-assisted needle direct tracheostomy puncture in patients requiring prolonged mechanical ventilation. Front. Robot. AI. 7:1–10, 2020
Yamada, A., S. Naka, N. Nitta, S. Morikawa, and T. Tani. A Loop -Shaped Flexible Mechanism for Robotic Needle Steering. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 3:648–655, 2018
Yang, Z., and L. Zhang. Magnetic actuation systems for miniature robots: a review. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2:2000082, 2020
Yu, H., L. Wu, K. Wu, and H. Ren. Development of a multi-channel concentric tube robotic system with active vision for transnasal nasopharyngeal carcinoma procedures. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 1:1172–1178, 2016
Zhang, B., F. Chen, M. Yang, L. Huang, Z. Du, L. Sun, and W. Dong. Real-time curvature detection of a flexible needle with a bevel tip. Sensors. 18:1–15, 2018
Zhang, Y., and M. Lu. A review of recent advancements in soft and flexible robots for medical applications. Int. J. Med. Robot. Comp. 16:e2096, 2020
Zhang, X., F. Wang, Y. Yu, G. Chen, L. Shang, L. Sun, and Y. Zhao. Bio-inspired clamping microneedle arrays from flexible ferrofluid -configured moldings. Sci. Bull. 64:1110–1117, 2019
Zhang, W., Y. Zhang, and Y. Liu. Design and control of a bionic needle puncture robot. Int. J. Med. Robot. Comp. 17:e2200, 2021
Zhao, S., D. Gao, M. Zhao, and J. Fu. Trajectory estimation of flexible needle using PVA tissue material. in IOP Conf. Series: Materials Sci Eng. 646:2019, p. 012063.
Zhong, Y., L. Hu, and Y. Xu. Recent advances in design and actuation of continuum robots for medical applications. Actuators. 9(4):142, 2020
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge funding support from the National Medical Research Council Clinician Scientist grant (NMRC CSA-MOH-000326), the Hong Kong Research Grants Council (RGC) Collaborative Research Fund (CRF C4026-21GF: 2300075; C4063-18G: 2300056), General Research Fund (GRF Ref. No.: N_CUHK.420/22 and 14216022) and (GRS) #3110167#3110137, the Reserve Leader Funding Project of Leading Talent Echelon of Heilongjiang Province of China (No. 2501050628), and China Scholarship Council under CSC 202108230187.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Associate Editor Stefan M. Duma oversaw the review of this article.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, M., Zhang, Y., Lim, C.M. et al. Flexible Needle Steering with Tethered and Untethered Actuation: Current States, Targeting Errors, Challenges and Opportunities. Ann Biomed Eng 51, 905–924 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-023-03163-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-023-03163-8