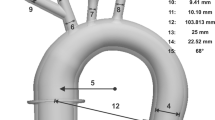
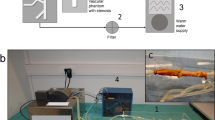
Abstract
During the last years, several kinds of Embolic Protection Devices (EPD) have been developed, with the aim of minimizing complication caused by thrombi generated during Carotid Artery Stenting (CAS). These devices are capable of capturing small particles generated during the intervention, avoiding cerebral stroke and improving the outcomes of the surgery. However, they have associated complications, like the increase on flow resistance associated by their use or the lack of knowledge on their actual filtration efficiency for thrombi of low size. Current work proposes a validated computational methodology in order to predict the hemodynamic features and filtering efficiency of a commercial EPD. It will be observed how Computational Fluid Dynamics predicts pressure drop with fair agreement with the experimental measurements. Finally, this work analyzes the filtration efficiency and the influence of the distribution of injected particles on this parameter. The capabilities of the filter for retaining particles of diameter below the pore size is, additionally, discussed.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson Jr, J. D. Fundamental of Aerodynamics. McGraw-Hill Education, 2010.
Coggia, M., O. Goëau-Brissonnière, J. L. Duval, J. P. Leschi, M. Letort, and M. D. Nagel. Embolic risk of the different stages of carotid bifurcation balloon angioplasty: an experimental study. J. Vasc. Surg. 31:550–557, 2000.
Cundall, P. A., and O. D. L. Strack. A discrete numerical model for granular assemblies. Géotechnique. 29:47–65, 1979.
Deyranlou, A., J. H. Naish, C. A. Miller, A. Revell, and A. Keshmiri. Numerical study of atrial fibrillation effects on flow distribution in aortic circulation. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 48:1–18, 2020.
Finol, E. A., C. M. Scotti, I. Verdinelli, C. H. Amon, and M. H. Wholey. Performance assessment of embolic protection filters for carotid artery stenting. Model. Med. Biol. VI. 1:133–142, 2005.
Finol, E. A., G. M. Siewiorek, C. M. Scotti, M. H. M. H. Wholey, and M. H. M. H. Wholey. Wall apposition assessment and performance comparison of distal protection filters. J. Endovasc. Ther. 15:177–185, 2008.
Graf, C., and J. P. Barras. Rheological properties of human blood plasma—a comparison of measurements with three different viscometers. Experientia. 35:224–225, 1979.
Haidekker, M. A., A. G. Tsai, T. Brady, H. Y. Stevens, J. A. Frangos, E. Theodorakis, and M. Intaglietta. A novel approach to blood plasma viscosity measurement using fluorescent molecular rotors. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 282:H1609–H1614, 2002.
Hart, J. P., P. Peeters, J. Verbist, K. Deloose, and M. Bosiers. Do device characteristics impact outcome in carotid artery stenting? J. Vasc. Surg. 44:725–730, 2006.
Heistad, D. D., M. L. Marcus, and S. Mueller. Measurement of cerebral blood flow with microspheres. Arch. Neurol. 34:657–659, 1977.
Hendriks, J. M., J. D. Zindler, A. Van Der Lugt, P. M. T. Pattynama, M. R. H. M. Van Sambeek, J. L. Bosch, and L. C. Van Dijk. Embolic protection filters for carotid stenting: differences in flow obstruction depending on filter construction. J. Endovasc. Ther. 13:47–50, 2006.
Howell, M., Z. Krajcer, K. Dougherty, N. Strickman, M. Skolkin, B. Toombs, and D. Paniagua. Correlation of periprocedural systolic blood pressure changes with neurological events in high-risk carotid stent patients. J. Endovasc. Ther. 9:810–816, 2002.
Johnson, S., S. Duffy, G. Gunning, M. Gilvarry, J. P. McGarry, and P. E. McHugh. Review of mechanical testing and modelling of thrombus material for vascular implant and device design. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 45:2494–2508, 2017.
Karimi, S., M. Dabagh, P. Vasava, M. Dadvar, B. Dabir, and P. Jalali. Effect of rheological models on the hemodynamics within human aorta: CFD study on CT image-based geometry. J. Non-Newton. Fluid Mech. 207:42–52, 2014.
Kurzhals, A., J. B. Matthies, R. Andresen, C. Wissgott, K. P. Schmitz, N. Grabow, and W. Schmidt. Efficiency test of current carotid embolic protection devices. Biomed. Tech. 62:349–355, 2017.
Kwon, B. J., M. H. Han, H. S. Kang, and C. Jung. Protection filter-related events in extracranial carotid artery stenting: a single-center experience. J. Endovasc. Ther. 13:711–722, 2006.
Kwon, O. K., S. H. Kim, E. A. Jacobsen, and M. P. Marks. Clinical implications of internal carotid artery flow impairment caused by filter occlusion during carotid artery stenting. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 33:494–499, 2012.
Lee, S. H., S. Kang, N. Hur, and S.-K. Jeong. A fluid-structure interaction analysis on hemodynamics in carotid artery based on patient-specific clinical data. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 26:3821–3831, 2012.
Louvelle, L., M. Doyle, G. Van Arsdell, C. Amon, G. Van Arsdell, and C. Amon. The effect of geometric and hemodynamic parameters on blood flow efficiency in repaired tetralogy of fallot patients. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-021-02771-6.
Markus, H. S., A. King, M. Shipley, R. Topakian, M. Cullinane, S. Reihill, N. M. Bornstein, and A. Schaafsma. Asymptomatic embolisation for prediction of stroke in the Asymptomatic Carotid Emboli Study (ACES): a prospective observational study. Lancet Neurol. 9:663–671, 2010.
Menter, F. R. Zonal two equation κ-ω turbulence models for aerodynamic flows. AIAA 23rd Fluid Dynamics, Plasmadynamics, and Lasers Conference, 1993, 1993.
Montorsi, P., L. Caputi, S. Galli, E. Ciceri, G. Ballerini, M. Agrifoglio, P. Ravagnani, D. Trabattoni, G. Pontone, F. Fabbiocchi, A. Loaldi, E. Parati, D. Andreini, F. Veglia, and A. L. Bartorelli. Microembolization during carotid artery stenting in patients with high-risk, lipid-rich plaque: a randomized trial of proximal versus distal cerebral protection. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 58:1656–1663, 2011.
Morris, D. R., K. Ayabe, T. Inoue, N. Sakai, R. Bulbulia, A. Halliday, and S. Goto. Evidence-based carotid interventions for stroke prevention: state-of-the-art review. J Atheroscler Thromb 24:0–000, 2017.
Mousa, A. Y., J. E. Campbell, A. F. Aburahma, and M. C. Bates. Current update of cerebral embolic protection devices. J. Vasc. Surg. 56:1429–1437, 2012.
Mukherjee, D., N. D. Jani, J. Narvid, and S. C. Shadden. The role of circle of willis anatomy variations in cardio-embolic stroke: a patient-specific simulation based study. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 46:1128–1145, 2018.
Nevárez, M. I. S., E. P. Andani, and M. M. Hernández. Hemodynamic impact analysis of mesh-type embolic protection devices in an in vitro model. Angiologia. 72:178–185, 2020.
Papamanolis, L., H. J. Kim, C. Jaquet, M. Sinclair, M. Schaap, I. Danad, P. van Diemen, P. Knaapen, L. Najman, H. Talbot, C. A. Taylor, and I. Vignon-Clementel. Myocardial perfusion simulation for coronary artery disease: a coupled patient-specific multiscale model. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 49:1432–1447, 2021.
Pope, S. B. Turbulent Flows. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2012.
Di Renzo, A., and F. P. Di Maio. Comparison of contact-force models for the simulation of collisions in DEM-based granular flow codes. Chem. Eng. Sci. 59:525–541, 2004.
Ryan, N. W., and M. M. Johnson. Transistion from laminar to turbulent flow in pipes. AIChE J. 5:433–435, 1959.
Shadden, S. C., and A. Arzani. Lagrangian postprocessing of computational hemodynamics. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 43:41–58, 2014.
Siewiorek, G. M., M. K. Eskandari, and E. A. Finol. The AngioguardTM embolic protection device. Expert Rev. Med. Devices. 5:287–296, 2008.
Siewiorek, G. M., and E. A. Finol. Computational modeling of distal protection filters. J. Endovasc. Ther. 17:777–788, 2010. https://doi.org/10.1583/10-3178.1.
Siewiorek, G. M., and E. A. Finol. Experimental and Computational Evaluation of Embolic Protection. ASME 2010 Summer Bioengineering Conference, SBC 2010 627–628, 2013. https://doi.org/10.1115/SBC2010-19693
Siewiorek, G. M., R. T. Krafty, M. H. Wholey, and E. A. Finol. The association of clinical variables and filter design with carotid artery stenting thirty-day outcome. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 42:282–291, 2011.
Siewiorek, G. M., M. H. Wholey, and E. A. Finol. Vascular resistance in the carotid artery: an in vitro investigation of embolic protection filters. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 19:1467–1476, 2008.
Siewiorek, G. M., M. H. Wholey, and E. A. Finol. In vitro performance assessment of distal protection filters: Pulsatile flow conditions. Journal of Endovascular Therapy. 16:735–743, 2009.
Spiegel, M., T. Redel, J. J. Zhang, T. Struffert, J. Hornegger, R. G. Grossman, A. Doerfler, and C. Karmonik. Tetrahedral vs. polyhedral mesh size evaluation on flow velocity and wall shear stress for cerebral hemodynamic simulation. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Eng. 14:9–22, 2011.
The American Society of Mechanical Engineers. V&V 40-2018 Assessing Credibility of Computational Modeling Through Verification and Validation: Application to Medical Devices. 2018.
Traenka, C., S. T. Engelter, M. M. Brown, J. Dobson, C. Frost, and L. H. Bonati. Silent brain infarcts on diffusion-weighted imaging after carotid revascularisation: a surrogate outcome measure for procedural stroke? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. Stroke J. 4:127–143, 2019.
Wilcox, D. C. Multiscale model for turbulent flows. AIAA J. 26:1311–1320, 1988.
Zhou, W., B. D. Baughman, S. Soman, M. Wintermark, L. C. Lazzeroni, E. Hitchner, J. Bhat, and A. Rosen. Volume of subclinical embolic infarct correlates to long-term cognitive changes after carotid revascularization. J. Vasc. Surg. 65:686–694, 2017.
Funding
This study ws funded by upv-la fe 2020 subprograma proyectos de innovación (Grant No. DPECFD).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Associate Editor Stefan M. Duma oversaw the review of this article.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gil, A., Quintero, P., Mares, A. et al. In Silico Hemodynamics and Filtering Evaluation of a Commercial Embolic Protection Device. Ann Biomed Eng 49, 2659–2670 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-021-02846-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-021-02846-4