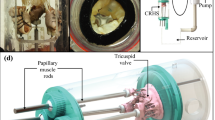
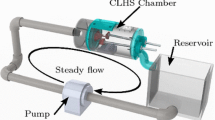
Abstract
Despite the growing clinical interest in the tricuspid valve (TV), there is an incomplete understanding of TV biomechanics which is important in normal TV function and successful TV repair techniques. Computational models with patient-specific human TV geometries can provide a quantitative understanding of TV biomechanic. Therefore, this study aimed to develop finite element (FE) models of human TVs from multi-slice computed tomography (MSCT) images to investigate chordal forces and leaflet stresses and strains. Three FE models were constructed for human subjects with healthy TVs from MSCT images and incorporated detailed leaflet geometries, realistic nonlinear anisotropic hyperelastic material properties of human TV, and physiological boundary conditions tracked from MSCT images. TV closure from diastole to systole was simulated. Chordal lengths were iteratively adjusted until the simulated TV geometries were in good agreement with the “true” geometries reconstructed from MSCT images at systole. Larger chordal forces were found on the strut (or basal) chords than on the rough zone chords and the total forces applied on the anterior papillary muscles by the strut chords were higher than those on the posterior or septal papillary muscles. At peak systolic pressure, the average maximum stress on the middle sections of the leaflets ranged from 30 to 90 kPa, while the average maximum principal strain values ranged from 0.16 to 0.30. The results from healthy TVs can serve as baseline biomechanical metrics of TV mechanics and may be used to inform TV repair device design. The computational approach developed could be one step towards developing computational models that may support pre-operative planning in complex TV repair procedures in the future.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amini Khoiy, K., and R. Amini. On the biaxial mechanical response of porcine tricuspid valve leaflets. J. Biomech. Eng. 138:104506, 2016.
Bruce, C. J., and H. M. Connolly. Right-sided valve disease deserves a little more respect. Circulation 119:2726–2734, 2009.
Campelo-Parada, F., G. Perlman, F. Philippon, J. Ye, C. Thompson, E. Bédard, O. Abdul-Jawad Altisent, M. Del Trigo, J. Leipsic, P. Blanke, D. Dvir, R. Puri, J. G. Webb, and J. Rodés-Cabau. First-in-man experience of a novel transcatheter repair system for treating severe tricuspid regurgitation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 66:2475–2483, 2015.
Fukuda, S., G. Saracino, Y. Matsumura, M. Daimon, H. Tran, N. L. Greenberg, T. Hozumi, J. Yoshikawa, J. D. Thomas, and T. Shiota. Three-dimensional geometry of the tricuspid annulus in healthy subjects and in patients with functional tricuspid regurgitation. Circulation 114:I-492–I-498, 2006.
Gasser, T. C., R. W. Ogden, and G. A. Holzapfel. Hyperelastic modelling of arterial layers with distributed collagen fibre orientations. J. R. Soc. Interface 3:15–35, 2006.
Gunnal, S. A., R. N. Wabale, and M. S. Farooqui. Morphological study of chordae tendinae in human cadaveric hearts. Heart Views 16:1–12, 2015.
He, Z., J. Ritchie, J. S. Grashow, M. S. Sacks, and A. P. Yoganathan. In vitro dynamic strain behavior of the mitral valve posterior leaflet. J. Biomech. Eng. 127:504–511, 2005.
Holzapfel, G. A., T. C. Gasser, and R. W. Ogden. A new constitutive framework for arterial wall mechanics and a comparative study of material models. J. Elast. Phys. Sci. Solids 61:1–48, 2000.
Jimenez, J. H., D. D. Soerensen, Z. He, S. He, and A. P. Yoganathan. Effects of a saddle shaped annulus on mitral valve function and chordal force distribution: an in vitro study. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 31:1171–1181, 2003.
Jouan, J., M. R. Pagel, M. E. Hiro, K. H. Lim, E. Lansac, and C. M. Duran. Further information from a sonometric study of the normal tricuspid valve annulus in sheep: geometric changes during the cardiac cycle. J. Heart Valve Dis. 16:511–518, 2007.
Kragsnaes, E. S., J. L. Honge, J. B. Askov, J. M. Hasenkam, H. Nygaard, S. L. Nielsen, and M. O. Jensen. In-plane tricuspid valve force measurements: development of a strain gauge instrumented annuloplasty ring. Cardiovasc. Eng. Technol. 4:131–138, 2013.
Latib, A., E. Agricola, A. Pozzoli, P. Denti, M. Taramasso, P. Spagnolo, J.-M. Juliard, E. Brochet, P. Ou, M. Enriquez-Sarano, F. Grigioni, O. Alfieri, A. Vahanian, A. Colombo, and F. Maisano. First-in-man implantation of a tricuspid annular remodeling device for functional tricuspid regurgitation. JACC 8:e211–e214, 2015.
Liang, L., F. Kong, C. Martin, T. Pham, Q. Wang, J. Duncan, and W. Sun. Machine learning-based 3-D geometry reconstruction and modeling of aortic valve deformation using 3-D computed tomography images. Int. J. Numer. Methods Biomed. Eng. 33:e2827, 2017.
Liang, L., M. Liu, C. Martin, and W. Sun. A deep learning approach to estimate stress distribution: a fast and accurate surrogate of finite-element analysis. J. R. Soc. Interface 15:20170844, 2018.
Lim, K. O. Mechanical properties and ultrastructure of normal human tricuspid valve chordae tendineae. Jpn. J. Physiol. 30:455–464, 1980.
Liu, H., and W. Sun. Computational efficiency of numerical approximations of tangent moduli for finite element implementation of a fiber-reinforced hyperelastic material model. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Eng. 19:1171–1180, 2016.
Mansi, T., I. Voigt, B. Georgescu, X. Zheng, E. A. Mengue, M. Hackl, R. I. Ionasec, T. Noack, J. Seeburger, and D. Comaniciu. An integrated framework for finite-element modeling of mitral valve biomechanics from medical images: application to MitralClip intervention planning. Med. Image Anal. 16:1330–1346, 2012.
Martin, C., and W. Sun. Biomechanical characterization of aortic valve tissue in humans and common animal models. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 100:1591–1599, 2012.
Meduri, C. U., V. Rajagopal, M. A. Vannan, K. Feldt, and A. Latib. Transcatheter tricuspid valve therapies. Card. Interv. Today 11:48–53, 2017.
Morgan, A. E., J. L. Pantoja, J. Weinsaft, E. Grossi, J. M. Guccione, L. Ge, and M. Ratcliffe. Finite element modeling of mitral valve repair. J. Biomech. Eng. 138:0210091–0210098, 2016.
Nath, J., E. Foster, and P. A. Heidenreich. Impact of tricuspid regurgitation on long-term survival. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 43:405–409, 2004.
Pham, T., F. Kong, C. Martin, Q. Wang, C. Primiano, R. McKay, J. Elefteriades, and W. Sun. Finite element analysis of patient-specific mitral valve with mitral regurgitation. Cardiovasc. Eng. Technol. 8:3–16, 2017.
Pham, T., F. Sulejmani, E. Shin, D. Wang, and W. Sun. Quantification and comparison of the mechanical properties of four human cardiac valves. Acta Biomater. 54:345–355, 2017.
Sacks, M. S., Z. He, L. Baijens, S. Wanant, P. Shah, H. Sugimoto, and A. P. Yoganathan. Surface strains in the anterior leaflet of the functioning mitral valve. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 30:1281–1290, 2002.
Sadeghpour, A., M. Hassanzadeh, M. Kyavar, H. Bakhshandeh, N. Naderi, B. Ghadrdoost, and Talab A. Haghighat. Impact of severe tricuspid regurgitation on long term survival. Res. Cardiovasc. Med. 2:121–126, 2013.
Schofer, J., K. Bijuklic, C. Tiburtius, L. Hansen, A. Groothuis, and R. T. Hahn. First-in-human transcatheter tricuspid valve repair in a patient with severely regurgitant tricuspid valve. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 65:1190–1195, 2015.
Schueler, R., M. Malasa, C. Hammerstingl, and G. Nickenig. Transcatheter interventions for tricuspid regurgitation: MitraClip. EuroIntervention 12:Y108–Y109, 2016.
Shiran, A., and A. Sagie. Tricuspid regurgitation in mitral valve disease. Incid. Progn. Implic. Mech. Manage. 53:401–408, 2009.
Silver, M. D., J. H. C. Lam, N. Ranganathan, and E. D. Wigle. Morphology of the human tricuspid valve. Circulation 43:333–348, 1971.
Spinner, E. M., D. Buice, C. H. Yap, and A. P. Yoganathan. The effects of a three-dimensional, saddle-shaped annulus on anterior and posterior leaflet stretch and regurgitation of the tricuspid valve. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 40:996–1005, 2012.
Stevanella, M., E. Votta, M. Lemma, C. Antona, and A. Redaelli. Finite element modelling of the tricuspid valve: a preliminary study. Med. Eng. Phys. 32:1213–1223, 2010.
Stuge, O., and J. Liddicoat. Emerging opportunities for cardiac surgeons within structural heart disease. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 132:1258–1261, 2006.
Sun, W., and M. S. Sacks. Finite element implementation of a generalized Fung-elastic constitutive model for planar soft tissues. Biomech. Model. Mechanobiol. 4:190–199, 2005.
Troxler, L. G., E. M. Spinner, and A. P. Yoganathan. Measurement of strut chordal forces of the tricuspid valve using miniature C ring transducers. J. Biomech. 45:1084–1091, 2012.
van Rosendael, P. J., V. Delgado, and J. J. Bax. The tricuspid valve and the right heart: anatomical, pathological and imaging specifications. EuroIntervention 11(Suppl W):W123–W127, 2015.
Votta, E., E. Caiani, F. Veronesi, M. Soncini, F. M. Montevecchi, and A. Redaelli. Mitral valve finite-element modelling from ultrasound data: a pilot study for a new approach to understand mitral function and clinical scenarios. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A 366:3411–3434, 2008.
Wang, Q., and W. Sun. Finite element modeling of mitral valve dynamic deformation using patient-specific multi-slices computed tomography scans. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 41:142–153, 2013.
Wengenmayer, T., M. Zehender, W. Bothe, C. Bode, and S. Grundmann. First transfemoral percutaneous edge-to-edge repair of the tricuspid valve using the MitraClip system. EuroIntervention 11:1541–1544, 2016.
Xanthos, T., I. Dalivigkas, and K. A. Ekmektzoglou. Anatomic variations of the cardiac valves and papillary muscles of the right heart. Italian J. Anat. Embryol. 116:111–126, 2011.
Acknowledgment
Research for this project was funded in part by NIH HL104080 and HL127570 Grants. The authors would like to thank Erica Shin for tissue mechanical testing of TV tissues.
Disclosures
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Associate Editor Ellen Kuhl oversaw the review of this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kong, F., Pham, T., Martin, C. et al. Finite Element Analysis of Tricuspid Valve Deformation from Multi-slice Computed Tomography Images. Ann Biomed Eng 46, 1112–1127 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-018-2024-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-018-2024-8