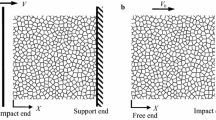
Abstract
Dual-level stress plateaus (i.e., relatively short peak stress plateaus, followed by prolonged crushing stress plateaus) in metallic hexagonal honeycombs subjected to out-of-plane impact loading are characterized using a combined numerical and analytical study, with the influence of the strain-rate sensitivity of the honeycomb parent material accounted for. The predictions are validated against existing experimental measurements, and good agreement is achieved. It is demonstrated that honeycombs exhibit dual-level stress plateaus when bucklewaves are initiated and propagate in cell walls, followed by buckling and progressive folding of the cell walls. The abrupt stress drop from peak to crushing plateau in the compressive stress versus strain curve can be explained in a way similar to the quasi-static buckling of a clamped plate. The duration of the peak stress plateau is more evident for strain-rate insensitive honeycombs.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wierzbicki, T.: Crushing analysis of metal honeycombs. Int. J. Impact Eng. 1, 157–174 (1983)
Zhang, J., Ashby, M.F.: The out-of-plane properties of honeycombs. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 34, 475–489 (1992)
Zhang, Q.C., Yang, X.H., Li, P., et al.: Bioinspired engineering of honeycomb structure—using nature to inspire human innovation. Prog. Mater. Sci. 74, 332–400 (2015)
Côté, F., Deshpande, V.S., Fleck, N.A., et al.: The out-of-plane compressive behavior of metallic honeycombs. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 380, 272–280 (2004)
Wilbert, A., Jang, W.Y., Kyriakides, S., et al.: Buckling and progressive crushing of laterally loaded honeycomb. Int. J. Solids Struct. 48, 803–816 (2011)
Enboa, W., Jiang, W.S.: Axial crush of metallic honeycombs. Int. J. Impact Eng. 19, 439–456 (1997)
Hu, L.L., He, X.L., Wu, G.P., et al.: Dynamic crushing of the circular-celled honeycombs under out-of-plane impact. Int. J. Impact Eng. 75, 150–161 (2015)
Xu, S.Q., Beynon, J.H., Ruan, D., et al.: Experimental study of the out-of-plane dynamic compression of hexagonal honeycombs. Compos. Struct. 94, 2326–2336 (2012)
Sun, D., Zhang, W., Wei, Y.: Mean out-of-plane dynamic plateau stresses of hexagonal honeycomb cores under impact loadings. Compos. Struct. 92, 2609–2621 (2010)
Hou, X.H., Deng, Z.C., Zhang, K.: Dynamic crushing strength analysis of auxetic honeycombs. Acta Mech. Solida Sin. 29, 490–501 (2016)
Calladine, C.R., English, R.W.: Strain-rate and inertia effects in the collapse of two types of energy-absorbing structure. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 26, 689–701 (1984)
Harrigan, J.J., Reid, S.R., Peng, C.: Inertia effects in impact energy absorbing materials and structures. Int. J. Impact Eng. 22, 955–979 (1999)
Ferri, E., Antinucci, E., He, M.Y., et al.: Dynamic buckling of impulsively loaded prismatic cores. J. Mech. Mater. Struct. 1, 1345–1365 (2006)
Tilbrook, M.T., Radford, D.D., Deshpande, V.S., et al.: Dynamic crushing of sandwich panels with prismatic lattice cores. Int. J. Solids Struct. 44, 6101–6123 (2007)
Radford, D.D., Mcshane, G.J., Deshpande, V.S., et al.: Dynamic compressive response of stainless-steel square honeycombs. ASME J. Appl. Mech. 74, 658–667 (2007)
Ferri, E., Deshpande, V.S., Evans, A.G.: The dynamic strength of a representative double layer prismatic core: a combined experimental, numerical, and analytical assessment. ASME J. Appl. Mech. 77, 061011 (2010)
Vaughn, D.G., Hutchinson, J.W.: Bucklewaves. Eur. J. Mech. A: Solids 25, 1–12 (2005)
Vaughn, D.G., Canning, J.M., Hutchinson, J.W.: Coupled plastic wave propagation and column buckling. ASME J. Appl. Mech. 72, 1–8 (2005)
Zhang, K., Deng, Z.C., Xu, X.J., et al.: Symplectic analysis for wave propagation of hierarchical honeycomb structures. Acta Mech. Solida Sin. 28, 150–161 (2015)
Hooputra, H., Gese, H., Dell, H., et al.: A comprehensive failure model for crashworthiness simulation of aluminum extrusions. Int. J. Crashworthiness 9, 449–464 (2004)
Cowper, G.R., Symonds, P.S.: Strain-hardening and strain-rate effects in the impact loading of cantilever beams. Division of Applied Mathematics Report No. 28, Brown University, Providence, RI, USA (1957)
Han, B., Qin, K.K., Yu, B., et al.: Honeycomb-corrugation hybrid as a novel sandwich core for significantly enhanced compressive performance. Mater. Des. 93, 271–282 (2016)
Han, B., Wang, W.B., Zhang, Z.J., et al.: Performance enhancement of sandwich panels with honeycomb-corrugation hybrid core. Theor. Appl. Mech. Lett. 6, 54–59 (2016)
Tao, Y., Chen, M., Pei, Y., et al.: Strain-rate effect on mechanical behavior of metallic honeycombs under out-of-plane dynamic compression. ASME J. Appl. Mech. 82, 021007 (2015)
Reid, S.R., Peng, C.: Dynamic uniaxial crushing of wood. Int. J. Impact Eng. 19, 531–570 (1997)
Karagiozova, D., Alves, M.: On the dynamic compression of cellular materials with local structural softening. Int. J. Impact Eng. 108, 153–170 (2017)
Tao, Y., Chen, M., Pei, Y., et al.: Strain-rate effect on the out-of-plane dynamic compressive behavior of metallic honeycombs: experiment and theory. Compos. Struct. 132, 644–651 (2015)
Hou, B., Zhao, H., Pattofatto, S., et al.: Inertia effects on the progressive crushing of aluminum honeycombs under impact loading. Int. J. Solids and Struct. 49, 2754–2762 (2012)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grants 11472209 and 11472208), the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (Grant 2016M600782), the Postdoctoral Scientific Research Project of Shaanxi Province (Grant 2016BSHYDZZ18), the Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant LGG18A020001), the Fundamental Research Funds for Xi’an Jiaotong University (Grant xjj2015102), the Jiangsu Province Key Laboratory of High-end Structural Materials (Grant hsm1305), and the Natural Science Basic Research Plan in Shaanxi Province of China (Grant 2018JQ1078).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, L., Zhao, Z., Zhang, R. et al. Dual-level stress plateaus in honeycombs subjected to impact loading: perspectives from bucklewaves, buckling and cell-wall progressive folding. Acta Mech. Sin. 35, 70–77 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10409-018-0800-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10409-018-0800-1