Abstract
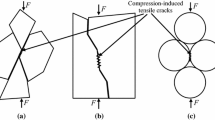
The Brazilian test is a widely used method for determining the tensile strength of rocks and for calibrating parameters in bonded-particle models (BPMs). In previous studies, the Brazilian disc has typically been trimmed from a compacted rectangular specimen. The present study shows that different tensile strength values are obtained depending on the compressive loading direction. Several measures are proposed to reduce the anisotropy of the disc. The results reveal that the anisotropy of the disc is significantly influenced by the compactibility of the specimen from which it is trimmed. A new method is proposed in which the Brazilian disc is directly generated with a particle boundary, effectively reducing the anisotropy. The stiffness (particle and bond) and strength (bond) of the boundary are set at less than and greater than those of the disc assembly, respectively, which significantly decreases the stress concentration at the boundary contacts and prevents breakage of the boundary particle bonds. This leads to a significant reduction in the anisotropy of the disc and the discreteness of the tensile strength. This method is more suitable for carrying out a realistic Brazilian test for homogeneous rock-like material in the BPM.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
The International Society for Rock Mechanics (ISRM): Suggested methods for determining tensile strength of rock materials. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. Geomech. Abstr. 15, 99–103 (1978)
Sundaram, P.N., Corrales, J.M.: Brazilian tensile strength of rocks with different elastic properties in tension and compression. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. Geomech. Abstr. 17, 131–133 (1980)
Basu, A., Mishra, D.A., Roychowdhury, K.: Rock failure modes under uniaxial compression, Brazilian, and point load tests. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 72, 457–475 (2013)
Newman, D.A., Bennett, D.G.: The effect of specimen size and stress rate for the Brazilian test: a statistical analysis. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 23, 123–134 (1990)
Fahimifar, A., Malekpour, M.: Experimental and numerical analysis of indirect and direct tensile strength using fracture mechanics concepts. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 71, 269–283 (2012)
Rocco, C., Guinea, G.V., Planas, J., et al.: Size effect and boundary conditions in the Brazilian test: experimental verification. Mater. Struct. 32, 210–217 (1999)
Perras, M., Diederichs, M.: A review of the tensile strength of rock: concepts and testing. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 32, 525–546 (2014)
Lanaro, F., Sato, T., Stephansson, O.: Microcrack modelling of brazilian tensile tests with the boundary element method. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 46, 450–461 (2009)
Malan, D.F., Napier, J.A.L., Watson, B.P.: Propagation of fractures from an interface in a Brazilian test specimen. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. Geomech. Abstr. 31, 581–596 (1994)
Yu, Y., Yin, J., Zhong, Z.: Shape effects in the brazilian tensile strength test and a 3D FEM correction. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 43, 623–627 (2006)
Zhou, X.P., Wang, Y., Qian, Q.: Numerical simulation of crack curving and branching in brittle materials under dynamic loads using the extended non-ordinary state-based peridynamics. Eur. J. Mech. A Solids 60, 277–299 (2016)
Zhu, W.C., Tang, C.A.: Numerical simulation of brazilian disk rock failure under static and dynamic loading. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 43, 236–252 (2006)
Tan, X., Konietzky, H., Fruhwirt, T., et al.: Brazilian tests on transversely isotropic rocks: laboratory testing and numerical simulations. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 48, 1341–1351 (2015)
Wang, Y., Zhou, X., Xu, X.: Numerical simulation of propagation and coalescence of flaws in rock materials under compressive loads using the extended non-ordinary state-based peridynamics. Eng. Fract. Mech. 163, 248–273 (2016)
Zhou, X.P., Wang, Y., Xu, X.: Numerical simulation of initiation, propagation and coalescence of cracks using the non-ordinary state-based peridynamics. Intl. J. Fract. 201, 1–22 (2016)
Zhou, X.P., Bi, J., Qian, Q.H.: Numerical simulation of crack growth and coalescence in rock-like materials containing multiple pre-existing flaws. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 48, 1097–1114 (2015)
Liakas, S., O’Sullivan, C., Saroglou, H.: Assessment of influence of heterogeneity on rock strength and stiffness using PFC. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. Eng. 9, 575–584 (2017)
Yang, S.Q., Tian, W.L., Huang, Y.H., et al.: An experimental and numerical study on cracking behavior of brittle sandstone containing two non-coplanar fissures under uniaxial compression. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 49, 1497–1515 (2016)
Zhang, X.P., Ji, P.Q., Liu, Q.S., et al.: Physical and numerical studies of rock fragmentation subject to wedge cutter indentation in the mixed ground. Tunn. Undergr. Sp. Technol. 71, 354–365 (2018)
Zhang, X.P., Liu, Q., Wu, S., et al.: Crack coalescence between two non-parallel flaws in rock-like material under uniaxial compression. Eng. Geol. 199, 74–90 (2015)
Zhang, X.P., Wong, L.N.Y.: Choosing a proper loading rate for bonded-particle model of intact rock. Int. J. Fract. 189, 163–179 (2014)
Zhang, X.P., Wong, L.N.Y.: Crack initiation, propagation and coalescence in rock-like material containing two flaws: a numerical study based on bonded-particle model approach. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 46, 1001–1021 (2013)
He, J., Afolagboye, L.O.: Influence of layer orientation and interlayer bonding force on the mechanical behavior of shale under Brazilian test conditions. Acta Mech. Sin. 1–10 (2017)
Potyondy, D.O., Cundall, P.A.: A bonded-particle model for rock. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 41, 1329–1364 (2004)
Cai, M., Kaiser, P.K.: Numerical simulation of the Brazilian test and the tensile strength of anisotropic rocks and rocks with pre-existing cracks. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 41, 450–451 (2004)
Yang, S.Q., Huang, Y.H.: Particle flow study on strength and meso-mechanism of Brazilian splitting test for jointed rock mass. Acta Mech. Sin. 30, 547–558 (2014)
Ghazvinian, A., Nejati, H.R., Sarfarazi, V., et al.: Mixed mode crack propagation in low brittle rock-like materials. Arab. J. Geosci. 6, 4435–4444 (2013)
Vesga, L.F., Vallejo, L.E., Lobo-Guerrero, S.: DEM analysis of the crack propagation in brittle clays under uniaxial compression tests. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Methods Geomech. 32, 1405–1415 (2008)
Chung, Y.C., Yang, Z.H., Lin, C.K.: Modelling micro-crack initiation and propagation of crystal structures with microscopic defects under uni-axial tension by discrete element method. Powder Technol. 315, 445–476 (2017)
Zhang, X.P., Wong, L.N.Y.: Loading rate effects on cracking behavior of flaw-contained specimens under uniaxial compression. Int. J. Fract. 180, 93–110 (2013)
Zhang, X.P., Wong, L.N.Y.: Cracking processes in rock-like material containing a single flaw under uniaxial compression: a numerical study based on parallel bonded-particle model approach. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 45, 711–737 (2012)
Zhang, X.P., Wong, L.N.Y.: Displacement field analysis for cracking processes in bonded-particle model. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 73, 13–21 (2014)
Zhang, Q., Zhang, X.P.: A numerical study on cracking processes in limestone by the b-value analysis of acoustic emissions. Comput. Geotech. 92, 1–10 (2017)
Fairhurst, C.: On the validity of the ‘Brazilian’ test for brittle materials. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. Geomech. Abstr. 1, 535–546 (1964)
Erarslan, N., Liang, Z.Z., Williams, D.J.: Experimental and numerical studies on determination of indirect tensile strength of rocks. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 45, 739–751 (2012)
Hiramatsu, Y., Oka, Y.: Determination of the tensile strength of rock by a compression test of an irregular test piece. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. Geomech. Abstr. 3, 89–90 (1966)
Hung, K.M., Ma, C.C.: Theoretical analysis and digital photoelastic measurement of circular disks subjected to partially distributed compressions. Exp. Mech. 43, 216–224 (2003)
Lavrov, A., Vervoort, A., Wevers, M., et al.: Experimental and numerical study of the kaiser effect in cyclic brazilian tests with disk rotation. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 39, 287–302 (2002)
Itasca: (Particle Flow Code in 2 Dimensions) version 3.1. Itasca Cons Group, Minneapolis (2004)
Wang, C., Tannant, D.D., Lilly, P.A.: Numerical analysis of the stability of heavily jointed rock slopes using PFC2D. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 40, 415–424 (2003)
Schubert, W., Khanal, M., Tomas, J.: Impact crushing of particle-particle compounds–experiment and simulation. Int. J. Miner. Process. 75, 41–52 (2005)
Khanal, M., Schubert, W., Tomas, J.: Dem simulation of diametrical compression test on particle compounds. Granul. Matter. 7, 83–90 (2005)
Al-Busaidi, A., Hazzard, J.F., Young, R.P.: Distinct element modeling of hydraulically fractured lac du bonnet granite. J. Geophys. Res. 110, 351–352 (2005)
Tan, Y., Yang, D., Sheng, Y.: Study of polycrystalline \( {\text{ Al }}_{2} {\text{ O }}_{3}\) machining cracks using discrete element method. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 48, 975–982 (2008)
Inoue, K., Shimizu, N., Funatsu, T.: Influence of clump radius on the mechanical properties of hard rock in the clumped particle model. In: Proceedings of Meeting, Korean, October, 153–160 (2009)
Tan, Y., Yang, D., Sheng, Y.: Discrete element method (DEM) modeling of fracture and damage in the machining process of polycrystalline SiC. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 29, 1029–1037 (2009)
Shimizu, H., Murata, S., Ishida, T.: The distinct element analysis for hydraulic fracturing in hard rock considering fluid viscosity and particle size distribution. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 48, 712–727 (2011)
Lee, H., Jeon, S.: An experimental and numerical study of fracture coalescence in pre-cracked specimens under uniaxial compression. Int. J. Solids Struct. 48, 979–999 (2011)
Sarmadivaleh, M.: Experimental and numerical study of interaction of a pre-existing natural interface and an induced hydraulic fracture. [PhD Thesis], Curtin University (2012)
Zhao, X.: Imaging the mechanics of hydraulic fracturing in naturally-fractured reservoirs using induced seismicity and numerical modeling. [PhD Thesis], University of Toronto (2012)
Ghazvinian, A., Sarfarazi, V., Schubert, W., et al.: A study of the failure mechanism of planar non-persistent open joints using PFC2D. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 45, 677–693 (2012)
Yoon, J.: Application of experimental design and optimization to pfc model calibration in uniaxial compression simulation. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 44, 871–889 (2013)
Manouchehrian, A., Sharifzadeh, M., Marji, M.F., et al.: A bonded particle model for analysis of the flaw orientation effect on crack propagation mechanism in brittle materials under compression. Arch. Civil Mech. Eng. 14, 40–52 (2013)
Wong, L.N.Y., Zhang, X.P.: Size effects on cracking behavior of flaw-containing specimens under compressive loading. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 47, 1921–1930 (2014)
Nakashima, S., Taguchi, K., Shimizu, N., et al.: Effect of element configuration on Brazilian tensile failure by DEM. In: ISRM International Symposium, Sapporo, Japan, October 14–16 (2014)
Duan, K., Kwok, C.Y.: Discrete element modeling of anisotropic rock under Brazilian test conditions. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 78, 46–56 (2015)
Tomac, I., Gutierrez, M.: Coupled hydro-thermo-mechanical modeling of hydraulic fracturing in quasi-brittle rocks using BPM-DEM. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. Eng. 9, 92–104 (2017)
Zhu, X., Liu, W., He, X.: The investigation of rock indentation simulation based on discrete element method. KSCE J. Civil Eng. 21, 1–12 (2016)
Zhang, X.P., Zhang, Q.: Distinction of crack nature in brittle rock-like materials: a numerical study based on moment tensors. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 50, 2837–2845 (2017)
Zhang, X.P., Zhang, Q., Wu, S.: Acoustic emission characteristics of the rock-like material containing a single flaw under different compressive loading rates. Comput. Geotech. 83, 83–97 (2017)
Acknowledgements
Support provided by the National Basic Research Program of China (2015CB258500, 2015CB058102, 2014CB046904) is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Q., Zhang, X.P. & Ji, P.Q. Reducing the anisotropy of a Brazilian disc generated in a bonded-particle model. Acta Mech. Sin. 34, 716–727 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10409-018-0754-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10409-018-0754-3