Abstract
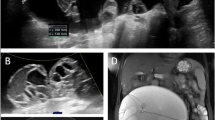
Hydatid disease, caused by Echinococcus granulosus, is a zoonotic infection encountered worldwide. Though involvement of the liver and lungs is quite common, pelvic involvement is rarely reported, with the incidence being 0.2–2.2 %. Ovarian and broad ligament hydatids are rare entities and are usually seen after rupture of a hepatic hydatid cyst. These cysts are usually asymptomatic, and a high index of clinical suspicion coupled with unequivocal imaging findings is required to make an accurate and timely diagnosis. We present a case of multifocal hydatid disease in a female child involving the lungs and liver and provide an account of the quintessential radiological findings.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tsaroucha AK, Polychronidis AC, Lyrantzopoulos N, et al. Hydatid disease of the abdomen and other locations. World J Surg. 2005;29:1161–5.
King CH. Cestodes (tapeworms). In: Mandell GL, Bennet JE, Dolin R, editors. Principles and practice of infectious disease. 6th ed. New York: Churchill Livingstone; 2005. p. 3290–2.
Karaoglanoglu N, Kurkcuoglu IC, Gorguner M, et al. Giant hydatid lung cysts. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2001;19(6):914–7.
Gueddana F, Chemmen Lebbene L, Lebi I, et al. Intrauterine hydatidosis: a case report. J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol (Paris). 1990;19:725–7.
Komongui DG, Diouf A, Dao B, et al. Hydatid cyst of the uterus (apropos of a case seen at the gynecologic and obstetrical clinic of the C.H.U. of Dakar). Dakar Med. 1990;35:162–7.
Tarcoveanu E, Dimofte G, Bradea C, et al. Multiple peritoneal hydatid disease after rupture of a multivesicular hepatic hydatid cyst: case report. J Gastrointestin Liver Dis. 2006;15:301–5.
Pumarola A, Rodriguez-Torres A, García-Rodriguez JA, et al. Microbiología y parasitologíamédica. 2nd ed. Spain: Salvat; 1990.
King CH. Cestodes (tapeworms). In: Mandell GL, Bennett JE, Dolin R, editors. Principles and practice of infectious diseases. 4th ed. New York: Churchill Livingstone; 1995. p. 2544–53.
Moguillanski SJ, Gimenez CR, Villavicencio RL. Radiología de la hidatidosis abdominal. In: Stoopen ME, Kimura K, Ros PR, editors. Radiología e imagendiagnóstica y terapeútica: abdomen, vol. 2. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 1999. p. 47–72.
Gharbi HA, Hassine W, Brauner MW, et al. Ultrasound examination of the hydatid liver. Radiology. 1981;139:459–63.
Davolio SA, Canossi GC, Nicoli FA, et al. Hydatid disease: MR imaging study. Radiology. 1990;175:701–6.
Bickers WM. Hydatid disease of the female pelvis. Am J Obstet Gynaecol. 1970;107:477–83.
Xu MQ. Hydatid disease of the lung. Am J Surg. 1985;150(5):568–73.
Conflict of interest
The authors report no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Jha, A., Ullah, E., Gupta, P. et al. Sonography of multifocal hydatidosis involving lung and liver in a female child. J Med Ultrasonics 40, 471–474 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10396-013-0444-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10396-013-0444-5