Abstract
Purpose
Lymph node (LN) recurrence is frequently encountered in esophageal cancer. The aim of this study was to determine the effects of various factors, including loco-regional treatment of LN-only recurrence, on the survival rate.
Methods
Among 941 patients who underwent curative resection for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma in 2003–2016, we retrospectively reviewed 117 patients (12.4%) who developed LN-only recurrence.
Results
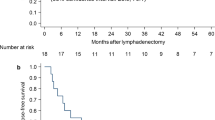
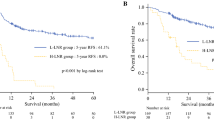
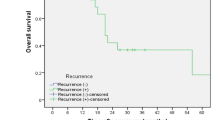
One, 2, 3, and 4 or more metastatic LNs were found in 72, 22, 6, and 17 patients, respectively, after a median disease-free interval of 8.4 months (range 1.1–62.0). Among all cases, recurrence was out of the surgical field in 53 cases (45.3%). Recurrent LNs were controlled by loco-regional treatment in 29 (43.9%) and by chemotherapy alone in 3 patients (7.0%). The 3-year survival rates of patients who did and did not achieve local control were 53.2% and 5.2%, respectively. Univariate analysis showed significant relationships between post-recurrence survival rate and pStage I–II at initial surgery, no history of radiotherapy, recurrence in ≤ 2 LN, and loco-regional treatment of LN recurrence. Multivariate analysis identified recurrence in ≤ 2 LN (HR 0.3169, 95% CI 0.1023–0.5314, p = 0.0038) and loco-regional treatment (HR 0.1973, 95% CI 0.0075–0.3871, p = 0.0416) as the only two significant and independent prognostic factors of survival.
Conclusions
Recurrence limited to ≤ 2 LN and loco-regional treatment (chemoradiotheapy or surgery) for LN recurrence were associated with favorable survival of patients with history of radical esophagectomy followed by LN recurrence. Our results emphasize the importance of local control of LN recurrence regardless of location.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61:69–90.
Dresner SM, Griffin SM. Pattern of recurrence following radical oesophagectomy with two-field lymphadenectomy. Br J Surg. 2000;87:1426–33.
Hiyoshi Y, Morita M, Kawano H, Otsu H, Ando K, Ito S, et al. Clinical significance of surgical resection for the recurrence of esophageal cancer after radical esophagectomy. Ann Surg Oncol. 2015;22:240–6.
Nakagawa S, Kanda T, Kosugi S, Ohashi M, Suzuki T, Hatakeyama K. Recurrence pattern of squamous cell carcinoma of the thoracic esophagus after extended radical esophagectomy with three-field lymphadenectomy. J Am Coll Surg. 2004;198:205–11.
Yamashita K, Watanabe M, Mine S, Kurogochi T, Okamura A, Hayami M, et al. Patterns and outcomes of recurrent esophageal cancer after curative esophagectomy. World J Surg. 2017;41:2337–444.
Nakamura T, Ota M, Narumiya K, Sato T, Ohki T, Yamamoto M, et al. Multimodal treatment for lymph node recurrence of esophageal carcinoma after curative resection. Ann Surg Oncol. 2008;15:2451–7.
Blom RL, Lagarde SM, van Oudenaarde K, Klinkenbijl JH, Hulshof MC, van Laarhoven HW, et al. Survival after recurrent esophageal carcinoma has not improved over the past 18 years. Ann Surg Oncol. 2013;20:2693–8.
Doki Y, Ishikawa O, Takachi K, Miyashiro I, Sasaki Y, Ohigashi H, et al. Association of the primary tumor location with the site of tumor recurrence after curative resection of thoracic esophageal carcinoma. World J Surg. 2005;29:700–7.
Sugiyama M, Morita M, Yoshida R, Ando K, Egashira A, Takefumi O, et al. Patterns and time of recurrence after complete resection of esophageal cancer. Surg Today. 2012;42:752–8.
Nemoto K, Ariga H, Kakuto Y, Matsushita H, Takeda K, Takahashi C, et al. Radiation therapy for loco-regionally recurrent esophageal cancer after surgery. Radiother Oncol. 2001;61:165–8.
Lu JC, Kong C, Tao H. Radiotherapy with or without concurrent chemotherapy for lymph node recurrence after radical surgery of thoracic esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2010;78:710–4.
Jingu K, Ariga H, Nemoto K, Narazaki K, Umezawa R, Takeda K, et al. Long-term results of radiochemotherapy for solitary lymph node metastasis after curative resection of esophageal cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2012;83:172–7.
Kaisaki S, Kitayama J, Ishigami H, Nagawa H. Solitary nodal recurrence in the dorsal area of the thoracic aorta after a curative resection of esophageal cancer: report of two cases. Surg Today. 2007;37:243–7.
Yamasaki M, Yasuda T, Yano M, Hirao M, Kobayashi K, Fujitani K, et al. Multicenter randomized phase II study of cisplatin and fluorouracil plus docetaxel (DCF) compared with cisplatin and fluorouracil plus Adriamycin (ACF) as preoperative chemotherapy for resectable esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (OGSG1003). Ann Oncol. 2017;28(1):116–20.
Yamashita K, Katada N, Moriya H, Hosoda K, Mieno H, Katada C, et al. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy of triplet regimens of docetaxel/cisplatin/5-FU (DCF NAC) may improve patient prognosis of cStage II/III esophageal squamous cell carcinoma-propensity score analysis. Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2016;64:209–15.
Miyata H, Yano M, Doki Y, Yasuda T, Yoshioka S, Sugita Y, et al. A prospective trial for avoiding cervical lymph node dissection for thoracic esophageal cancers, based on intra-operative genetic diagnosis of micrometastasis in recurrent laryngeal nerve chain nodes. J Surg Oncol. 2006;93:477–84.
Cuesta MA, van der Wielen N, Straatman J, van der Peet DL. Video-assisted thoracoscopic esophagectomy: keynote lecture. Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2016;64:380–5.
Wada H, Doki Y, Nishioka K, Ishikawa O, Kabuto T, Yano M, et al. Clinical outcome of esophageal cancer patients with history of gastrectomy. J Surg Oncol. 2005;89:67–74.
Watanabe M, Mine S, Nishida K, Kurogochi T, Okamura A, Imamura Y. Reconstruction after esophagectomy for esophageal cancer patients with a history of gastrectomy. Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2016;64:457–63.
Akiyama H, Tsurumaru M, Udagawa H, Kajiyama Y. Radical lymph node dissection for cancer of the thoracic esophagus. Ann Surg. 1994;220:364–72 (discussion 72–3).
Shinoda M, Ando N, Kato K, Ishikura S, Kato H, Tsubosa Y, et al. Randomized study of low-dose versus standard-dose chemoradiotherapy for unresectable esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (JCOG0303). Cancer Sci. 2015;106:407–12.
Tomihara H, Yamada D, Eguchi H, Iwagami Y, Noda T, Asaoka T, et al. MicroRNA-181b-5p, ETS1, and the c-Met pathway exacerbate the prognosis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma after radiation therapy. Cancer Sci. 2017;108:398–407.
Nguyen GH, Murph MM, Chang JY. Cancer stem cell radioresistance and enrichment: where frontline radiation therapy may fail in lung and esophageal cancers. Cancers (Basel). 2011;3:1232–52.
Shimada A, Tsushima T, Tsubosa Y, Booka E, Takebayashi K, Niihara M, et al. Validity of surgical resection for lymph node or pulmonary recurrence of esophageal cancer after definitive treatment. World J Surg. 2019;43:1286–93.
Watanabe M, Mine S, Yamada K, Shigaki H, Baba Y, Yoshida N, et al. Outcomes of lymphadenectomy for lymph node recurrence after esophagectomy or definitive chemoradiotherapy for squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus. Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2014;62:685–92.
Yano M, Takachi K, Doki Y, Miyashiro I, Kishi K, Noura S, et al. Prognosis of patients who develop cervical lymph node recurrence following curative resection for thoracic esophageal cancer. Dis Esophagus. 2006;19:73–7.
Motoyama S, Kitamura M, Saito R, Maruyama K, Okuyama M, Ogawa J. Outcome and treatment strategy for mid- and lower-thoracic esophageal cancer recurring locally in the lymph nodes of the neck. World J Surg. 2006;30:191–8.
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Statement
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tanaka, K., Yamasaki, M., Makino, T. et al. Analysis of prognostic factors in patients with lymph node recurrence after radical esophagectomy: importance of locoregional therapy. Esophagus 18, 195–202 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10388-020-00778-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10388-020-00778-x