Abstract
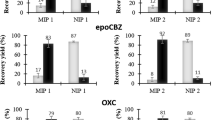
Eight molecularly imprinted polymers (MIPs) were synthesized for the determination of the antibacterial agent gemifloxacin mesylate (GFM). The polymers were prepared using GFM as a template, methacrylic acid (MAA) or 4-vinylpyridine (4-VP) as functional monomers, ethylene glycol dimethacrylate (EGDMA) as a cross linker, 2,2′-azobisisobutyronitrile (AIBN) as an initiator and a mixture of dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO)/acetonitrile (ACN) (1:1, v/v) as a porogen. The optimized polymer was utilized as a solid-phase extraction (SPE) sorbent material for GFM from different matrices. Different loading, washing and elution protocols were investigated. Quantitative analysis of the extracts was performed using a newly developed ultra-performance liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry (UPLC–MS/MS) method on an Acquity BEH C18 column (100 mm × 2.1 mm, particle size of 1.7 µm). The isocratic mobile phase was a mixture of methanol (MeOH)/water (H2O) with 0.1% formic acid (70:30, v/v), the flow rate was 0.3 mL min−1 and the column temperature was 40 °C. Lomefloxacin (LOM) was used as an internal standard. The developed method was validated based on the recommendations of the International Conference on Harmonization (ICH) and was found suitable for the extraction of GFM from a pharmaceutical drug preparation and spiked human urine samples. Recovery % values ranged from 90.24 to 112.8% with relative standard deviation (RSD) of less than 7%.
Graphic Abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Haupt K, Mosbach K (2000) Molecularly imprinted polymers and their use in biomimetic sensors. Chem Rev 100(7):2495–2504
Haupt K (2001) Molecularly imprinted polymers in analytical chemistry. Analyst 126(6):747–756
Murray GM, Southard GE (2005) Metal ion selective molecularly imprinted polymers. In: Yan M, Ramström O (eds) Molecularly imprinted materials: science and technology. Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 579–602. https://doi.org/10.1201/9781420030303.ch22
He C, Liu F, Li K, Liu H (2006) Molecularly imprinted polymer film grafted from porous silica for selective recognition of testosterone. Anal Lett 39(2):275–286
Yang HH, Zhang SQ, Tan F, Zhuang ZX, Wang XR (2005) Surface molecularly imprinted nanowires for biorecognition. J Am Chem Soc 127(5):1378–1379
Turiel E, Martín-Esteban A, Tadeo JL (2007) Molecular imprinting-based separation methods for selective analysis of fluoroquinolones in soils. J Chromatogr A 1172(2):97–104
Wang GN, Yang K, Liu HZ, Feng MX, Wang JP (2016) Molecularly imprinted polymer-based solid phase extraction combined high performance liquid chromatography for determination of fluoroquinolones in milk. Anal Methods 8(27):5511–5518
Benito-Peña E, Urraca JL, Sellergren B, Moreno-Bondi MC (2008) Solid-phase extraction of fluoroquinolones from aqueous samples using a water-compatible stoichiometrically imprinted polymer. J Chromatogr A 1208(1):62–70
Urraca J, Castellari M, Barrios C, Moreno-Bondi M (2014) Multiresidue analysis of fluoroquinolone antimicrobials in chicken meat by molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction and high performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr A 1343:1–9
Wu X, Wu L (2015) Molecularly imprinted polymers for the solid-phase extraction of four fluoroquinolones from milk and lake water samples. J Sep Sci 38(20):3615–3621
Wang YF, Wang YG, Ouyang XK, Yang LY (2017) Surface-imprinted magnetic carboxylated cellulose nanocrystals for the highly selective extraction of six fluoroquinolones from egg samples. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9(2):1759–1769
Wang N, Wang YF, Omer AM, Ouyang XK (2017) Fabrication of novel surface-imprinted magnetic graphene oxide-grafted cellulose nanocrystals for selective extraction and fast adsorption of fluoroquinolones from water. Anal Bioanal Chem 409(28):6643–6653
Hu ZH, Wang YF, Omer AM, Ouyang XK (2018) Fabrication of ofloxacin imprinted polymer on the surface of magnetic carboxylated cellulose nanocrystals for highly selective adsorption of fluoroquinolones from water. Int J Biol Macromol 107:453–462
Lomaestro BM (2000) Gemifloxacin: a broad-spectrum oral quinolone for treatment of respiratory and urinary tract infections. Formulary 35(12):961
Drlica K, Zhao X (1997) DNA gyrase, topoisomerase IV, and the 4-quinolones. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 61(3):377–392
https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2007/021158s007lbl.pdf. Accessed 01 Nov 2018
Al-Hadiya BMH, Khady AA, Mostafa GAE (2010) Validated liquid chromatographic-fluorescence method for the quantitation of gemifloxacin in human plasma. Talanta 83:110–116
Kaiser M, Gruenspan LD, Dalla Costa T, Tasso L (2011) Reversed phase liquid chromatography method with fluorescence detection of gemifloxacin in rat plasma and its application to the pharmacokinetic study. J Chromatogr B 879(30):3639–3644
Abdallah N (2014) HPLC and densitometric TLC methods for simultaneous determination of gemifloxacin with some co-administered drugs in human plasma. J Chromatogr Sep Tech 5(2):1–9. https://doi.org/10.4172/2157-7064.1000220
Sagirli O, Demirci S, Onal A (2015) A very simple high-performance liquid chromatographic method with fluorescence detection for the determination of gemifloxacin in human breast milk. Luminescence 30(8):1326–1329
Szultkaa M, Krzeminskib R, Walczaka J, Jackowskib M, Buszewski B (2014) Pharmacokinetic study of amoxicillin in human plasma by solid-phase microextraction followed by high-performance liquid chromatography–triple quadrupole mass spectrometry. Biomed Chromatogr 28(2):255–264
Ranjane PN, Gandhi SV, Kadukar SS, Bothara KG (2010) Stability indicating RP-LC method for the determination of gemifloxacin mesylate. Chromatographia 71(11–12):1113–1117
Doyle E, Fowles SE, McDonnell DF, McCarthy R, White SA (2000) Rapid determination of gemifloxacin in human plasma by high performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B 746(2):191–198
Roy B, Das A, Bhaumik U, Sarkar AK, Bose A, Mukharjee J, Chakrabarty US, Das AK, Pal TK (2010) Determination of gemifloxacin in different tissues of rat after oral dosing of gemifloxacin mesylate by LC–MS/MS and its application in drug tissue distribution study. J Pharm Biomed Anal 52(2):216–226
Elbashir AA, Saad B, Salhin A, Ali M, Al-Azzam KMM, Aboul-Enein HY (2008) Validated stability indicating assay of gemifloxacin and lomefloxacin in tablet formulations by capillary electrophoresis. J Liq Chromatogr Relat Technol 31(10):1465–1477
Tavares VF, Patto DCS, Singh AK, Aurora-Prado MS, KedorHackmann ERM, Santoro MIRM (2011) Quantitative determination of gemifloxacin mesylate in tablets by capillary zone electrophoresis and high performance liquid chromatography. Lat Am J Pharm 30(4):746–752
Jain R, Rather JA (2011) Voltammetric determination of antibacterial drug gemifloxacin in solubilized systems at multi-walled carbon nanotubes modified glassy carbon electrode. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 83(2):340–346
El-Shal MA, Attia AK, Abdulla SA (2013) β-Cyclodextrin modified carbon paste electrode for the determination of gemifloxacin and nadifloxacin. J Adv Sci Res 4(2):25–30
Radi A, Khafagy A, El-shobaky A, El-mezayen H (2013) Anodic voltammetric determination of gemifloxacin using screen-printed carbon electrode. J Pharm Anal 3(2):132–136
Abo-talib NF (2013) Ion selective electrodes for stability-indicating determination of gemifloxacin mesylate. Anal Bioanal Chem 5(1):74–86
Al-Mohaimeed AM, Al-Tamimi SA, Alarfaj NA, Aly FA (2012) New coated wire sensors for potentiometric determination of gemifloxacin in pure form, pharmaceutical formulations and biological fluids. Int J Electrochem Sci 7:12518–12530
Zhao F, Zhao WH, Xiong W (2013) Chemiluminescence determination of gemifloxacin based on diperiodatoargentate(III)–sulphuric acid reaction in a micellar medium. Luminescence 28:108–113
Madhuri D, Chandrasekhar K, Devanna N, Somasekhar G (2010) Direct and derivative spectrophotometric determination of gemifloxacin mesylate in pure form and pharmaceutical preparations using p acceptors. Int J Pharm Sci Res 1(4):222–231
Paim CS, Fuehr F, Steppe M, Scherman Schapoval EE (2012) Gemifloxacin mesylate: UV spectrophotometric method for quantitative determination using experimental design for robustness. Quim Nova 35(1):193–197
Ebraheem SAM, Elbashir AA, Aboul-Enein HY (2011) Spectrophotometric methods for the determination of gemifloxacin in pharmaceutical formulations. Acta Pharm Sin B 1(4):248–253
Tekkeli SEK, Onal A (2011) Spectrofluorimetric methods for the determination of gemifloxacin in tablets and spiked plasma samples. J Fluoresc 21(3):1001–1007
Abdallah NA, Ibhrahim HF, Hegabe NH (2017) Comparative study of molecularly imprinted polymer and magnetic molecular imprinted nanoparticles as recognition sites for the potentiometric determination of gemifloxacin mesylate. Int J Electrochem Sci 12:10894–10910. https://doi.org/10.20964/2017.11.74
Moreira FT, Freitas VA, Sales MG (2011) Biomimetic norfloxacin sensors made of molecularly-imprinted materials for potentiometric transduction. Microchim Acta 172(1–2):15–23
Validation of Analytical Procedures: Methodology. In: International conference on harmonisation (ICH) guidance for industry, Geneva, Switzerland, 1996
Xiao D, Dramou P, Xiong N, He H, Yuan D, Dai H, Li H, He X, Peng J, Li N (2013) Preparation of molecularly imprinted polymers on the surface of magnetic carbon nanotubes with a pseudo template for rapid simultaneous extraction of four fluoroquinolones in egg samples. Analyst 138(11):3287–3296
Shi X, Wu A, Qu G, Li R, Zhang D (2007) Development and characterisation of molecularly imprinted polymers based on methacrylic acid for selective recognition of drugs. Biomaterials 28(25):3741–3749
Bravo JC, Fernández P, Durand JS (2005) Flow injection fluorimetric determination of β-estradiol using a molecularly imprinted polymer. Analyst 130(10):1404–1409
El Gohary NA, Madbouly A, El Nashar RM, Mizaikoff B (2015) Synthesis and application of a molecularly imprinted polymer for the voltammetric determination of famciclovir. Biosens Bioelectron 65:108–114
Saad EM, Madbouly A, Ayoub N, El Nashar RM (2015) Preparation and application of molecularly imprinted polymer for isolation of chicoric acid from Cichorium intybus L. medicinal plant. Anal Chim Acta 877:80–89
Yilmaz V, Hazer O, Kartal S (2013) Synthesis, characterization and application of a novel ion-imprinted polymer for selective solid phase extraction of copper(II) ions from high salt matrices prior to its determination by FAAS. Talanta 116:322–329
Wu N, Luo Z, Ge Y, Guo P, Du K, Tang W, Du W, Zeng A, Chang C, Fu Q (2016) A novel surface molecularly imprinted polymer as the solid-phase extraction adsorbent for the selective determination of ampicillin sodium in milk and blood samples. J Pharm Anal 6(3):157–164
Sikiti P, Msagati TA, Mamba BB, Mishra AK (2014) Synthesis and characterization of molecularly imprinted polymers for the remediation of PCBs and dioxins in aqueous environments. J Environ Health Sci Eng 12(1):82–90
Pardeshi S, Dhodapkar R, Kumar A (2014) Molecularly imprinted microspheres and nanoparticles prepared using precipitation polymerisation method for selective extraction of gallic acid from Emblica officinalis. Food Chem 146(2014):385–393
Lagha A, Adhoum N, Monser L (2011) A molecularly imprinted polymer for the selective solid-phase extraction of ibuprofen from urine samples. Open Chem Biomed Methods J 4:7–13
Jing T, Gao XD, Wang P, Wang Y, Lin YF, Hu XZ, Hao QL, Zhou YK, Mei SR (2009) Determination of trace tetracycline antibiotics in foodstuffs by liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry coupled with selective molecular-imprinted solid-phase extraction. Anal Bioanal Chem 393(8):2009–2018
Atlabachew M, Torto N, Chandravanshi BS, Redi-Abshiro M, Chigome S, Mothibedi K, Combrinck S (2016) A (−)-norephedrine-based molecularly imprinted polymer for the solid-phase extraction of psychoactive phenylpropylamino alkaloids from Khat (Catha edulis Vahl. Endl.) chewing leaves. Biomed Chromatogr 30:1007–1015
Sellergren B, Lanza F (2001) Molecularly imprinted polymers in solid phase extractions. In: Sellergren B (ed) Molecularly imprinted polymers: man-made mimics of antibodies and their applications in analytical chemistry. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 355–373
Kadi AA, Angawi RF, Attwa MW, Darwish HW, Abdelhameed AS (2013) High throughput quantitative bioanalytical LC/MS/MS determination of gemifloxacin in human urine. J Chem 2013:905704. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/905704
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the Institute of Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry (IABC), University of Ulm, Germany and the German University in Cairo for supporting this work by allowing the first author to conduct part of her practical work in the Laboratory of Prof. Boris Mizaikoff. The authors would also like to thank MSc Adel Madbouly for his valuable contributions to this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors hereby declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human urine samples were approved by the ethical committee of the German University in Cairo.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Omran, N.H., Wagdy, H.A., Abdel-Halim, M. et al. Validation and Application of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for SPE/UPLC–MS/MS Detection of Gemifloxacin Mesylate. Chromatographia 82, 1617–1631 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10337-019-03782-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10337-019-03782-1