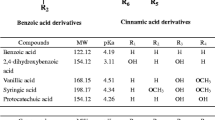
Abstract
This paper reports the results of a study performed to investigate the dependence of the performance of protein separation by capillary zone electrophoresis (CZE) on the anionic component of the electrolyte solutions consisting of 20 mM N,N,N′,N′-tetramethyl-1,3-butanediamine (TMBD) titrated to either pH 4.0 or pH 6.5 with either a monoprotic or a polyprotic acid. With the exception of hydrochloric acid, the acids were selected among those commonly used as the constituents of the solutions employed for protein analysis by either HPLC or CZE. TMBD was chosen for its effectiveness at preventing the interactions of proteins with the inner wall of bare fused-silica capillaries. The performance of separations was evaluated using four basic model proteins having pI value and molecular mass ranging from 9.5 to 11.0 and from 12,400 to 25,000 Da, respectively. It is shown that the different acids used as the components of the background electrolyte solutions, all containing the same concentration of TMBD, affect to different extents both migration time and peak shape of the tested proteins. The performance displayed by the BGE containing phosphate ions is enhanced using TMBD in combination with diethylenetriamine, an aliphatic vicinal triamine having effective buffering capacity at pH 4.0 and capability at minimizing protein–capillary wall interactions. The reported experimental evidences are discussed based on the possible interactions that the phosphate ions are known to establish with both the protein molecules and the surface of bare fused-silica capillaries.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Corradini D (2010) Capillary electromigration techniques. In: Corradini D (ed) Handbook of HPLC, 2nd edn. CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group, USA, pp 155–206
Geiger L, Veuthey J-L (2007) Electrophoresis 28:45–57
Reijenga JC, Gagliardi LG, Kenndler E (2007) J Chromatogr A 1155:142–145
Wang Z, Ouyang J, Baeyens WRG (2008) J Chromatogr B 862:1–14
Popa TV, Mant CT, Hodges RS (2006) J Chromatogr A 1111:192–199
Jáč P, Polášek M, Pospíšilová M (2006) J Pharm Biomed Anal 40:805–814
López-Pastor M, Simonet BM, Lendl B, Valcárel M (2008) Electrophoresis 29:94–107
Varenne A, Descroix S (2008) Anal Chim Acta 674:243–248
Elbashir AA, Aboul-Enein HY (2010) Curr Pharm Anal 6:9–23
Corradini D, Nicoletti I, Bonn GK (2009) Electrophoresis 30:1869–1876
Li J, Han H, Wang Q, Liu X, Jang SJ (2010) Anal Chim Acta 674:243–248
Corradini D (1997) J Chromatogr B 699:221–257
Znaleziona J, Radim Knob JP, Maier V, Ševičik J (2008) Chromatographia 67:S5–S12
Dolnik V (2008) Electrophoresis 29:143–156
El Rassi Z (2010) Electrophoresis 31:174–191
Lucy CA, MacDonald AM, Gulcev MD (2008) J Chromatogr A 1184:81–105
Doherty EAS, Meagher RJ, Albarghouthi MN, Baron AE (2003) Electrophoresis 24:34–54
Corradini D, Cannarsa G (1995) Electrophoresis 16:630–635
Corradini D, Cannarsa G, Corradini C, Nicoletti I, Pizzoferrato L, Vivanti V (1996) Electrophoresis 17:120–124
Melander WY, Stoveken J, Horváth Cs (1979) J Chromatogr 185:111–127
Kalman F, Ma S, Fox RO, Horváth Cs (1995) J Chromatogr A 705:135–154
Corradini D, Cannarsa G (1996) LC-GC 14:326–332
Perrin, DD, Dempsey, B (1974) Buffers for pH and metal ion control. Chapman & Hall, London
Righetti PG, Caravaggio T (1976) J Chromatogr 127:1–28
Worthington, CC (ed) (1988) Worthington enzyme manual. Worthington Biochemical Corporation, Freehold, p. 219, 299
McCormick RM (1988) Anal Chem 60:471–473
Stutz H (2009) Electrophoresis 30:2032–2061
Corradini D, Cannarsa G, Fabbri E, Corradini C (1995) J Chromatogr A 709:127–134
Rabiller-Baudry M, Chaufer B (2001) J Chromatogr B 753:67–77
Stutz H, Bordin G, Rodriguez AS (2004) Electrophoresis 25:1071–1089
Corradini D, Sprecacenere L (2003) Chromatographia 58:587–596
Corradini D, Bevilacqua L, Nicoletti I (2005) Chromatographia 62:S43–S50
Butler JN (1964) Ionic equilibrium—a mathematical approach. Addison-Wesley, Reading
Wei T, Kaewtathip S, Shing K (2009) J. Phys Chem C 113:2053–2062
Corradini D, Cogliandro E, D’Alessandro L, Nicoletti I (2003) J Chromatogr A 1013:221–232
Mohabbati S, Westerlund D et al (2006) J Chromatogr A 1121:32–39
Mohabbati S, Hjerten S, Westerlund D (2008) Anal Bioanal Chem 390:667–678
Murray DK (2010) J Colloid Interf Sci 352:163–170
Acknowledgments
This paper has been presented in the Plenary Session V of the 16th ISSS dedicated to the memory of Prof. Csaba Horváth, who would have celebrated his 80th birthday in 2010. All lectures of this session were presented by separation scientists who, as the corresponding author of this paper, worked with him at Yale University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Corradini, D., De Rossi, A. & Nicoletti, I. Interactions of Proteins with the Acidic Components of the Electrolyte Solution and Their Role in the Performance of Separations by CZE. Chromatographia 73 (Suppl 1), 103–111 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10337-011-2018-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10337-011-2018-2