Abstract
Objective
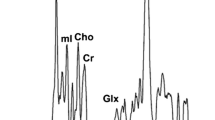
The effects of aging, magnetic field and the voxel localization on measured concentrations of citrate (Cit), creatine (Cr), cholines (Cho) and polyamines (PA) in a healthy prostate were evaluated.
Materials and methods
36 examinations at both 1.5T and 3T imagers of 52 healthy subjects aged 19–71 years were performed with PRESS 3D-CSI sequences (TE = 120 and 145 ms). Concentrations in laboratory units and their ratios to citrate were calculated using the LCModel technique. Absolute concentrations were also obtained after the application of correction coefficients. Statistical analysis was performed using a robust linear mixed effects model.
Results
Significant effects of aging, the magnetic field strength and the voxel position in central (CZ) or peripheral (PZ) zones on all measured metabolites were found. The concentrations (mmol/kg wet tissue) including prediction intervals in a range of 20–70 years were found: Cit: 7.9–17.2; Cho: 1.4–1.7; Cr: 2.8-2.5; PA (as spermine): 0.6–2.1 at 3T in CZ. In PZ, the concentrations were higher by about 10 % as compared to CZ.
Conclusion
Increasing citrate and spermine concentrations with age are significant and correlate well with a recently described increase of zinc in the prostate. These findings should be considered in decision-making if the values obtained from a subject are in the range of control values.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Weinreb JC, Barentsz JO, Choyke PL, Cornud F, Haider MA, Macura KJ, Margolis D, Schnall MD, Shtern F, Tempany CM, Thoeny HD, Verma S (2016) PI RADS prostate imaging—reporting and data system: 2015, version 2. Eur Urol 69:16–40
Kobus T, Wright AJ, Weiland E, Heerschap A, Scheenen TW (2015) Metabolite ratios in 1H MR spectroscopic imaging of the prostate. Magn Reson Med 73(1):1–12
Lowry M, Liney GP, Turnbull LW, Manton DJ, Blackband SJ, Horsman A (1996) Quantification of citrate concentration in the prostate by proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy: zonal and age-related differences. Magn Reson Med 36(3):352–358
Mescher M, Merkle H, Kirsch J, Garwood M, Gruetter R (1998) Simultaneous in vivo spectral editing and water suppression. NMR Biomed 11:266–272
Scheenen TWJ, Gambarota G, Weiland E, Klomp DW, Fütterer JJ, Barentsz JO, Heerschap A (2005) Optimal timing for in vivo 1H-MR spectroscopic imaging of the human prostate at 3T. Magn Reson Med 53:1268–1274
Provencher SW (1993) Estimation of metabolite concentrations from localized in vivo proton NMR spectra. Magn Reson Med 30(6):672–679
Jiru F, Skoch A, Wagnerova D, Dezortova M, Hajek M (2013) jSIPRO—analysis tool for magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging. Comp Methods Programs Biomed 112(1):173–188
https://www.sites.google.com/site/jsiprotool/. Accessed 28 Apr 2016
Bak M, Rasmussen JT, Nielsen NC (2000) SIMPSON: a general simulation program for solid-state NMR spectroscopy. J Magn Reson 147:296–330
Weis J, Ortiz-Nieto F, Ahlström H (2013) MR spectroscopy of the prostate at 3T: measurements of relaxation times and quantification of prostate metabolites using water as an internal reference. Magn Reson Med Sci 12(4):289–296
Liney GP, Turnbull LW, Lowry M, Turnbull LS, Knowles AJ, Horsman A (1997) In vivo quantification of citrate concentration and water T2 relaxation time of the pathologic prostate gland using 1H MRS and MRI. Magn Reson Imaging 15(10):1177–1186
Chen AP, Cunningham CH, Kurhanewicz J, Xu D, Hurd RE, Pauly JM, Carvajal L, Karpodinis K, Vigneron DB (2006) High-resolution 3D MR spectroscopic imaging of the prostate at 3 T with the MLEV-PRESS sequence. Magn Reson Imaging 24(7):825–832
Heerschap A, Jager GJ, De Koster A, Barentsz JO, de la Rosette J, Debruyne F, Ruijs SH (1993) 1H MRS of prostate pathology. In: Proceedings of the 12th Annual Scientific Meeting, Society of Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, New York, p 213
Liney GP, Lowry M, Turnbull LW, Manton DJ, Knowles AJ, Blackband SJ, Horsman A (1996) Proton MR T2 Maps correlate with the citrate concentration in the prostate. NMR Biomed 9:59–64
Heerschap A, Jager GJ, van der Graaf M, Barentsz JO, Ruijs SH (1997) Proton MR spectroscopy of the normal human prostate with an endorectal coil and a double spin-echo pulse sequence. Magn Reson Med 37(2):204–213
http://mestrelab.com/software/. Accessed 28 Apr 2016
R Development Core Team (2013) R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria: the R Foundation for Statistical Computing. ISBN 3-900051-07-0. http://www.R-project.org/
Decelle EA, Cheng LL (2014) High-resolution magic angle spinning 1H MRS in prostate cancer. NMR Biomed 27(1):90–99
Swanson MG, Zektzer AS, Tabatabai ZL, Simko J, Jarso S, Keshari KR, Schmitt L, Carroll PR, Shinohara K, Vigneron DB, Kurhanewicz J (2006) Quantitative analysis of prostate metabolites using 1H HR-MAS spectroscopy. Magn Reson Med 55:1257–1264
Kurhanewicz J, Vigneron DB, Hricak H, Narayan P, Carroll P, Nelson SJ (1996) Three-dimensional H-1 MR spectroscopic imaging of the in situ human prostate with high (0.24–0.7-cm3) spatial resolution. Radiology 198(3):795–805
Weis J, Jorulf H, Bergman A, Ortiz-Nieto F, Häggman M, Ahlström H (2011) MR spectroscopy of the human prostate using surface coil at 3 T: metabolite ratios, age-dependent effects, and diagnostic possibilities. J Magn Reson Imaging 34(6):1277–1284
Giskeødegård GF, Bertilsson H, Selnæs KM, Wright AJ, Bathen TF, Viset T, Halgunset J, Angelsen A, Gribbestad IS, Tessem MB (2013) Spermine and citrate as metabolic biomarkers for assessing prostate cancer aggressiveness. PLoS One 8(4):e62375
Basharat M, Jafar M, deSouza NM, Payne GS (2014) Evaluation of short-TE (1)H MRSI for quantification of metabolites in the prostate. NMR Biomed 27(4):459–467
Basharat M, Payne GS, Morgan VA, Parker C, Dearnaley D, deSouza NM (2015) TE = 32 ms vs TE = 100 ms echo-time (1)H-magnetic resonance spectroscopy in prostate cancer: tumor metabolite depiction and absolute concentrations in tumors and adjacent tissues. J Magn Reson Imaging 42(4):1086–1093
Cheng LL, Wu C, Smith MR, Gonzalez RG (2001) Non-destructive quantitation of spermine in human prostate tissue samples using HRMAS 1H NMR spectroscopy at 9.4 T. FEBS Lett 494(1–2):112–116
Costello LC, Franklin RB (1989) Prostate epithelial cells utilize glucose and aspartate as the carbon sources for net citrate production. Prostate 15(4):335–342
Costello LC, Franklin RB (2006) The clinical relevance of the metabolism of prostate cancer; zinc and tumor suppression: connecting the dots. Mol Cancer 5:17
Costello LC, Franklin RB, Zou J, Naslund MJ (2015) Evidence that human prostate cancer is a ZIP1-deficient malignancy that could be effectively treated with a zinc ionophore (clioquinol) approach. Chemotherapy 4(2):152
Zaichick V, Zaichick S (2014) Age-related histological and zinc content changes in adult nonhyperplastic prostate glands. Age 36(1):167–181
McLean MA, Barrett T, Gnanapragasam VJ, Priest AN, Joubert I, Lomas DJ, Neal DE, Griffiths JR, Sala E (2011) Prostate cancer metabolite quantification relative to water in 1H-MRSI in vivo at 3 Tesla. Magn Reson Med 65(4):914–919
Scheenen TW, Heijmink SW, Roell SA, Hulsbergen-Van de Kaa CA, Knipscheer BC, Witjes JA, Barentsz JO, Heerschap A (2007) Three-dimensional proton MR spectroscopy of human prostate at 3 T without endorectal coil: feasibility. Radiology 245(2):507–516
Selnæs KM, Heerschap A, Jensen LR, Tessem MB, Schweder GJ, Goa PE, Viset T, Angelsen A, Gribbestad IS (2012) Peripheral zone prostate cancer localization by multiparametric magnetic resonance at 3 T: unbiased cancer identification by matching to histopathology. Invest Radiol 47(11):624–633
Acknowledgments
The study was supported by the Ministry of Health of the Czech Republic: Internal Grant Agency No. NT13017 and the grant project for development of research organization 00023001IKEM, Institutional support. We give thanks to Siemens for providing us with Work-In-Progress sequence GRESHIM.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Research involving human participants
All procedures performed in this study were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dezortova, M., Jiru, F., Skoch, A. et al. The aging effect on prostate metabolite concentrations measured by 1H MR spectroscopy. Magn Reson Mater Phy 30, 65–74 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10334-016-0584-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10334-016-0584-x