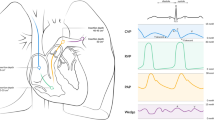
Abstract
Objective
Mayer wave (~10 s) blood pressure (BP) oscillations may represent rhythmic vasomotor activity. However, it remains unclear if volatile anesthetics disturb the coherence between heart rate (HR) and BP rhythms in this region, which may result in improperly affecting BP–HR modulation by the baroreflex, especially when sympathetic stimulation is evoked during general anesthesia using sevoflurane–nitrous oxide (Sev–N2O).
Methods
Twenty-seven patients were anesthetized with Sev–N2O, followed by surgical incision which induces Mayer wave augmentation. Baseline status before surgical incision was compared with that of 19 awake volunteers, and with status after surgical incision. Baroreflex function was assessed by gain and coherence by transfer function analysis, and the baroreflex effectiveness index (BEI). BP Mayer waves were measured by BP variability at a low frequency (LF) of ~0.1 Hz, and spontaneous baroreflex sensitivity (BRS) was obtained by assessing transfer function gain at LF (BRSLF), and the sequence technique (BRSSEQ).
Results
Sev–N2O anesthesia markedly reduced Mayer waves by 93%, BRSLF by 42%, BRSSEQ by 81%, BEI by 37%, coherence by 42%, and the number of coherent segments by 73%, compared with awake controls. During sympathetic stimulation by surgical incision, however, augmentation of Mayer waves (−1.57 ± 0.72 vs. −0.60 ± 1.00, ln mmHg2 P < 0.001) did not improve depressed coherence above 0.5 (0.37 ± 0.09 vs. 0.43 ± 0.11) or BEI (0.17 ± 0.13 vs. 0.13 ± 0.05).
Conclusions
Sev–N2O anesthesia alters the link between HR and BP Mayer wave oscillation even during sympathetic stimulation, indicating weak spontaneous baroreceptor-HR modulation during general anesthesia.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cohen MA, Taylor JA (2002) Short-term cardiovascular oscillations in man: measuring and modelling the physiologies. J Physiol 542:669–683
Pagani M, Lucini D, Rimoldi O, Furlan R, Piazza S, Porta A et al (1996) Low and high frequency components of blood pressure variability. Ann NY Acad Sci 783:10–23
Mancia G, Parati G, Castiglioni P, di Rienzo M (1999) Effect of sinoaortic denervation on frequency-domain estimates of baroreflex sensitivity in conscious cats. Am J Physiol 276:H1987–H1993
Castiglioni P, Di Rienzo M, Veicsteinas A, Parati G, Merati G (2007) Mechanisms of blood pressure and heart rate variability: an insight from low-level paraplegia. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 292:R1502–R1509
deBoer RW, Karemaker JM, Strackee J (1987) Hemodynamic fluctuations and baroreflex sensitivity in humans: a beat-to-beat model. Am J Physiol 253:H680–H689
Kotrly KJ, Ebert TJ, Vucins E, Igler FO, Barney JA, Kampine JP (1984) Baroreceptor reflex control of heart rate during isoflurane anesthesia in humans. Anesthesiology 60:173–179
Tanaka M, Nishikawa T (1999) Arterial baroreflex function in humans anaesthetized with sevoflurane. Br J Anaesth 82:350–354
Tanaka M, Nishikawa T (2005) The concentration-dependent effects of general anesthesia on spontaneous baroreflex indices and their correlations with pharmacological gains. Anesth Analg 100:1325–1332
Smyth HS, Sleight P, Pickering GW (1969) Reflex regulation of arterial pressure during sleep in man. A quantitative method of assessing baroreflex sensitivity. Circ Res 24:109–121
Hwang GS, Kim YK, Huh IY, Kang SJ (2006) Assessing arterial baroreflex control of heart rate during general anesthesia. Anesth Analg 102:1288
Cho SK, Hwang GS, Kim YK, Huh IY, Hahm KD, Han SM (2005) Low-dose atropine amplifies cardiac vagal modulation and increases dynamic baroreflex function in humans. Auton Neurosci 118:108–115
Kim YK, Hwang GS, Huh IY, Hwang JH, Park JY, Chung SL et al (2006) Altered autonomic cardiovascular regulation after combined deep and superficial cervical plexus blockade for carotid endarterectomy. Anesth Analg 103:533–539
Song JG, Hwang GS, Lee EH, Leem JG, Lee C, Park PH et al (2009) Effects of bilateral stellate ganglion block on autonomic cardiovascular regulation. Circ J 73:1909–1913
Task Force of the European Society of Cardiology and the North American Society of Pacing and Electrophysiology (1996) Heart rate variability: standards of measurement, physiological interpretation and clinical use. Circulation 93:1043–1065
Goldstein DS, Horwitz D, Keiser HR (1982) Comparison of techniques for measuring baroreflex sensitivity in man. Circulation 66:432–439
Parati G, Di Rienzo M, Bertinieri G, Pomidossi G, Casadei R, Groppelli A et al (1988) Evaluation of the baroreceptor-heart rate reflex by 24-hour intra-arterial blood pressure monitoring in humans. Hypertension 12:214–222
Blaber AP, Yamamoto Y, Hughson RL (1995) Methodology of spontaneous baroreflex relationship assessed by surrogate data analysis. Am J Physiol 268:H1682–H1687
Di Rienzo M, Parati G, Castiglioni P, Tordi R, Mancia G, Pedotti A (2001) Baroreflex effectiveness index: an additional measure of baroreflex control of heart rate in daily life. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 280:R744–R751
Montano N, Gnecchi-Ruscone T, Porta A, Lombardi F, Malliani A, Barman SM (1996) Presence of vasomotor and respiratory rhythms in the discharge of single medullary neurons involved in the regulation of cardiovascular system. J Auton Nerv Syst 57:116–122
Cevese A, Gulli G, Polati E, Gottin L, Grasso R (2001) Baroreflex and oscillation of heart period at 0.1 Hz studied by alpha-blockade and cross-spectral analysis in healthy humans. J Physiol 531:235–244
Kim YK, Jun IG, Kim SR, Hwang JH, Cho SK, Han SM et al (2008) Using 100% oxygen does not alter the cardiovascular autonomic regulation during non-invasively simulated haemorrhage in healthy volunteers. J Int Med Res 36:227–236
Pinna GD, La Rovere MT, Maestri R, Mortara A, Bigger JT, Schwartz PJ (2000) Comparison between invasive and non-invasive measurements of baroreflex sensitivity; implications for studies on risk stratification after a myocardial infarction. Eur Heart J 21:1522–1529
Lipman RD, Salisbury JK, Taylor JA (2003) Spontaneous indices are inconsistent with arterial baroreflex gain. Hypertension 42:481–487
Sato M, Tanaka M, Umehara S, Nishikawa T (2005) Baroreflex control of heart rate during and after propofol infusion in humans. Br J Anaesth 94:577–581
Stewart JM, Montgomery LD, Glover JL, Medow MS (2007) Changes in regional blood volume and blood flow during static handgrip. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 292:H215–H223
Ebert TJ, Harkin CP, Muzi M (1995) Cardiovascular responses to sevoflurane: a review. Anesth Analg 81:S11–S22
Mayer S (1877) Studien zur physiologie des herzens und der blutgefasse. V. Uber spontane blutdruckschwankungen. Sitzungsberichte Kaiserlich Akad Wissenschaft Mathemat-Naturwissenschaft Classe 74:281–307
de Boer RW, Karemaker JM, Strackee J (1985) Relationships between short-term blood-pressure fluctuations and heart-rate variability in resting subjects. I: a spectral analysis approach. Med Biol Eng Comput 23:352–358
Barres C, Cheng Y, Julien C (2004) Steady-state and dynamic responses of renal sympathetic nerve activity to air-jet stress in sinoaortic denervated rats. Hypertension 43:629–635
Ogawa Y, Iwasaki K, Shibata S, Kato J, Ogawa S, Oi Y (2006) Different effects on circulatory control during volatile induction and maintenance of anesthesia and total intravenous anesthesia: autonomic nervous activity and arterial cardiac baroreflex function evaluated by blood pressure and heart rate variability analysis. J Clin Anesth 18:87–95
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shin, WJ., Kang, SJ., Kim, YK. et al. Link between heart rate and blood pressure Mayer wave during general anesthesia. Clin Auton Res 21, 309–317 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10286-011-0115-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10286-011-0115-9